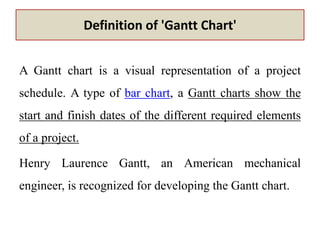
1) The document outlines a class on project management being taught at Assosa University in Ethiopia, covering topics such as the meaning and definitions of project management, tools used in project management like Gantt charts and critical path analysis, and the challenges and scope of project management.
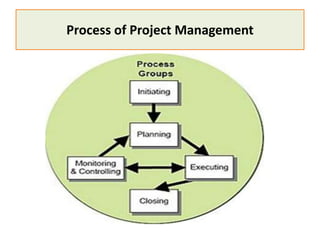
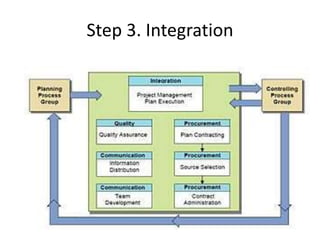
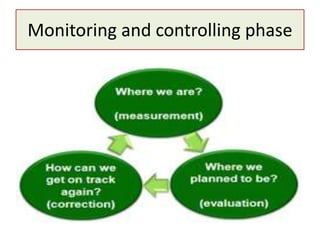
2) It also provides details on the process of project management, including initiation, planning, integration, execution, monitoring and control, and closing phases.
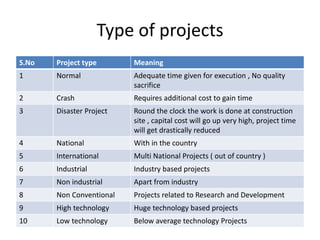
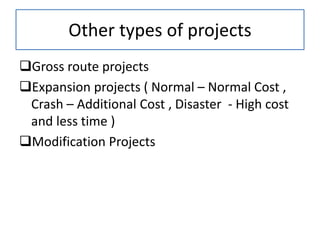
3) Key aspects of projects like meaning, types, features, factors affecting projects, and an overview of project management are summarized.