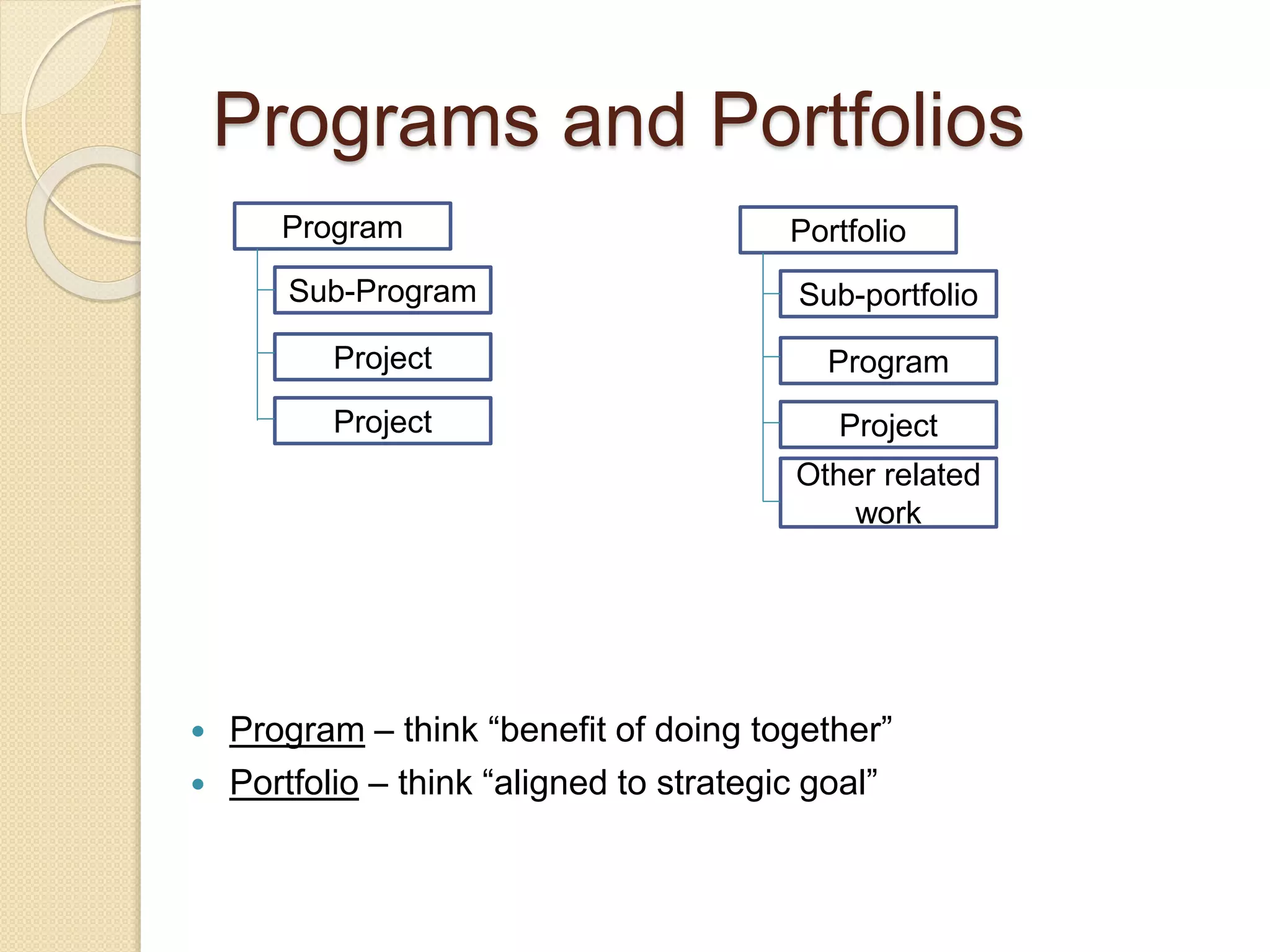
