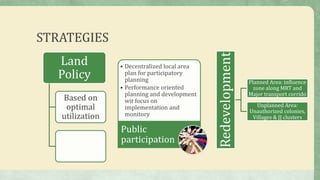
Delhi is the second most populated city in India with over 16 million people. It faces many problems related to unplanned development, lack of public participation, inadequate infrastructure, and environmental issues. The strategies outlined in the document propose decentralized local area planning, performance-oriented development focused on implementation, increasing public participation, planned redevelopment along transport corridors, increasing housing supply through group housing and PPPS, improving disaster management and the environment, regulating mixed-use development, developing trade centers, and enhancing infrastructure for health, education, and sports.