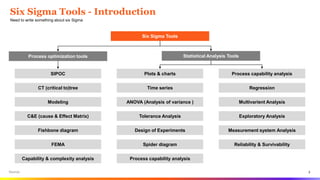
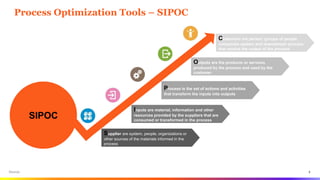
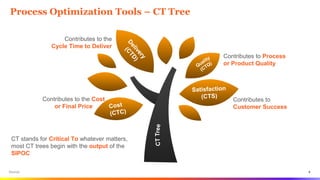
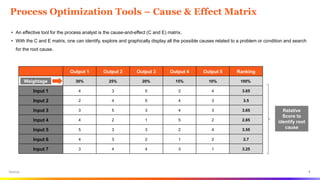
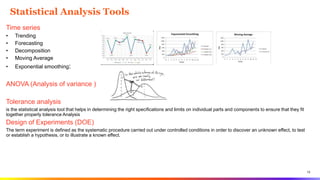
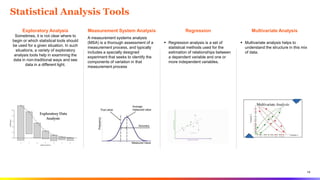
The document provides an overview of Six Sigma tools and process optimization techniques including SIPOC, critical to trees, cause-and-effect matrices, and various statistical analysis tools. It details methods for data collection, analysis, and risk management, along with visual aids such as histograms and scatter plots to facilitate understanding of process variations. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of reliability, survivability, and effective planning in Six Sigma projects.