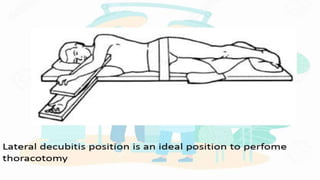
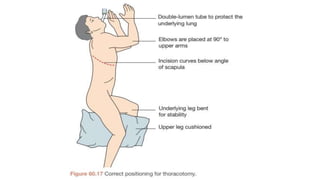
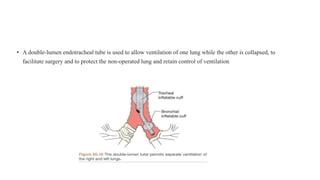
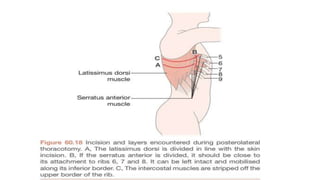
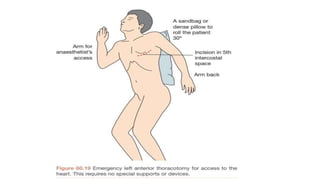
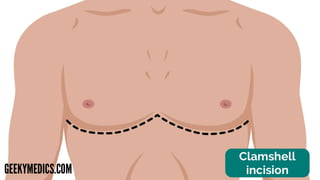
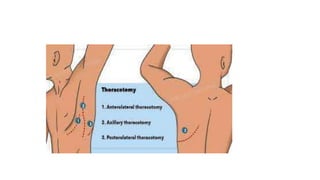
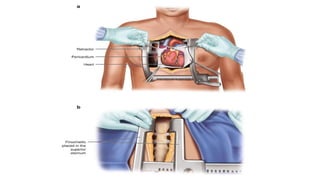
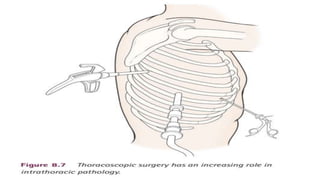
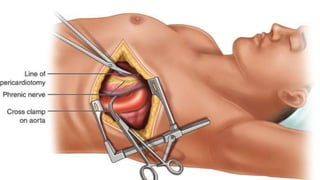
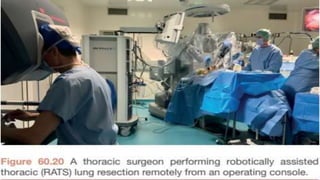
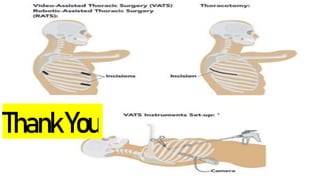
A thoracotomy is a major surgery that involves making an incision between the ribs to access the chest cavity. The most common reason for a thoracotomy is to treat lung cancer. A posterolateral thoracotomy is the standard incision approach, allowing access to lungs, bronchi, pleura, and other chest structures. Thoracotomies are also used to diagnose and treat other conditions affecting the lungs, heart, and chest. The surgery involves opening the chest wall and may require collapsing one lung. Possible complications include prolonged recovery, infection, and blood clots.