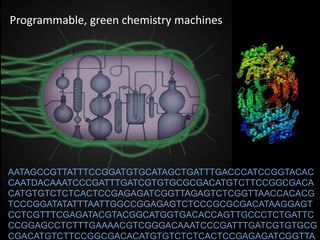
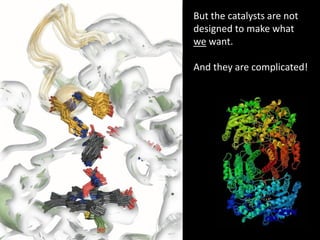
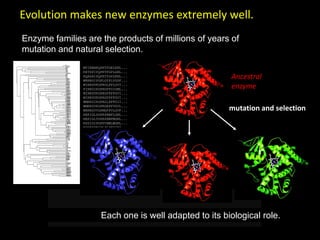
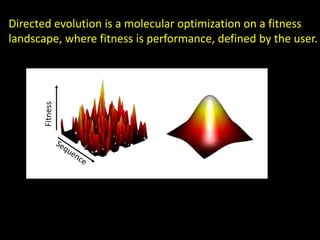
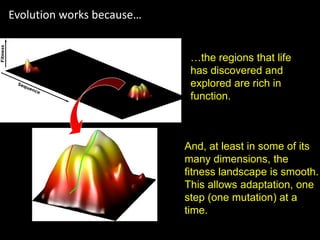
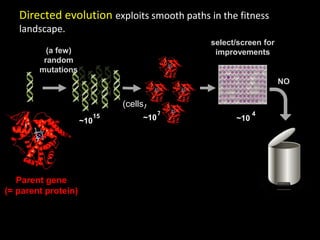
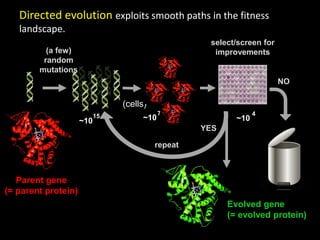
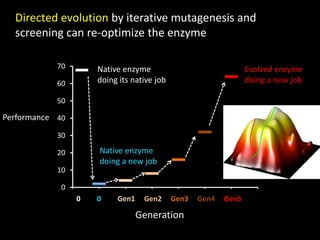
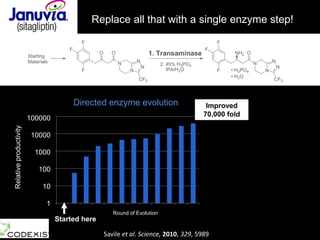
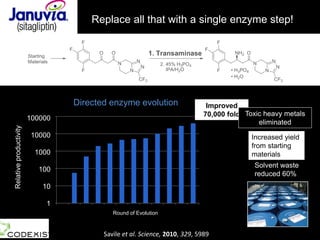
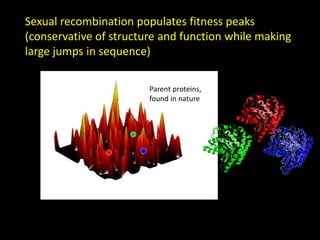
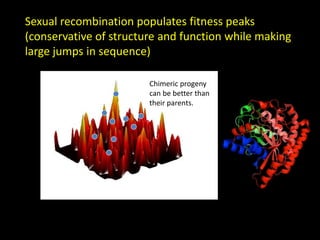
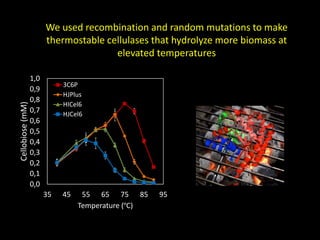
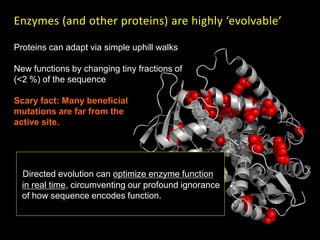
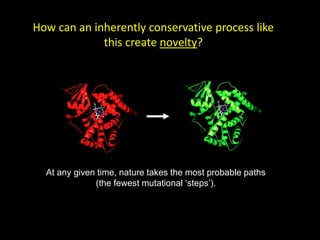
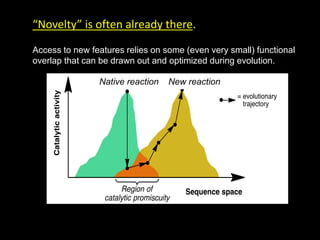
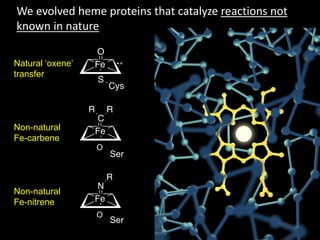
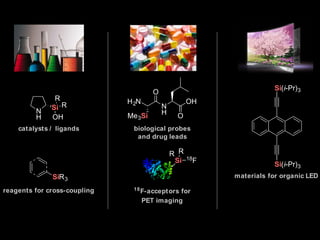
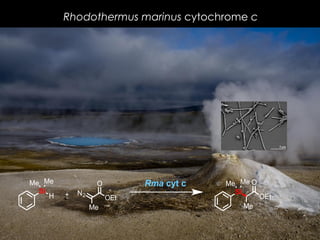
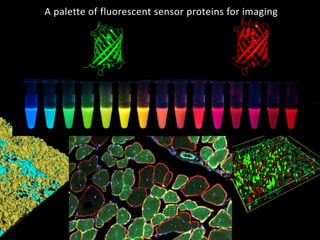
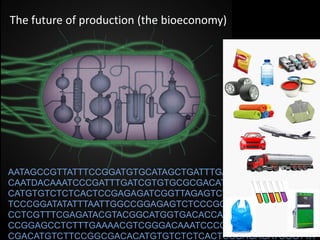
The document discusses the role of enzymes in breaking down proteins and fats, highlighting their importance in green chemistry and energy reduction. It emphasizes the evolution of enzymes through natural selection and directed evolution, which enhances their functions for various applications, including improved synthetic processes and environmental sustainability. The text also explores future possibilities for enzymatic engineering to generate novel reactions and tailored solutions in biochemistry and agriculture.