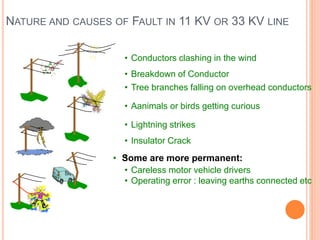
1. Faults on 11kV or 33kV power lines can be caused by conductors clashing in wind, breakdown of conductors, tree branches falling, animals or birds, careless drivers, lightning strikes, insulator cracks, or operating errors.
2. Faults can result in damage to equipment from short circuits, fire hazards, loss of system stability and blackouts, and interruption of power to consumers causing revenue loss.
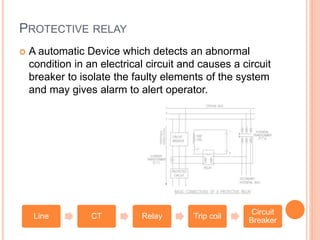
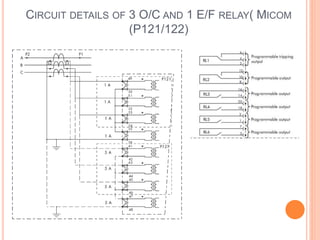
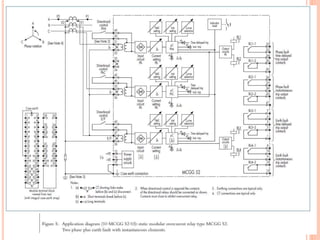
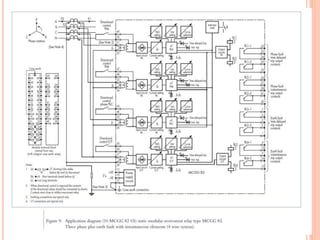
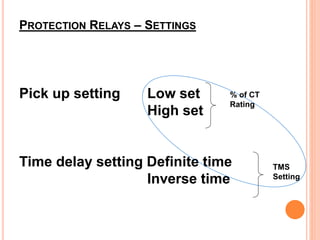
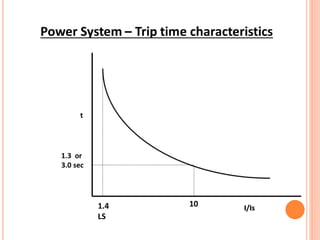
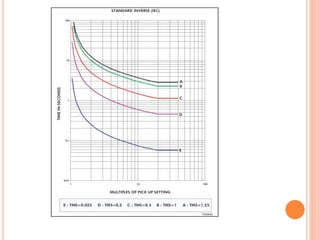
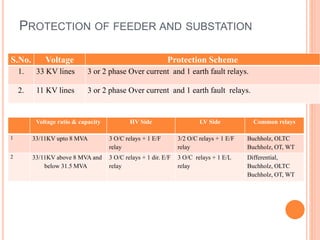
3. Protective relays automatically detect faults and cause circuit breakers to isolate faulty elements to protect the system and may alert operators. Common relays used include overcurrent, earth fault, and differential relays.