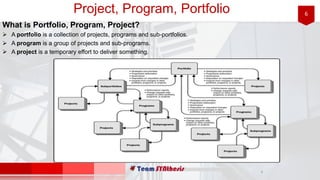
This document provides an introduction to project management. It defines a project as a temporary endeavor with a defined timeline and output. Project management is the application of processes, skills, tools, and techniques to meet project requirements. Key processes include integration, scope, time, cost, quality, and risk management. Projects are undertaken to achieve business value and outcomes. Stakeholders are those involved in or impacted by a project. The project management plan outlines how the project will be executed, monitored, and controlled. Ensuring executive support, user involvement, clear objectives, and other factors can contribute to project success.