The document discusses two phases of quality control operations - statistical process control and inspection control. It also describes the concept of quality circles, which are small groups of employees who regularly meet to improve quality-related problems. The key aspects covered are:
1) Statistical process control measures and continuously improves work processes before final inspection, while inspection control inspects raw materials, semi-finished and finished products.
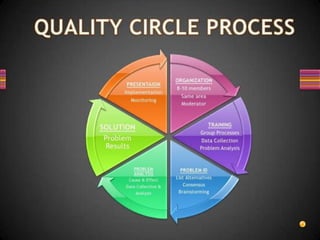
2) Quality circles typically have 6-12 volunteer members who receive training and work to solve quality and productivity problems within their work area.
3) Successful quality circles require buy-in from management and employees, with management supporting implementation of suggested solutions.