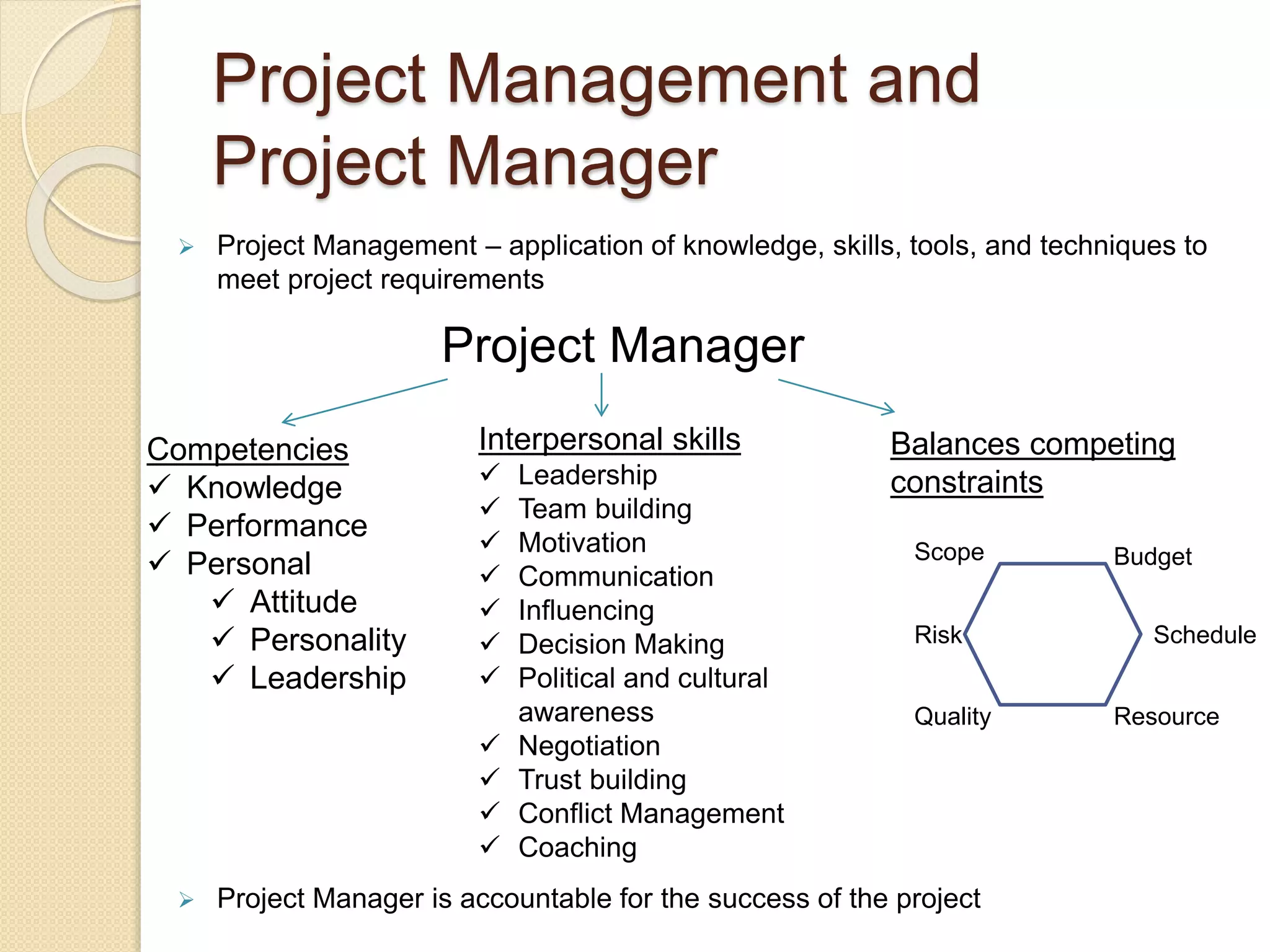
