This document provides a summary of quality control tools and applications, including:
- A brief history of quality control from ancient times to the modern development of statistical quality control methods.
- An overview of W. Edwards Deming's 14 principles for transforming quality management.
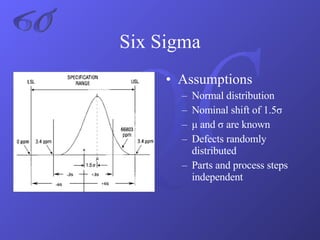
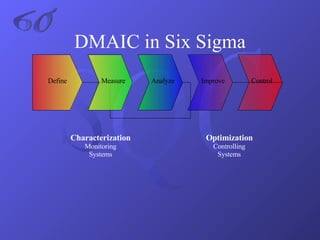
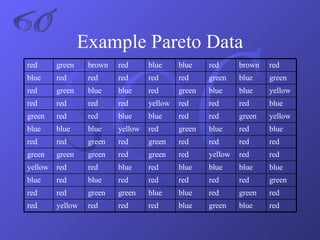
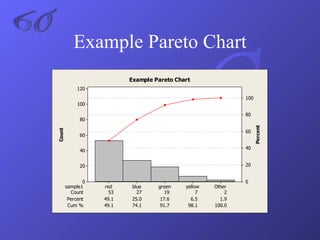
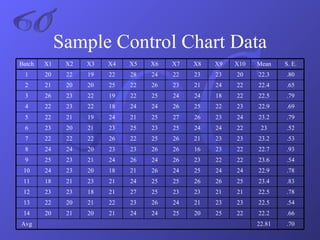
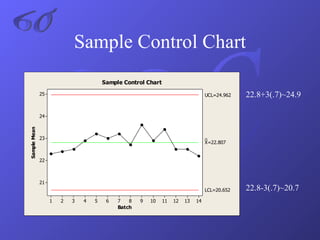
- An explanation of Six Sigma methodology and associated statistical measures and tools like DMAIC, control charts, and Pareto charts.
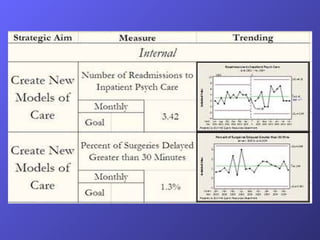
- A discussion of how balanced scorecards can be used to communicate strategy and align organizational goals across financial, customer, internal processes, and learning/growth perspectives.
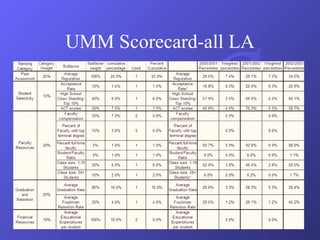
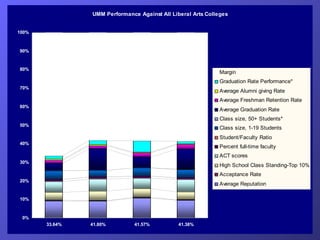
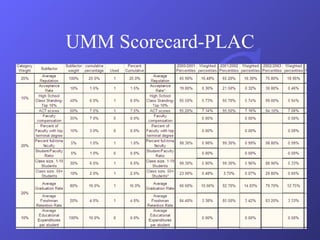
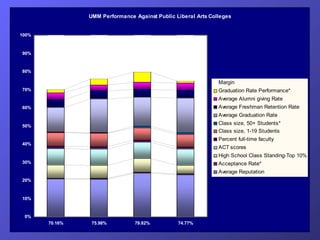
- Examples of balanced scorecards implemented at a healthcare organization and the University of Minnesota Morris campus.