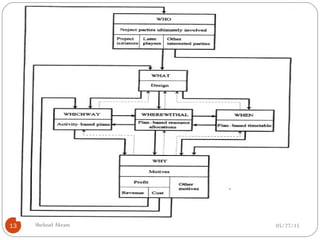
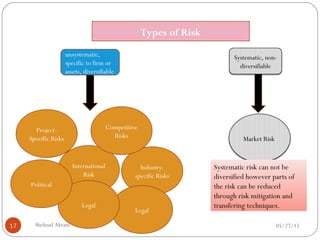
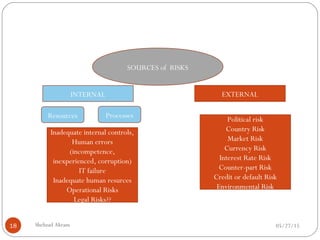
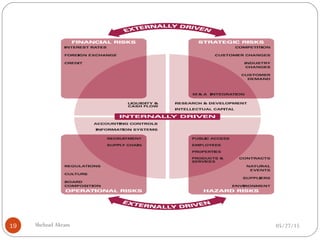
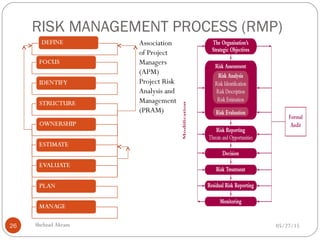
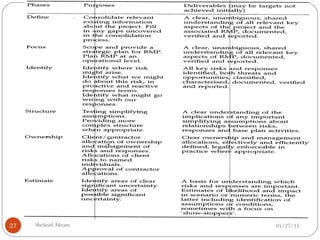
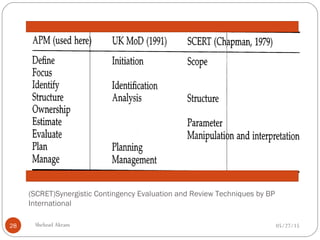
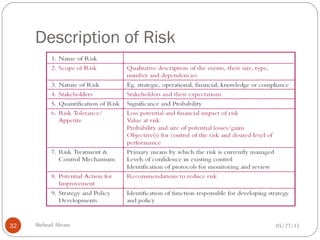
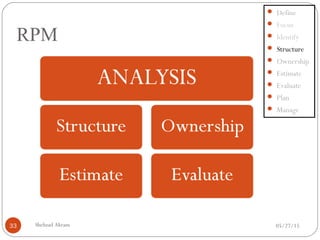
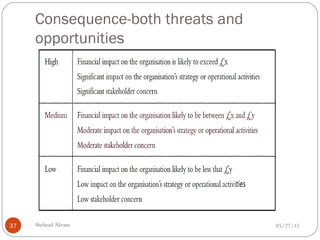
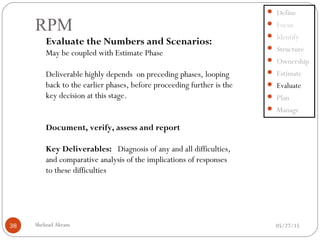
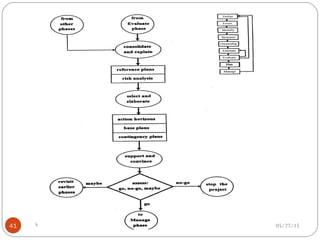
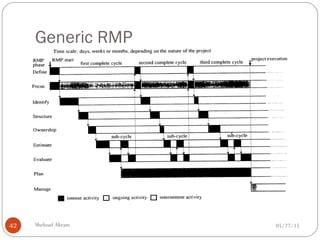
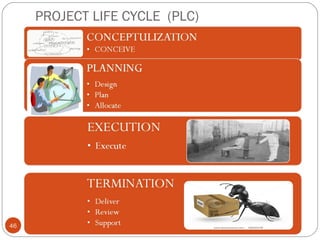
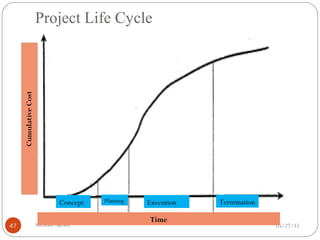
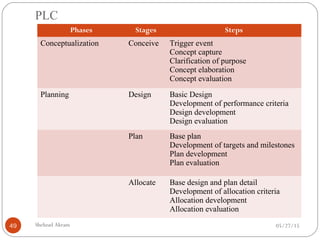
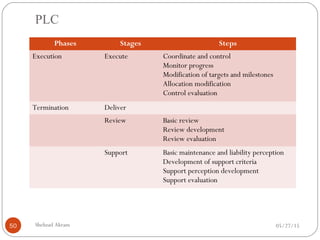
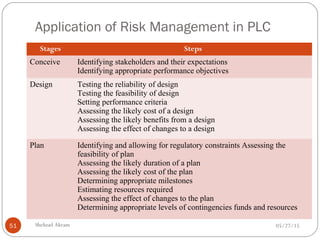
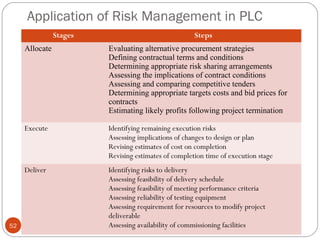
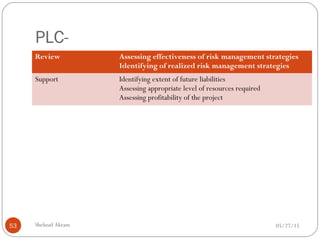
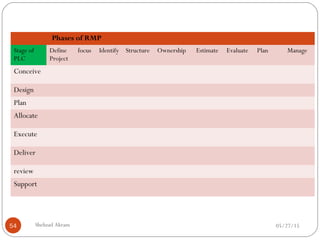
