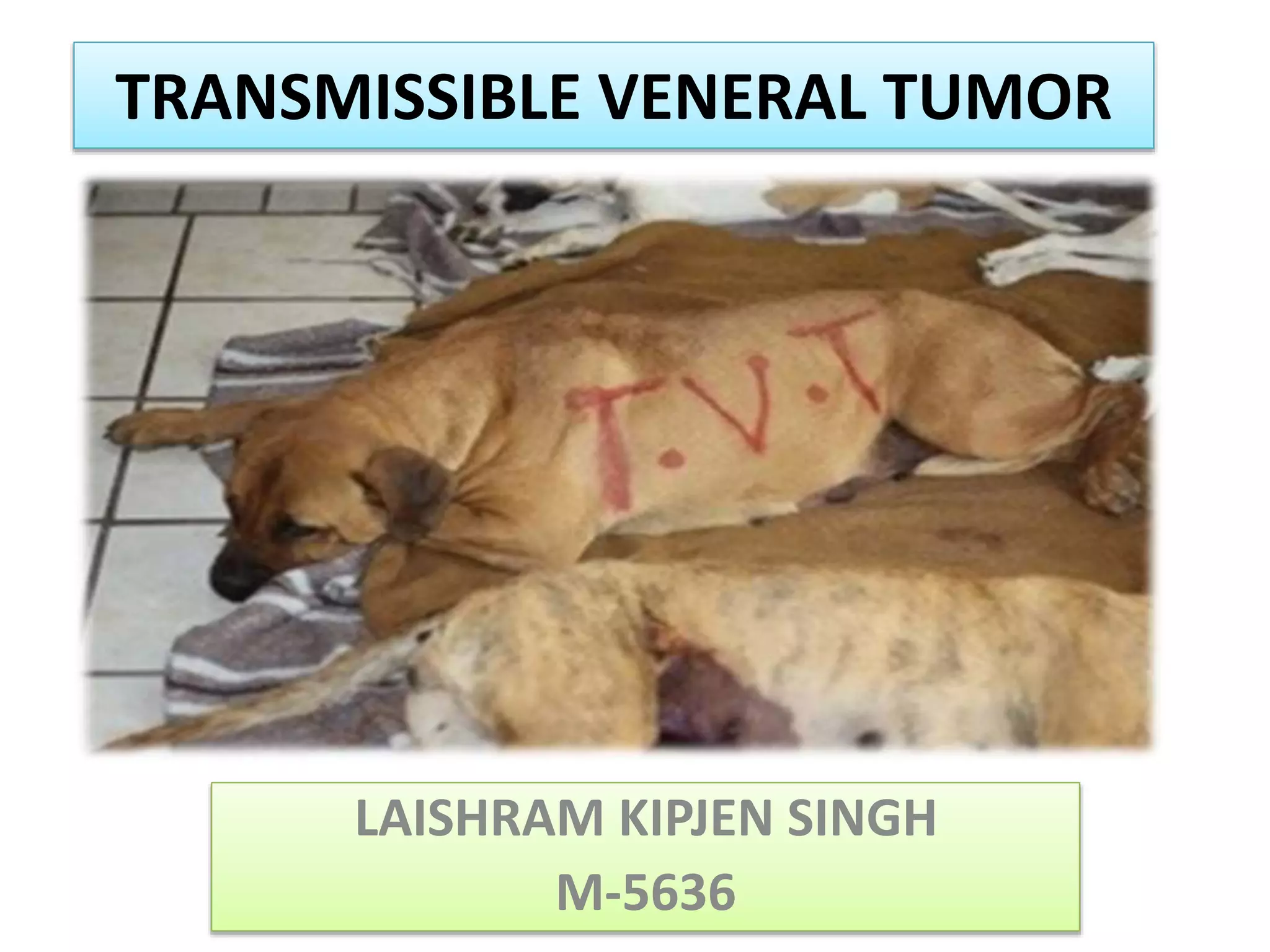
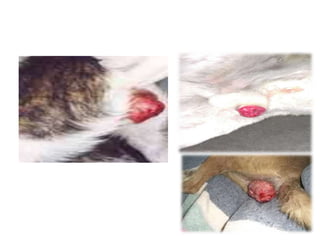
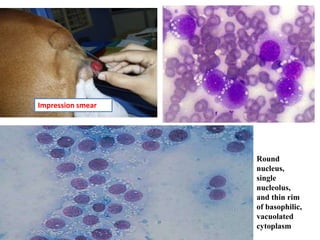
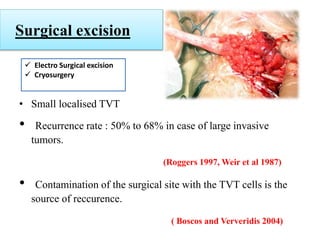
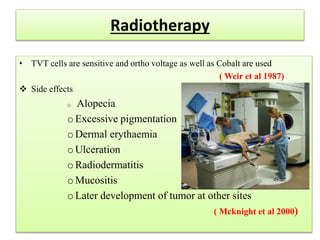
Transmissible venereal tumor (TVT) is a naturally occurring, sexually transmitted cancer that affects the external genitalia of dogs. It has a round cell origin and is transmitted between dogs through contact during mating or licking of affected areas. Common symptoms include genital bleeding or masses. Diagnosis involves identifying the characteristic round cells on smears or biopsies. Effective treatment includes chemotherapy, typically with vincristine, though surgery or radiation are also sometimes used. Recurrence is common without full removal of the tumor.