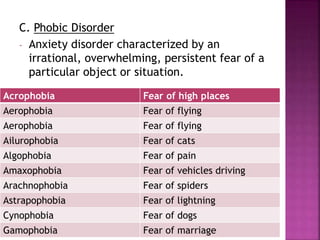
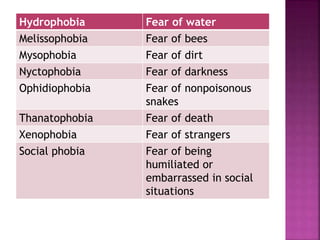
This document defines and describes various psychological disorders. It discusses approaches to understanding disorders including biological, psychological, sociocultural, and biopsychosocial models. Specific anxiety, mood, dissociative, psychotic, and personality disorders are defined. Treatments including biomedical therapies, electroconvulsive therapy, psychosurgery, and various psychotherapies are also summarized.