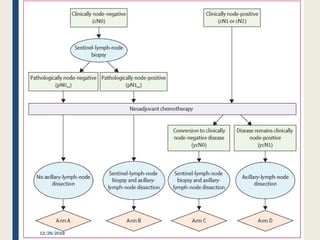
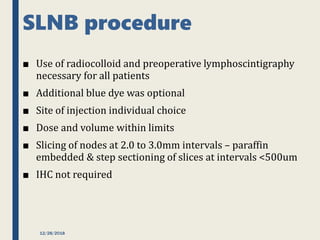
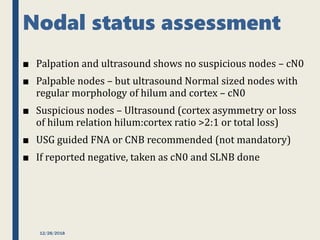
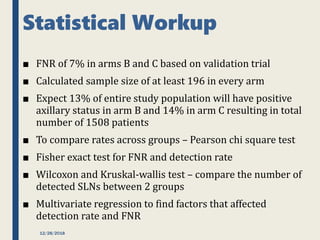
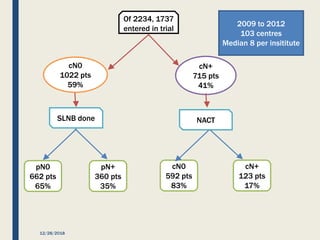
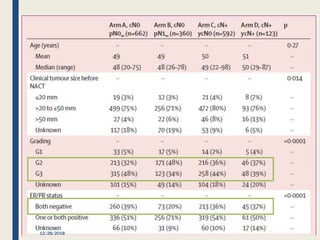
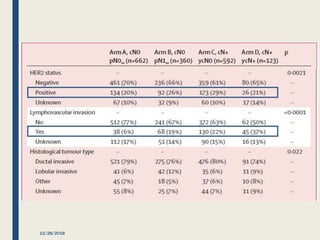
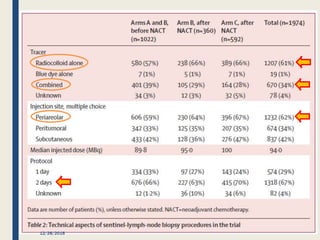
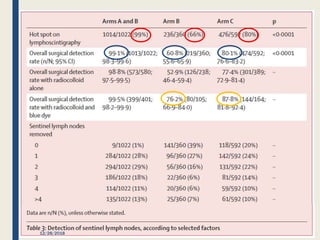
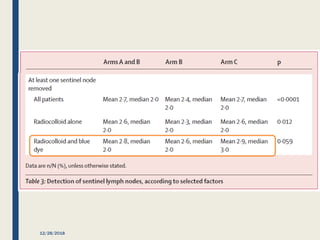
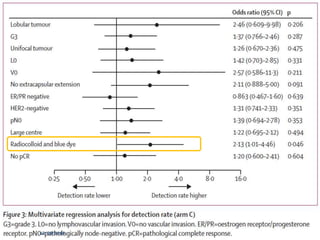
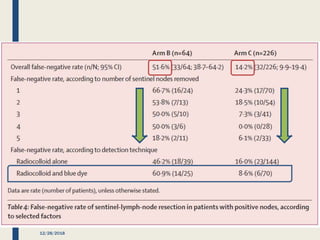
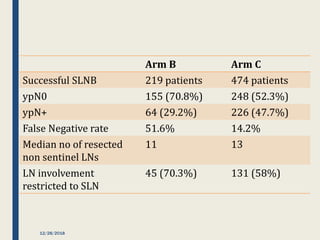
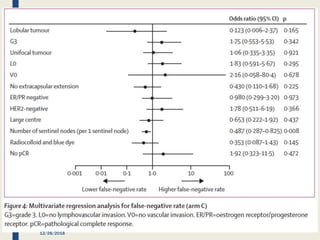
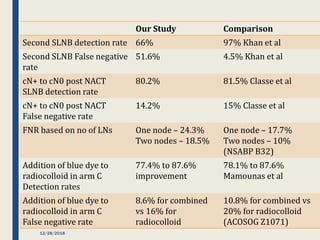
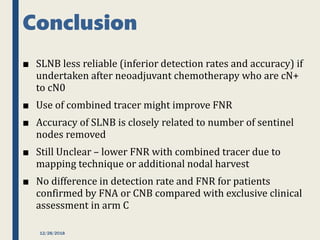
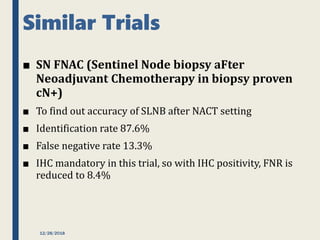
The SENTINA trial evaluated the accuracy of sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) for breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT). It was a prospective multicenter study with 4 arms based on clinical nodal status before and after NACT. The primary objective was to assess the accuracy of SLNB after NACT for patients who converted from clinically node-positive (cN+) to cN0. Secondary objectives included comparing detection rates of SLNB before versus after NACT and false negative rates between procedures. The trial found that SLNB was less reliable after NACT for originally cN+ patients, with lower detection rates and higher false negative rates compared to other studies. Improved identification may result from using