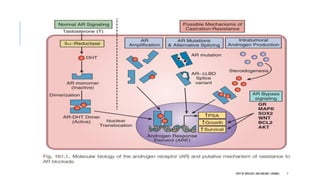
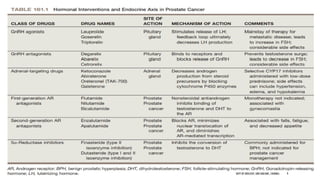
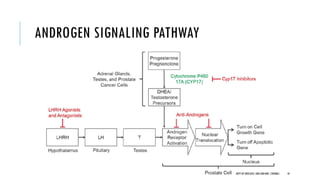
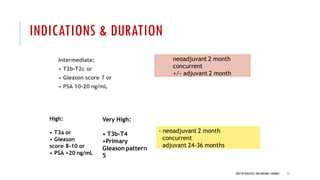
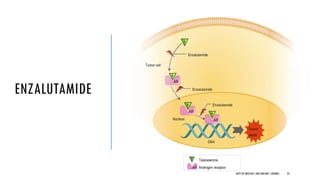
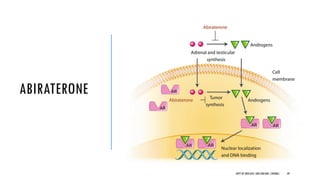
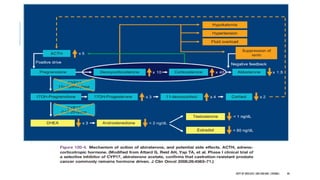
The document discusses hormonal therapy for prostate cancer. It provides a history of hormonal therapy and discusses key figures like Charles Huggins who demonstrated that castration improved outcomes for advanced prostate cancer. It then discusses the molecular biology of the androgen axis and different therapeutic approaches to hormonal therapy including ablation of androgen sources, anti-androgens, LHRH agonists/antagonists, and inhibition of androgen synthesis. Specific drugs are discussed for each class. Adverse effects of hormonal therapy like osteoporosis and hot flashes are also summarized.