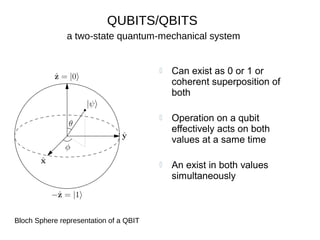
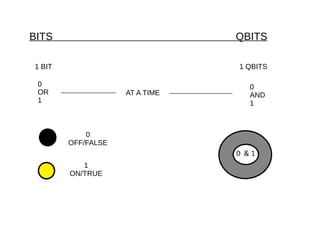
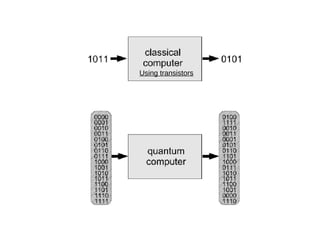
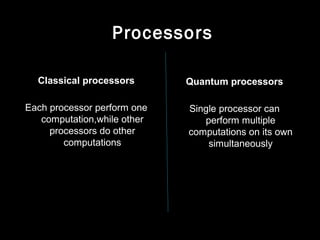
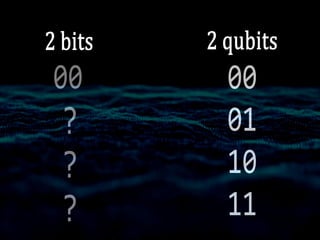
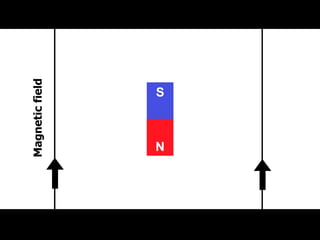
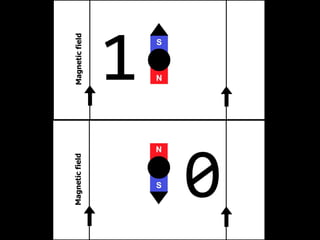
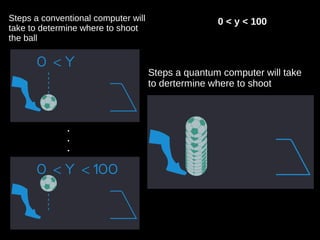
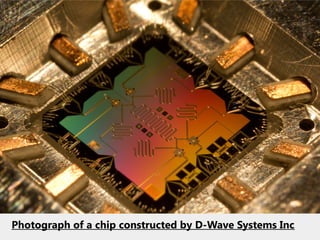
Quantum computers leverage quantum bits (qubits) which can exist in multiple states simultaneously, outperforming classical computers in specific computations. The concept was proposed by Yuri Manin in 1981 and further developed by Richard Feynman, emphasizing that classical computers cannot simulate certain quantum calculations effectively. Future quantum processors may achieve immense computational power, potentially surpassing the number of atoms in the observable universe.