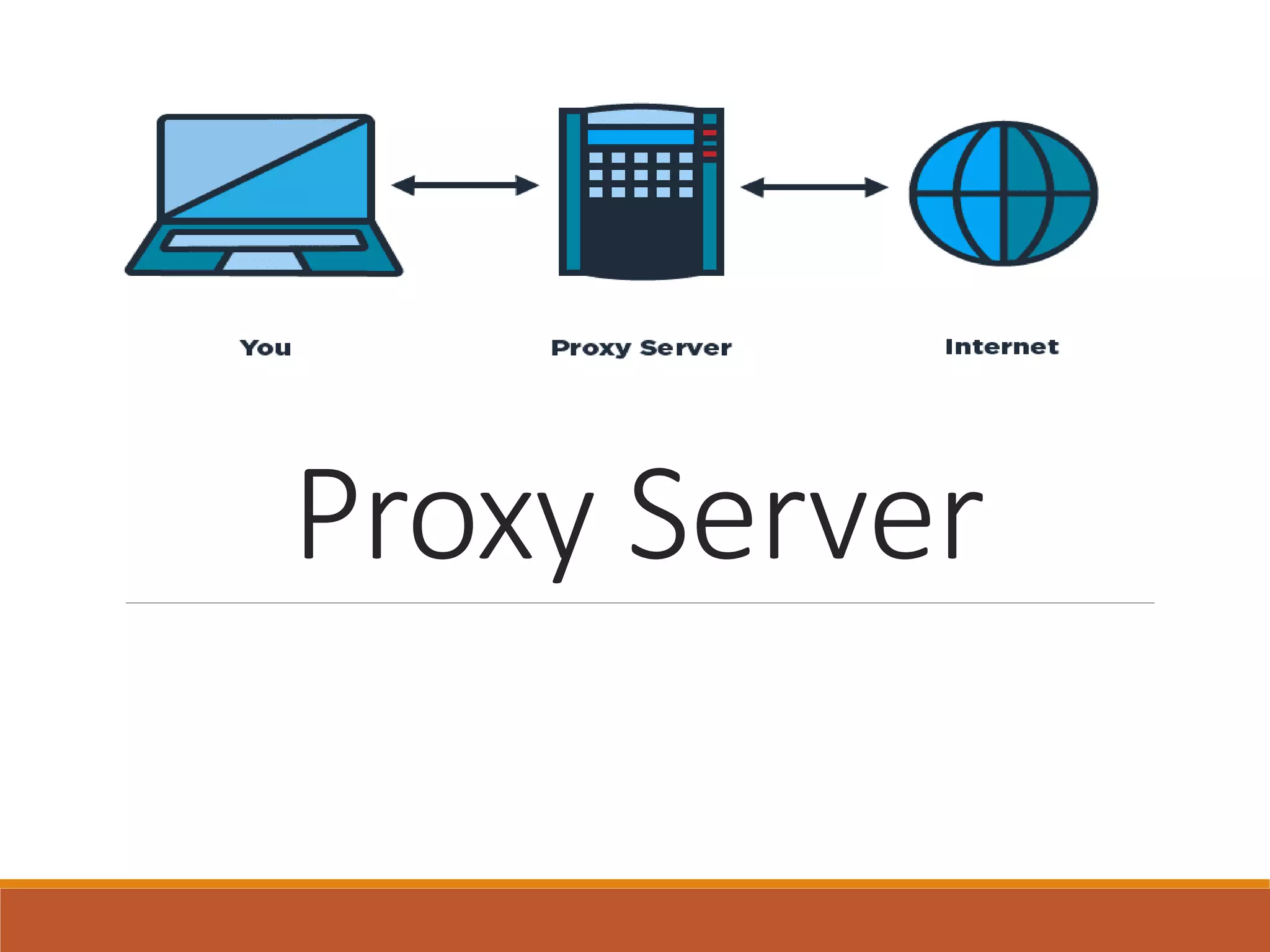
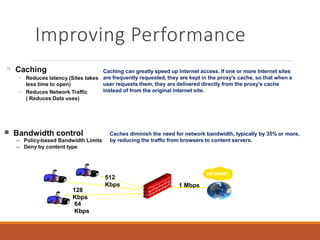
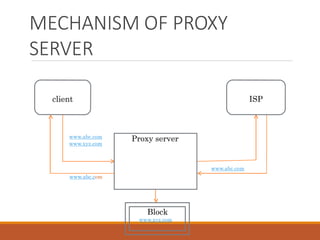
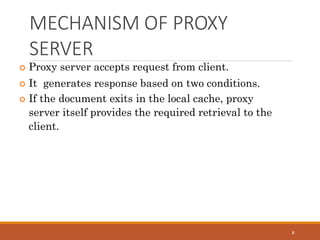
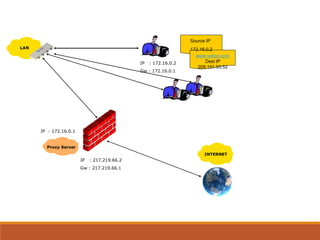
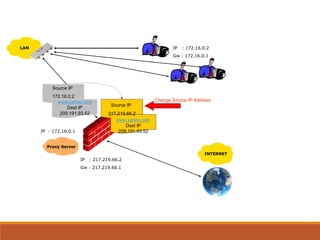
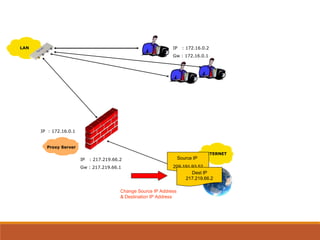
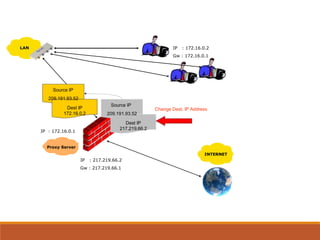
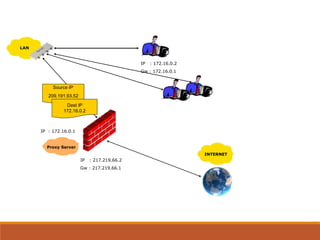
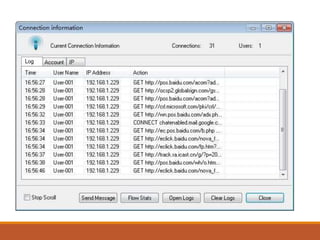
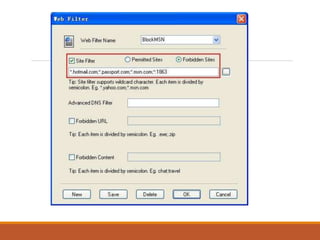
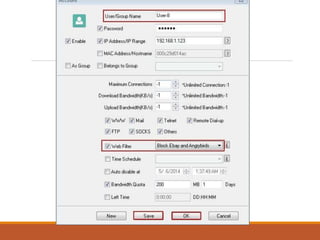
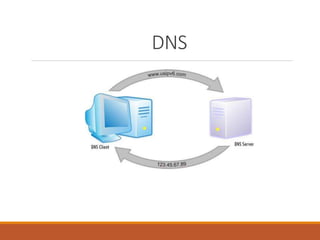
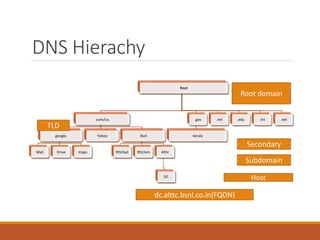
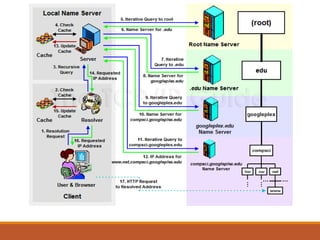
Proxy servers operate as an intermediary between a local network and services available on a larger network like the Internet. They improve performance by caching frequently requested web pages and filtering requests to prevent access to certain sites or protocols. The main types of proxy servers are caching proxy servers, web proxy servers, content-filtering web proxy servers, and anonymizing proxy servers.