This document provides an overview of HTTP including:
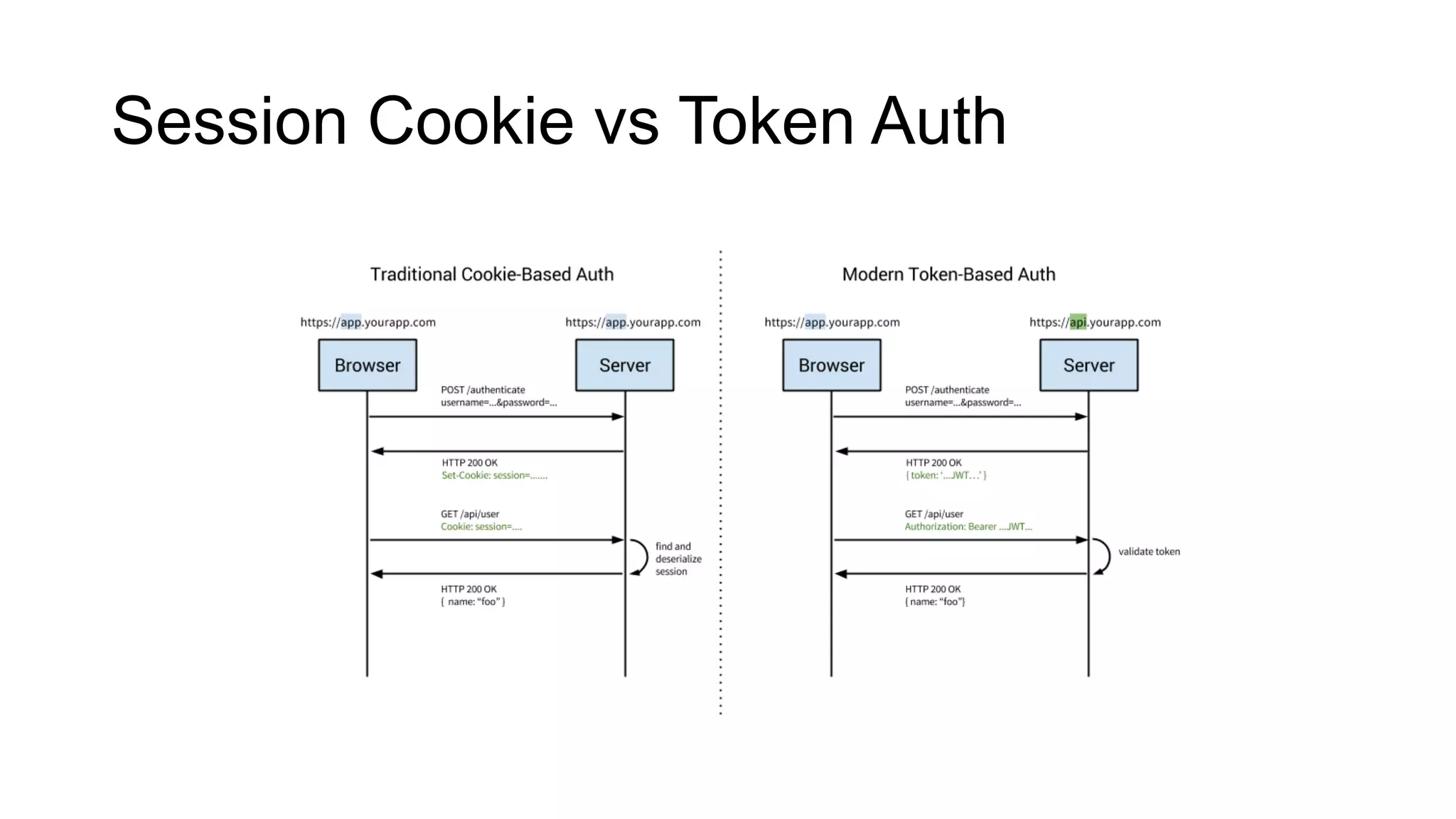
- HTTP is a stateless protocol that does not require servers to retain user information across requests.
