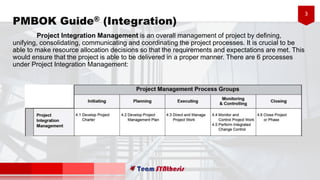
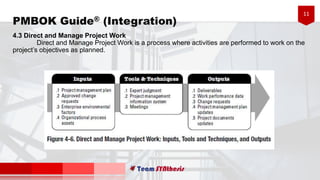
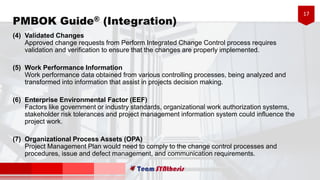
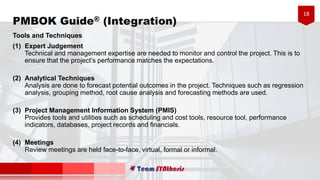
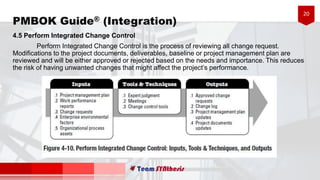
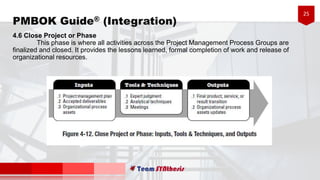
The document provides an overview of six processes under Project Integration Management according to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) Guide 5th Edition. The six processes are: develop project charter, develop project management plan, direct and manage project work, monitor and control project work, perform integrated change control, and close project or phase. For each process, the document lists the typical inputs, tools and techniques, and outputs involved in managing the project integration according to PMBOK best practices.