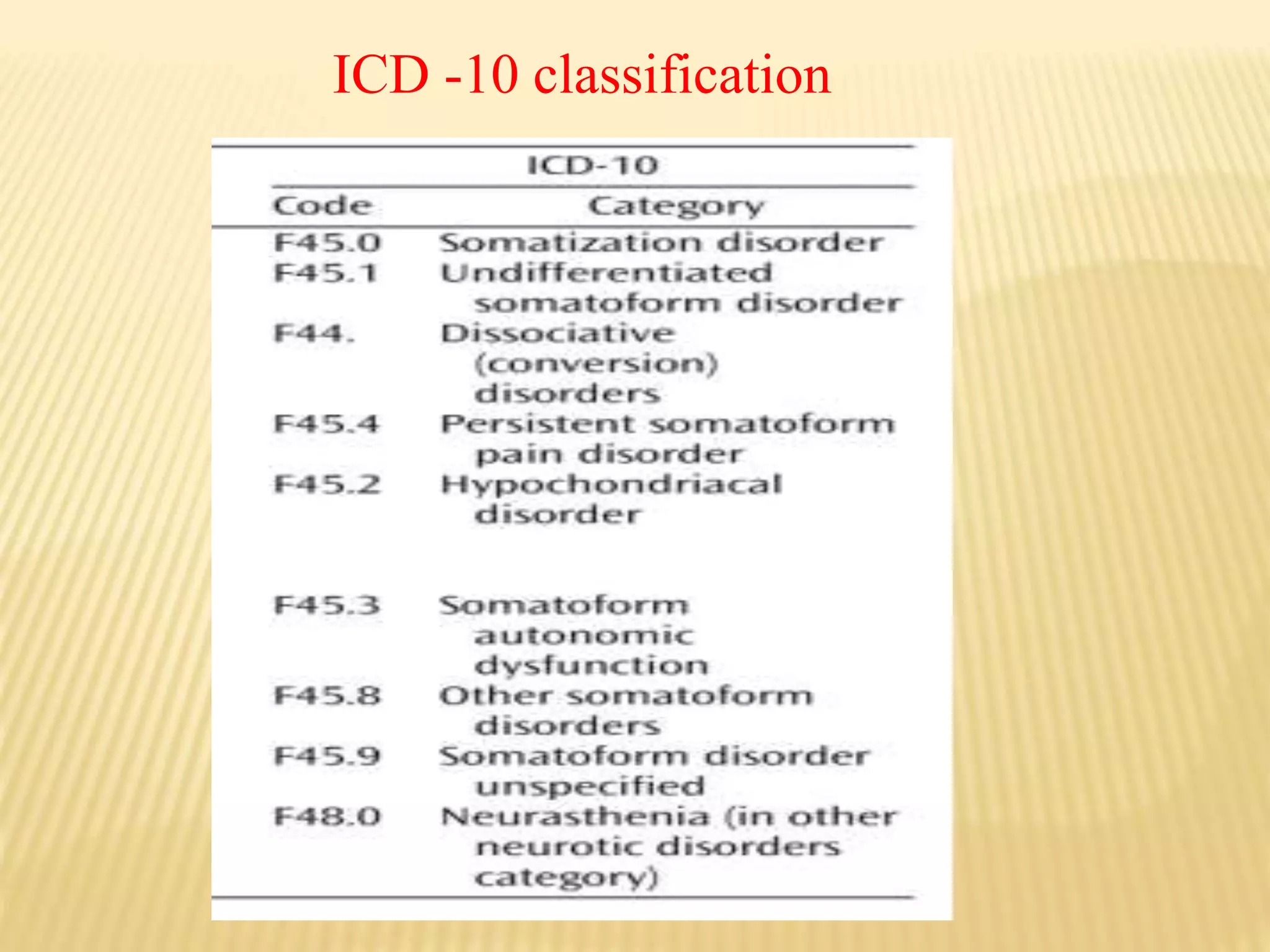
Somatoform disorders are mental illnesses characterized by physical symptoms without medical explanations, interfering with social or occupational functioning. Various types include somatization disorder, hypochondriasis, conversion disorder, and body dysmorphic disorder, each with specific diagnostic criteria and treatment approaches such as psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy. The disorders often involve a complex interplay of psychological and social factors, with the primary aim being symptom management and enhancing quality of life.