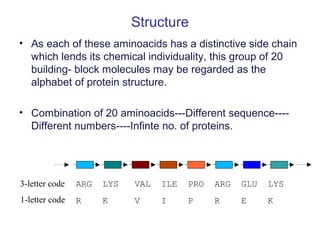
Proteins are organic macromolecules made of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. They range widely in size and function. The fundamental units are 20 different amino acids that make up the primary structure in different sequences. Secondary structures like alpha helices and beta sheets form due to hydrogen bonding of amino acid R groups. Tertiary and quaternary structures arise from further folding and interactions between polypeptide subunits. Proteins have important roles like enzymatic catalysis, transport, structure, regulation and defense. They are classified based on solubility and presence of non-protein groups.