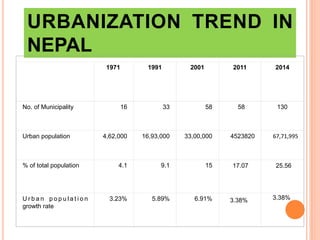
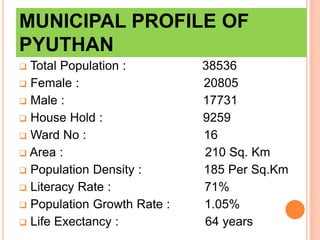
This document provides an overview of urban management policies and practices in Nepal. It discusses Nepal's population statistics and demographics. Urbanization has been increasing, with the urban population growing at 3.38% annually. The government has implemented various policies and legislation related to local governance, solid waste management, and urban development. Key challenges facing urban areas include a lack of basic infrastructure and services, high levels of poverty, and increasing pressure on municipalities as populations grow. The document also outlines opportunities to address these issues under Nepal's new constitution.