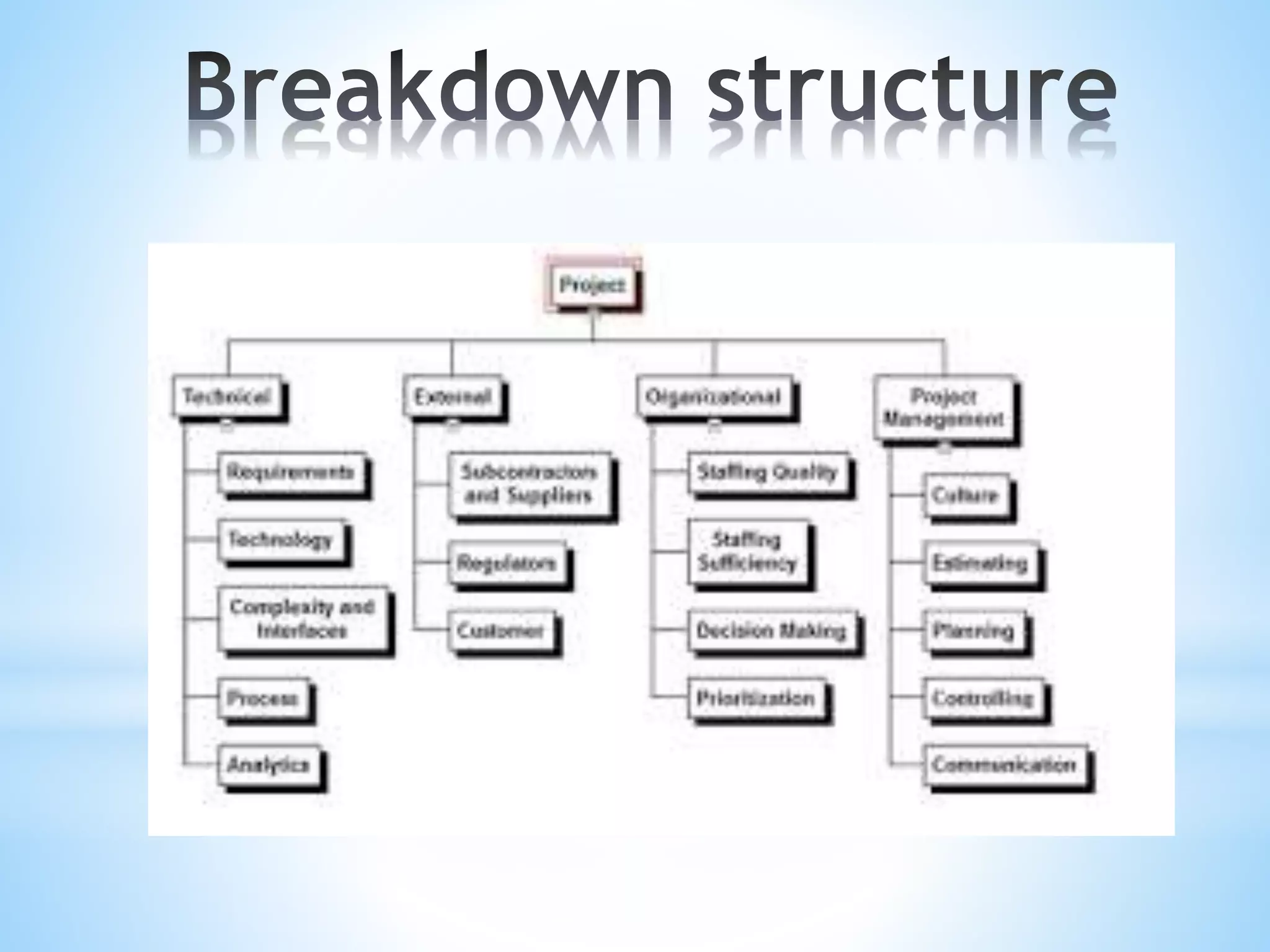
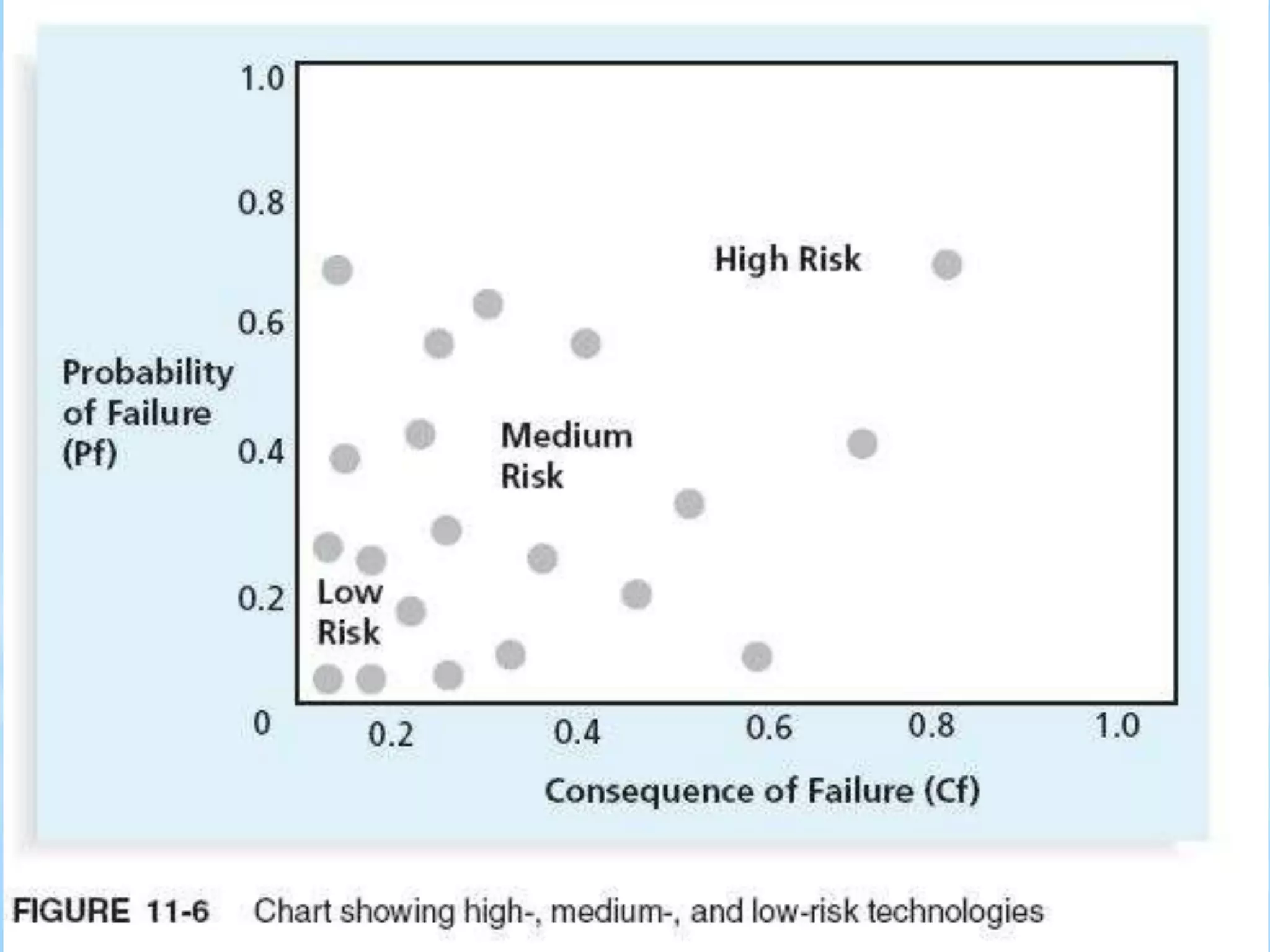
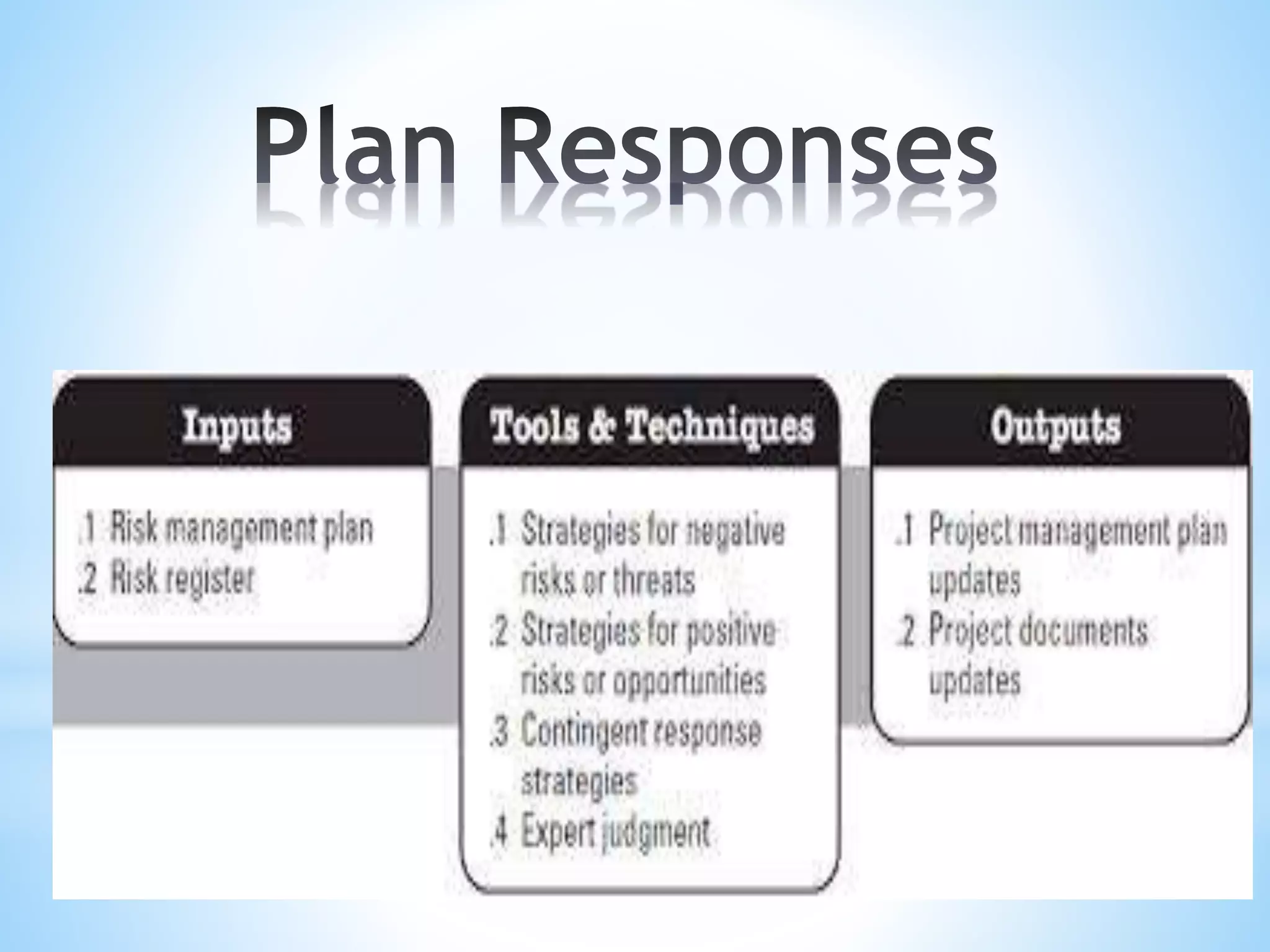
The document outlines risk management as a process involving identification, assessment, and control of risks to maximize project opportunities. It details the various groups in the risk management process, including planning, identifying, and analyzing risks, and emphasizes the importance of maintaining a risk register. Key tools and techniques for assessing and managing risk are also discussed, alongside the need for ongoing updates and monitoring within project management.