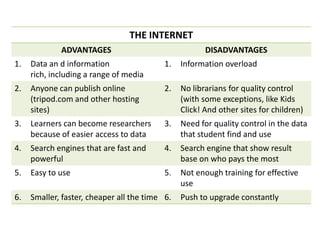
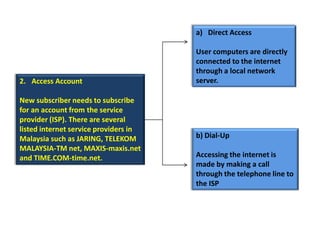
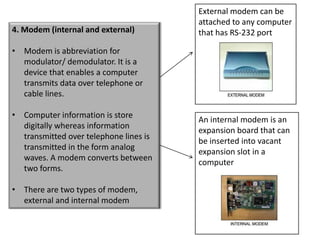
The document discusses the basics of the internet and its requirements. It provides advantages and disadvantages of using the internet. The main requirements to connect to the internet are a network interface card, an access account from an internet service provider, and various hardware such as modems, hubs, switches, routers, and wireless access points. The internet is the world's largest computer network connecting millions of computers globally.