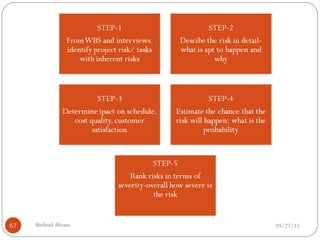
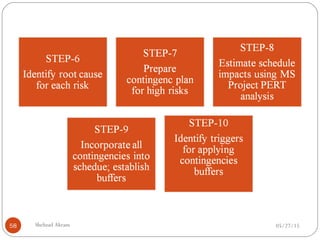
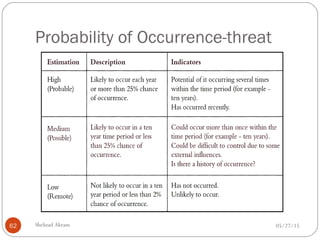
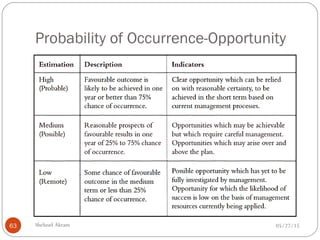
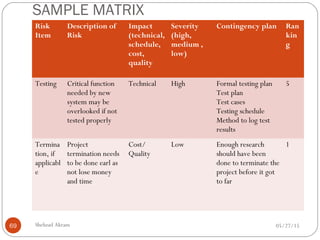
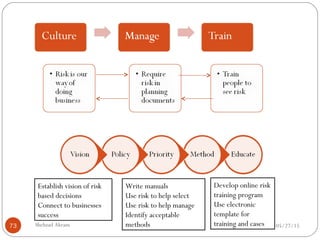
The document discusses project risk management from the perspective of a development institution. It provides definitions of risk, project, and project management. Project risk management involves planning, organizing, securing, and managing resources to control the effects of uncertainties on a project's objectives. The document outlines the roots of uncertainty in a project, types of risks, and the risk management process. It emphasizes that risk management should be integrated into an organization's culture and involve identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks.