Embed presentation
Downloaded 24 times




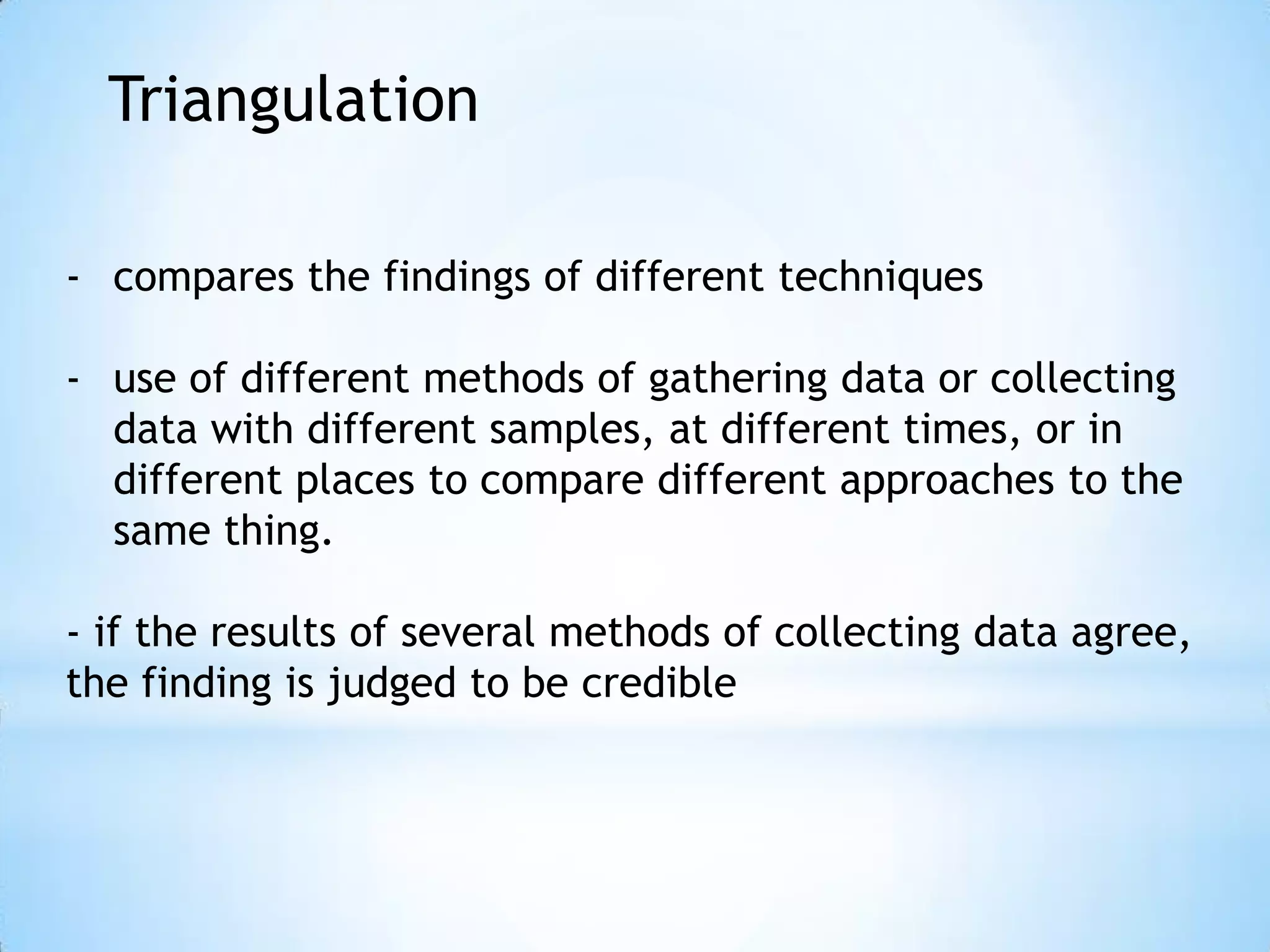

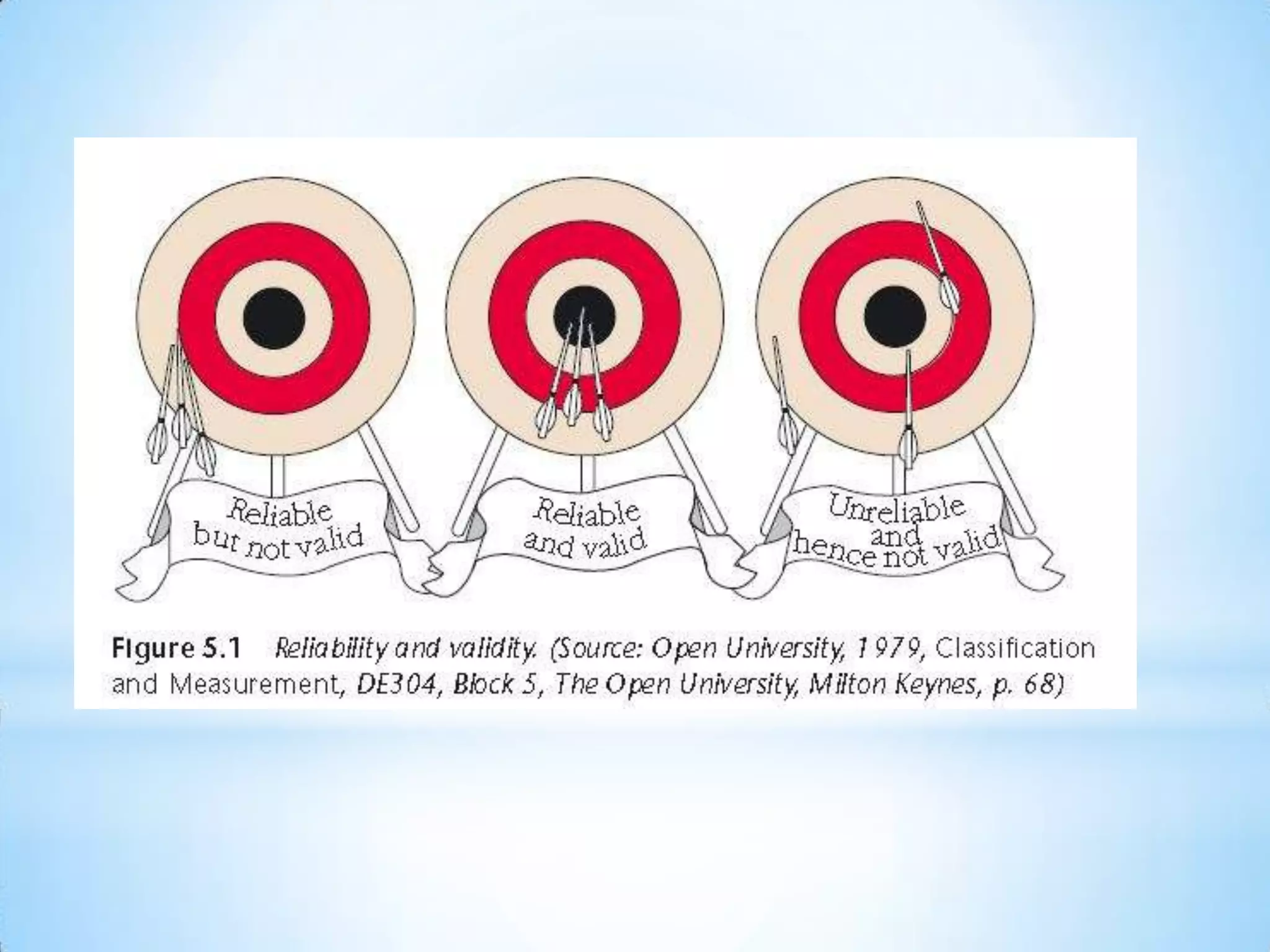
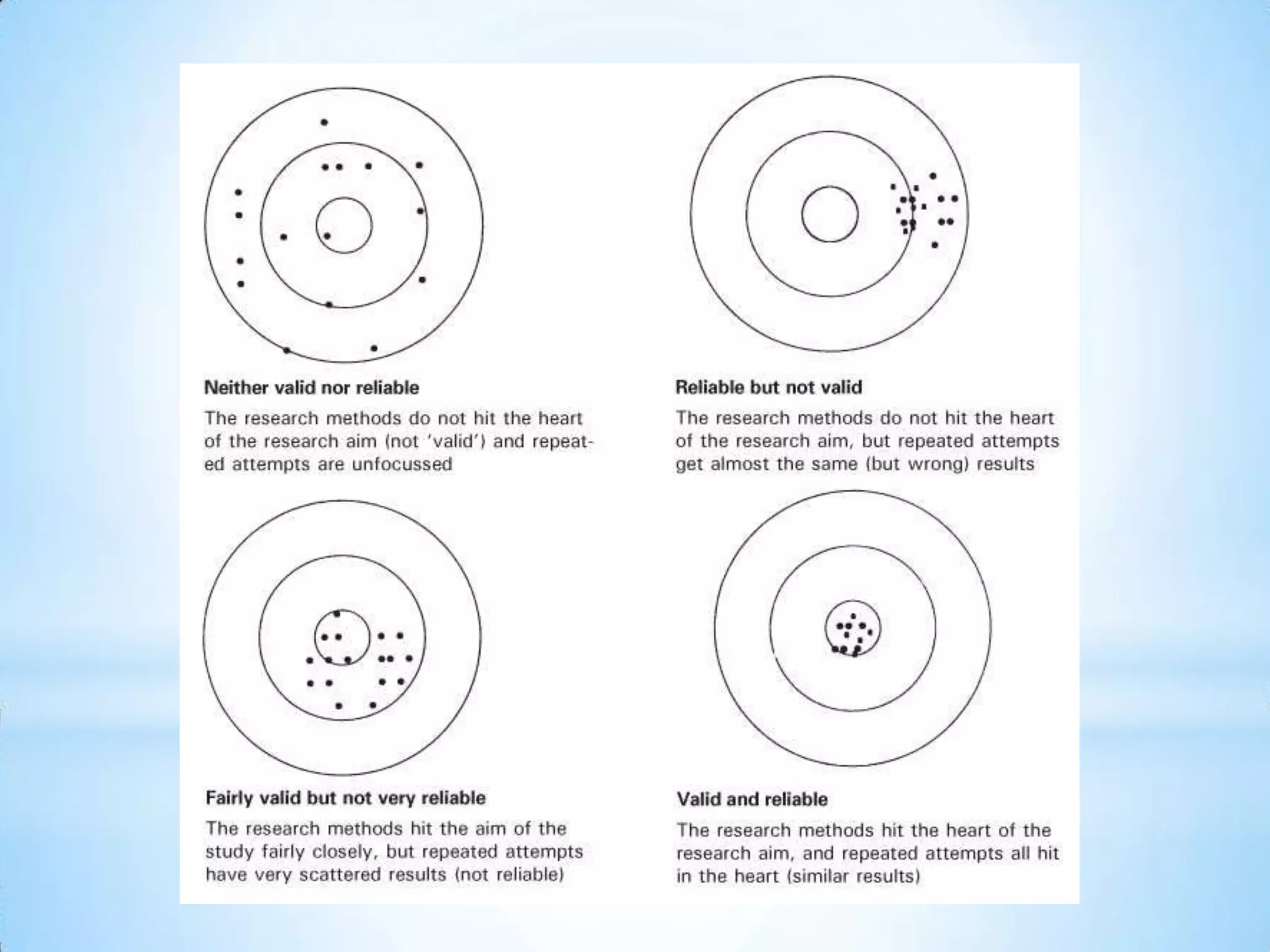


This document discusses key concepts for ensuring quality in qualitative research: Reliability refers to the accuracy and comprehensiveness of observations and inferences in a study. Qualitative research aims to be reliable but is difficult to replicate exactly. Validity means how well a test measures its intended subject. Qualitative research must have conclusions supported by data. Triangulation compares results from different data collection methods to improve credibility. The refutability principle seeks alternative explanations to achieve objectivity through constant comparison of data. Ensuring reliable methods and valid conclusions is important for qualitative research.








