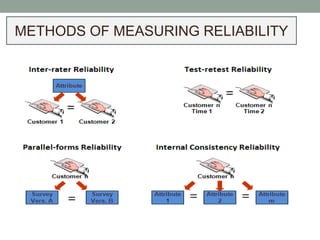
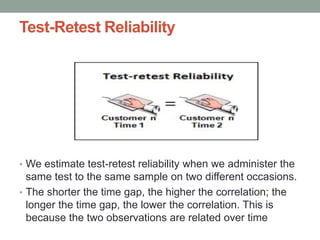
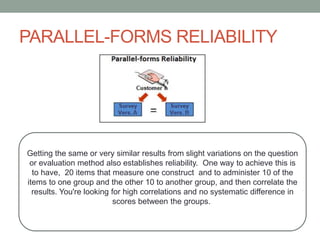
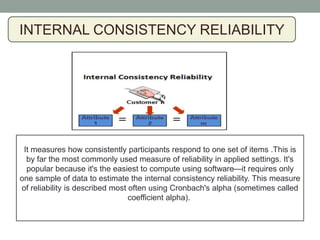
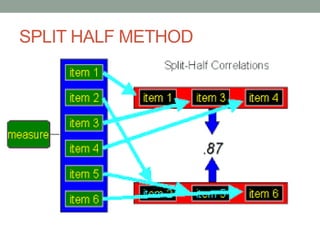
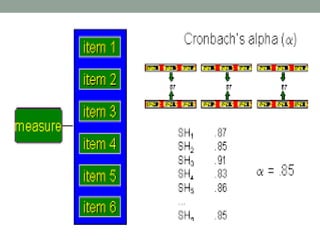
This document discusses various methods for measuring the reliability of assessment tools, including inter-rater reliability, test-retest reliability, parallel forms reliability, internal consistency reliability, and the split half method. Inter-rater reliability assesses consistency between raters, while test-retest reliability examines consistency over time. Parallel forms reliability looks for similar results between variations of a test. Internal consistency reliability uses Cronbach's alpha to measure item consistency, and the split half method correlates scores between halves of a test.