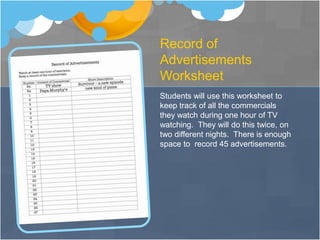
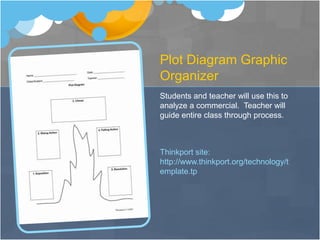
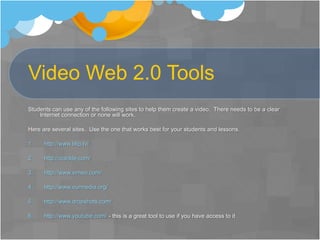
This unit introduces middle school students to digital media and advertising through various lessons and activities. Students analyze commercials and advertisements, track commercial data using spreadsheets, and create their own video commercial using a web 2.0 tool. Formative assessments include student presentations, peer critiques, and use of rubrics. The goal is for students to develop skills in technology and digital media important for future careers. Interviews with teachers found the project beneficial and engaging for all students when appropriately modified.