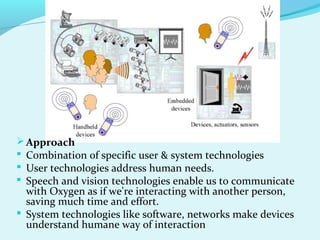
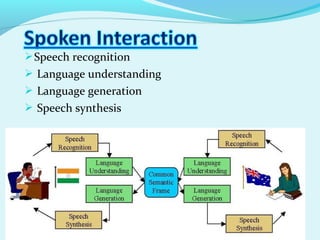
This document describes Project Oxygen, which aims to make computation human-centered by making it freely available everywhere through various integrated technologies. It discusses the vision of ubiquitous computing, the user and system technologies like speech/vision recognition and adaptive software. It outlines the intelligent room and handheld devices that are being developed, and how networks and perpetual interaction techniques will allow natural human communication with these systems. The challenges of developing a fully embedded, nomadic, adaptable and eternal computing system are also mentioned.