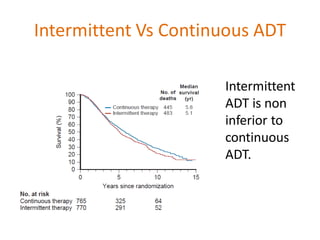
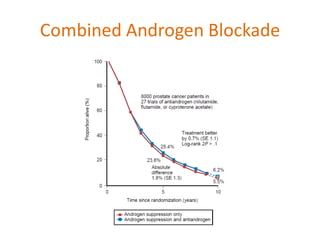
This document summarizes hormonal therapy approaches for prostate cancer, including ablation of androgen sources, anti-androgens, LHRH agonists/antagonists, and inhibition of androgen synthesis. It describes various drugs and their mechanisms of action and side effects. It also discusses testosterone testing, PSA response to ADT, adverse effects like osteoporosis and hot flashes, and indications for ADT in localized, locally advanced, biochemical recurrence, and metastatic prostate cancer.