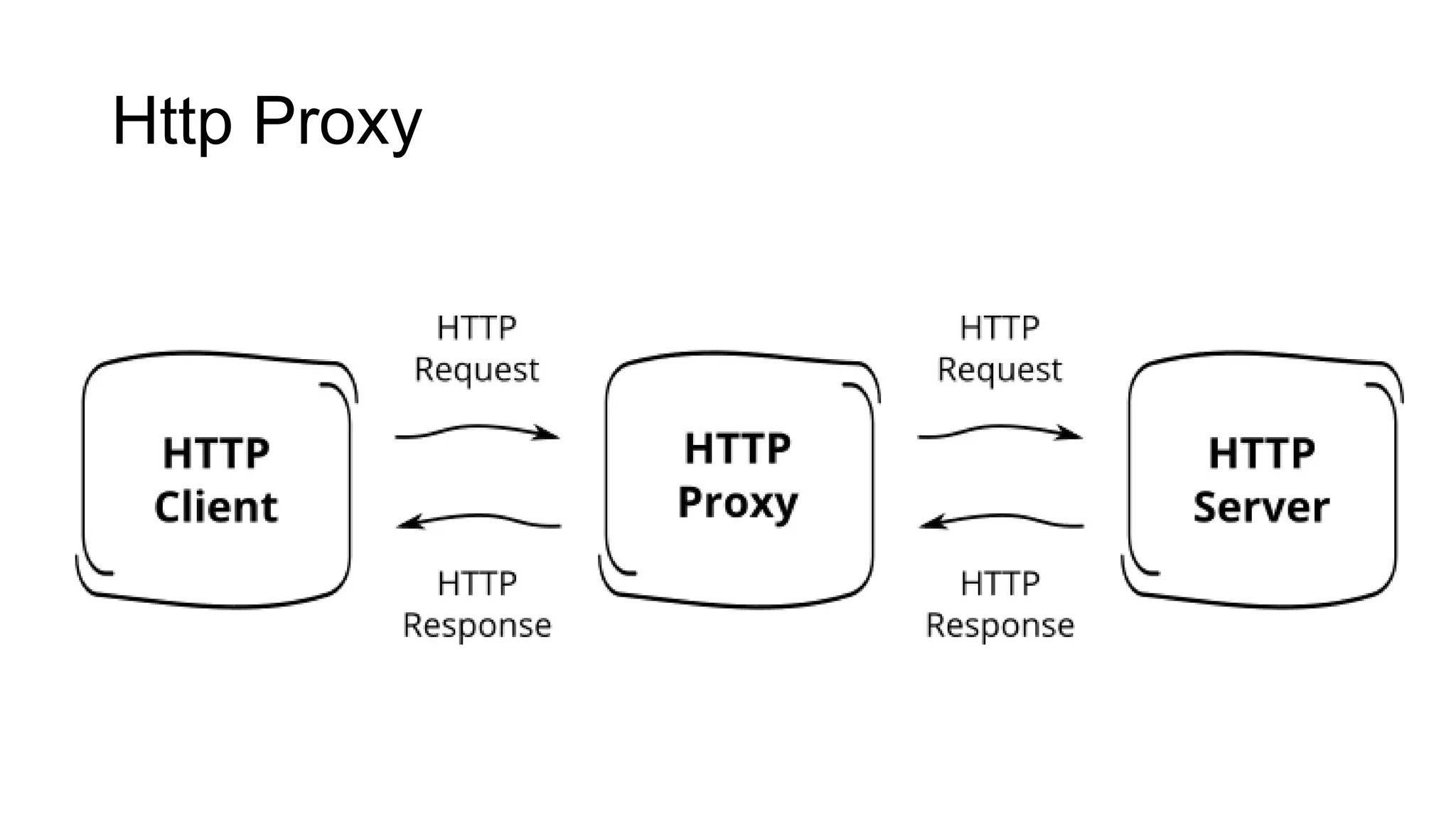
- Popular HTTP proxy tools like Fiddler and Burp Suite can be used to inspect and debug HTTP traffic.
