The document provides information about PRINCE2, a project management methodology. It discusses:
1) The history and origins of PRINCE2 as evolving from the earlier PRINCE methodology to be applicable to any project.
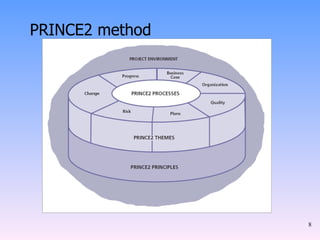
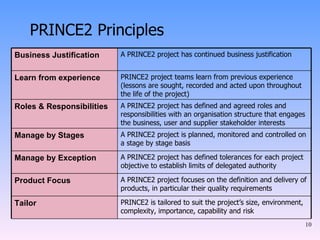
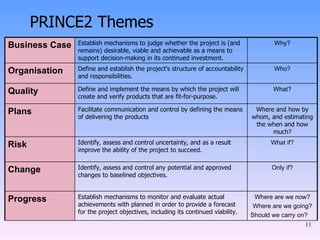
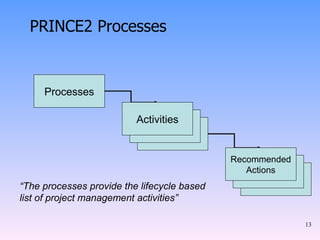
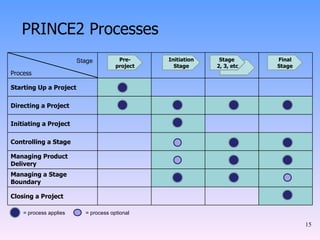
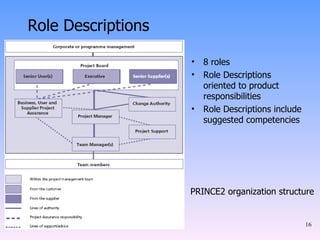
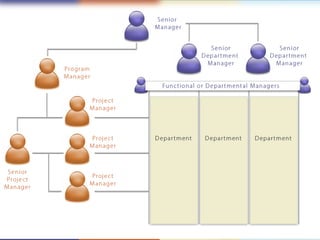
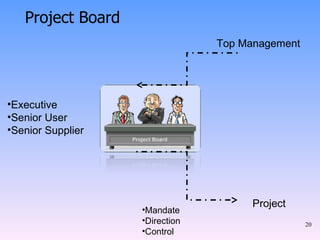
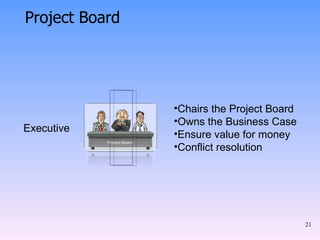
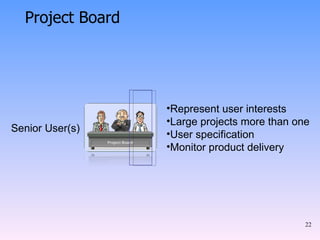
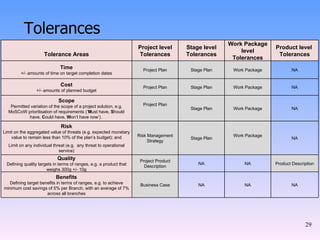
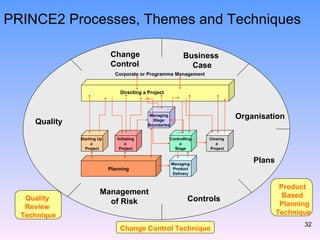
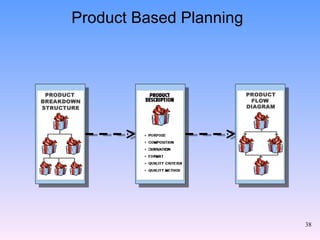
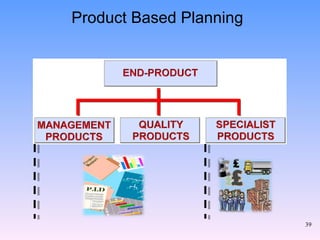
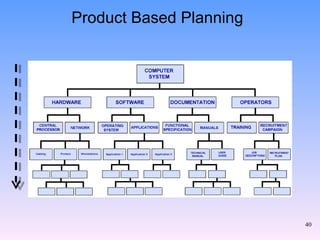
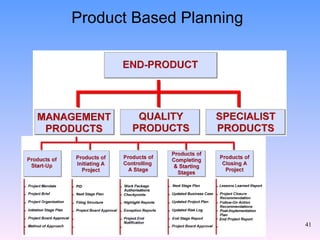
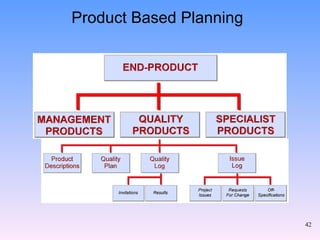
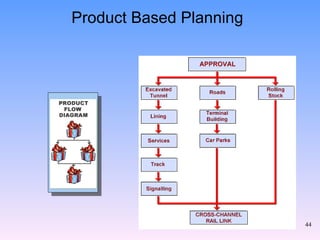
2) The key components of PRINCE2 including 7 principles, 7 themes, 7 processes, roles, and an emphasis on product-based planning.
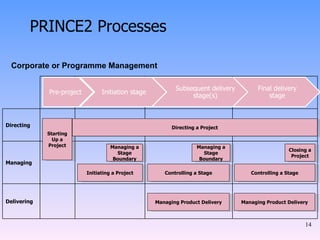
3) How PRINCE2 provides structure through processes, themes and techniques to start, direct, and close out a project through defined stages with controls and reviews.

![Contact Details Cell Phone: 250-507-4343 Victoria , BC Canada [email_address] 15 years healthcare specialist experience and practice management consulting. Utilizing extensive industry experience within medical equipments, IT healthcare (PACS/RIS/CIS & CVIS), pharma, biotech, clinical research and healthcare to execute and implement certain process as well as methodology into diverse operational roles at all organizational levels.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prince2presentation20103-12849164299822-phpapp01/85/Prince2-Methodology-2-320.jpg)