Embed presentation






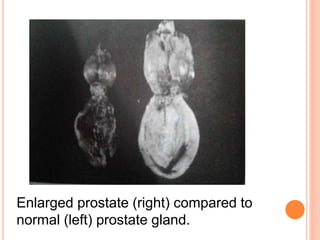




Prostate hyperplasia in dogs is a natural consequence of aging that occurs in most dogs over six years old, as both estrogen and androgen must be present for marked enlargement. The prostate gland is located near the bladder, and an enlarged prostate can be detected during rectal examination, ultrasound, or cytological examination. The most effective treatments are castration to cause involution of the enlarged gland or low dose estrogen treatment to depress hormone secretion.