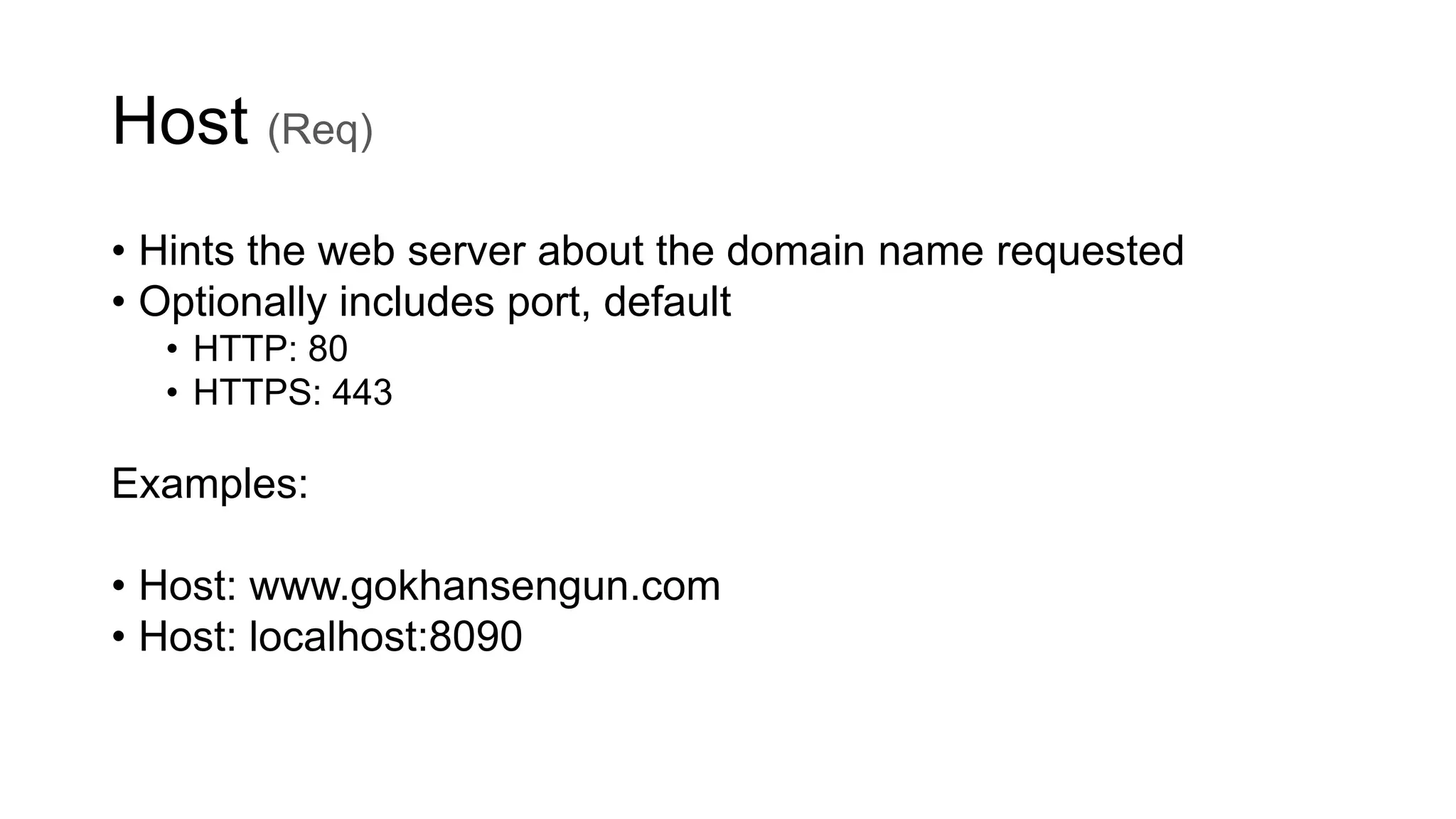
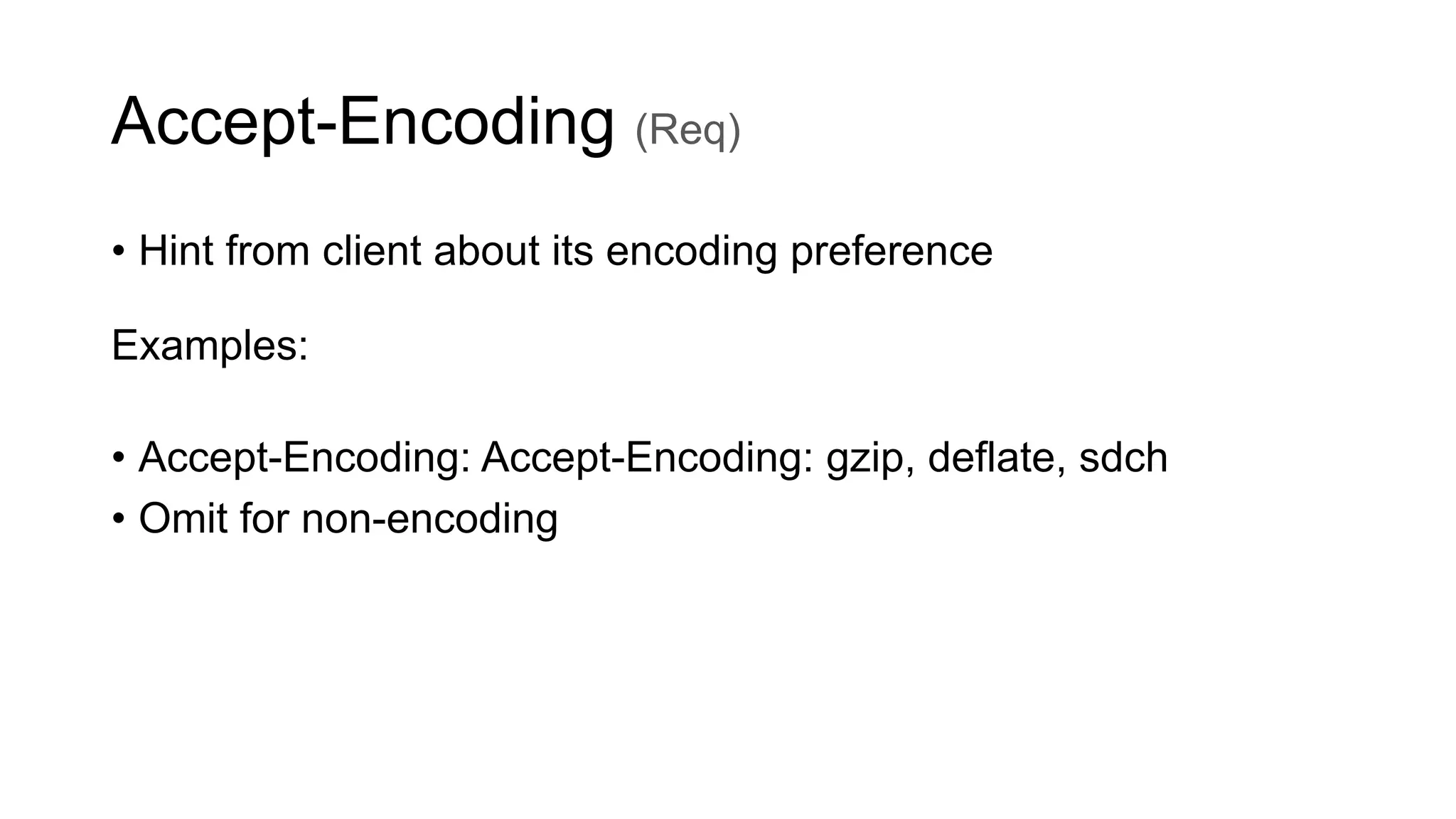
- Key parts of HTTP include requests methods, response codes, headers for accepting content types, encoding, authentication, and more.
