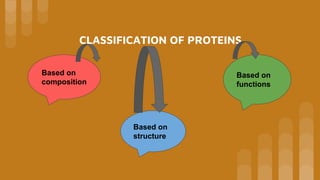
Proteins can be classified in several ways:
1. Based on composition - such as albumins, globulins, glycoproteins, etc. Simple proteins contain only amino acids, conjugated proteins contain non-protein groups, and derived proteins are modified from natural proteins.
2. Based on structure - globular proteins have a spherical shape like enzymes and hormones, while fibrous proteins have a fiber-like structure like collagen.
3. Based on function - enzymic proteins show catalytic activity, structural proteins form tissues, transport proteins move molecules in the body, storage proteins store nutrients, and toxic proteins provide protection against pathogens.