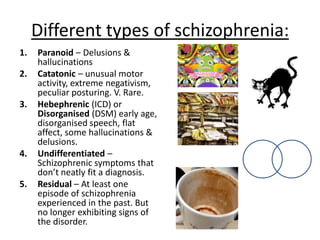
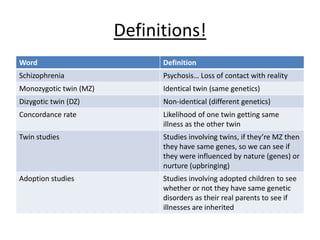
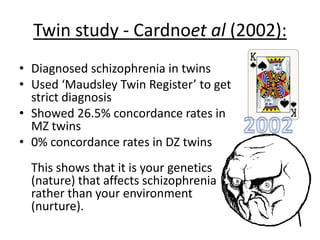
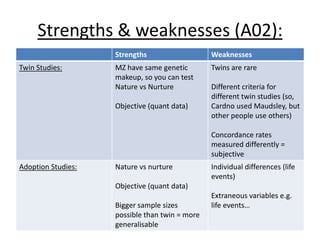
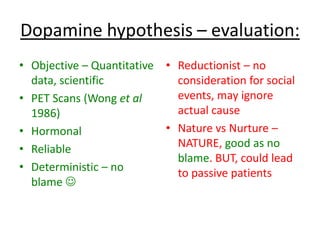
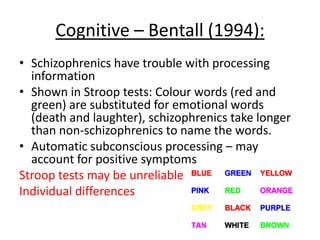
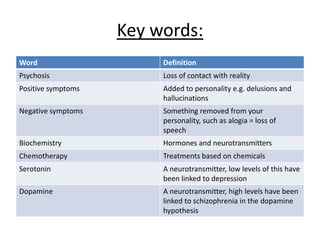
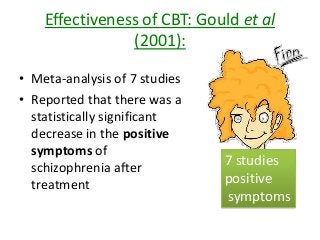
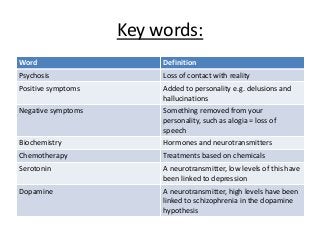
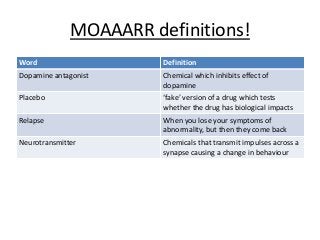
Schizophrenia is characterized by psychosis, or a loss of contact with reality. It has a prevalence of 1% of the population and is classified into positive and negative symptoms. Positive symptoms include delusions and hallucinations, while negative symptoms involve a reduction in emotions and behaviors. Biological factors like genetics and dopamine levels are thought to contribute to schizophrenia. Treatment involves atypical antipsychotic drugs which target both positive and negative symptoms with fewer side effects than conventional drugs. However, antipsychotics may also have disadvantages like sudden death or involuntary movements.