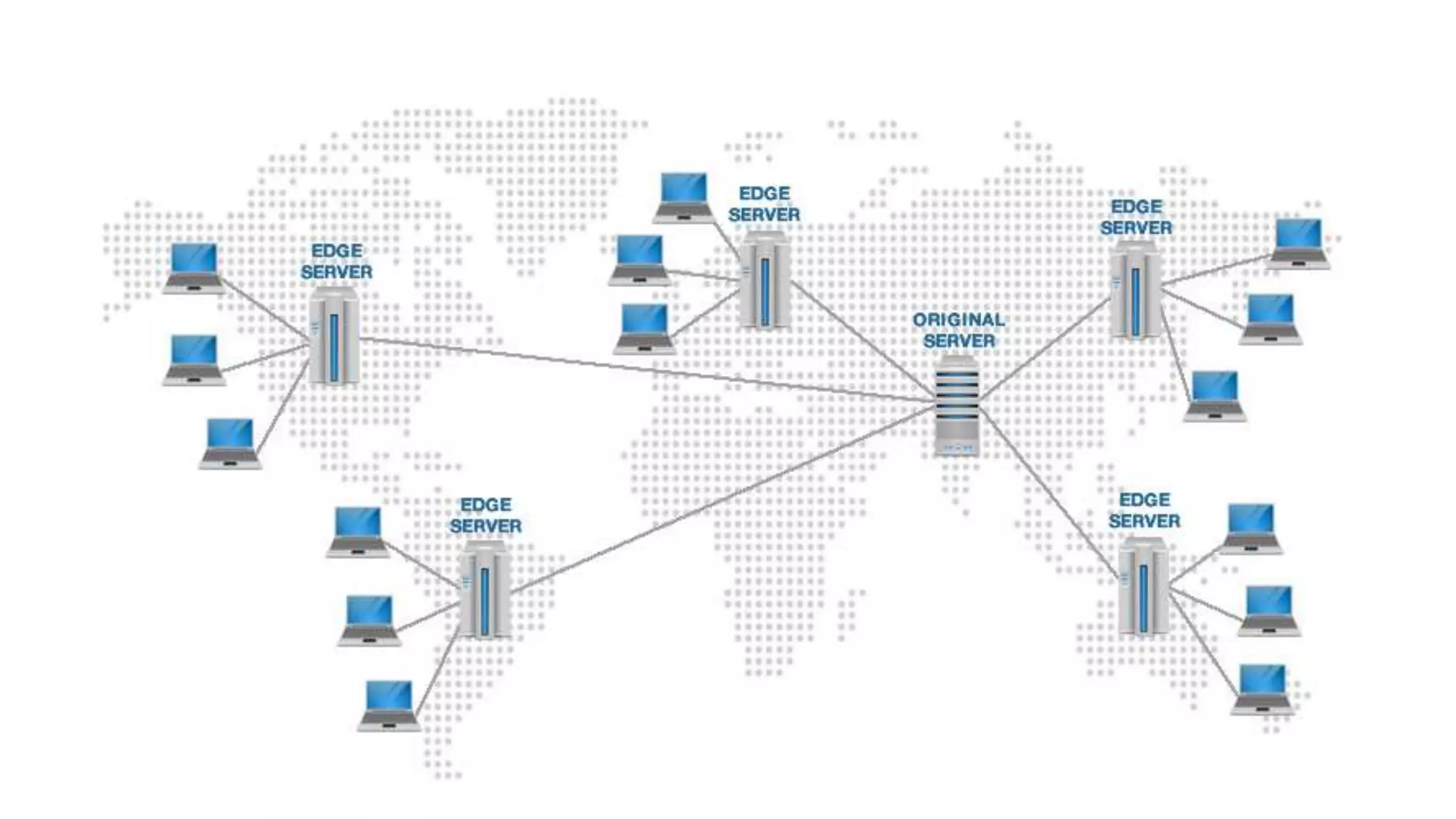
- Common players that interact with HTTP include web servers, load balancers, caching servers, CDNs, and security tools.











![Methods
Method Used for
GET Retrieve a resource
POST Create / Update a resource [Not Idempotent]
PUT Create / Update a resource [Idempotent]
DELETE Delete a resource
HEAD Retrieve a resource except the body](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/http-allyouneedtoknow-161125101227/75/Http-All-you-need-to-know-13-2048.jpg)