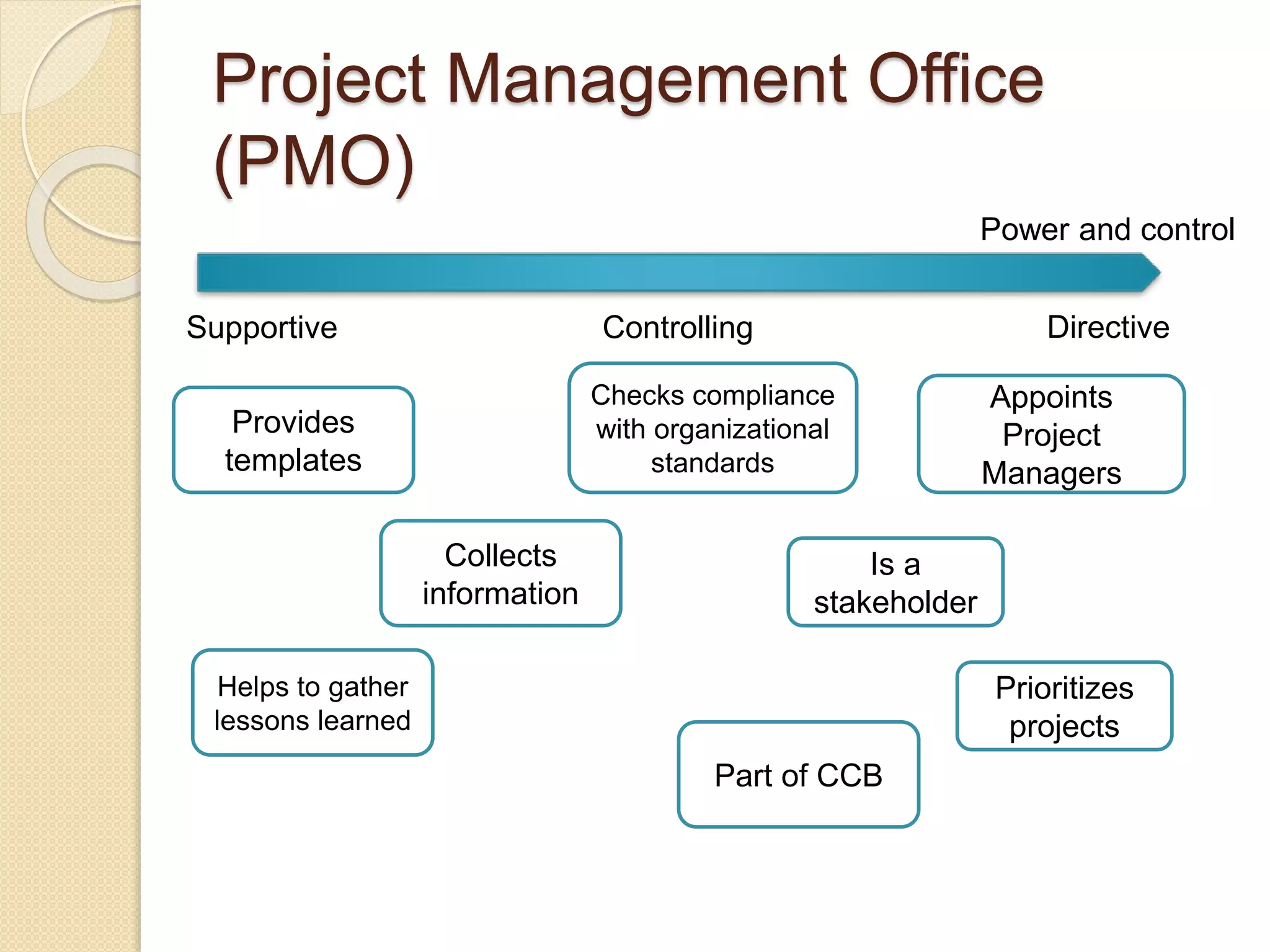
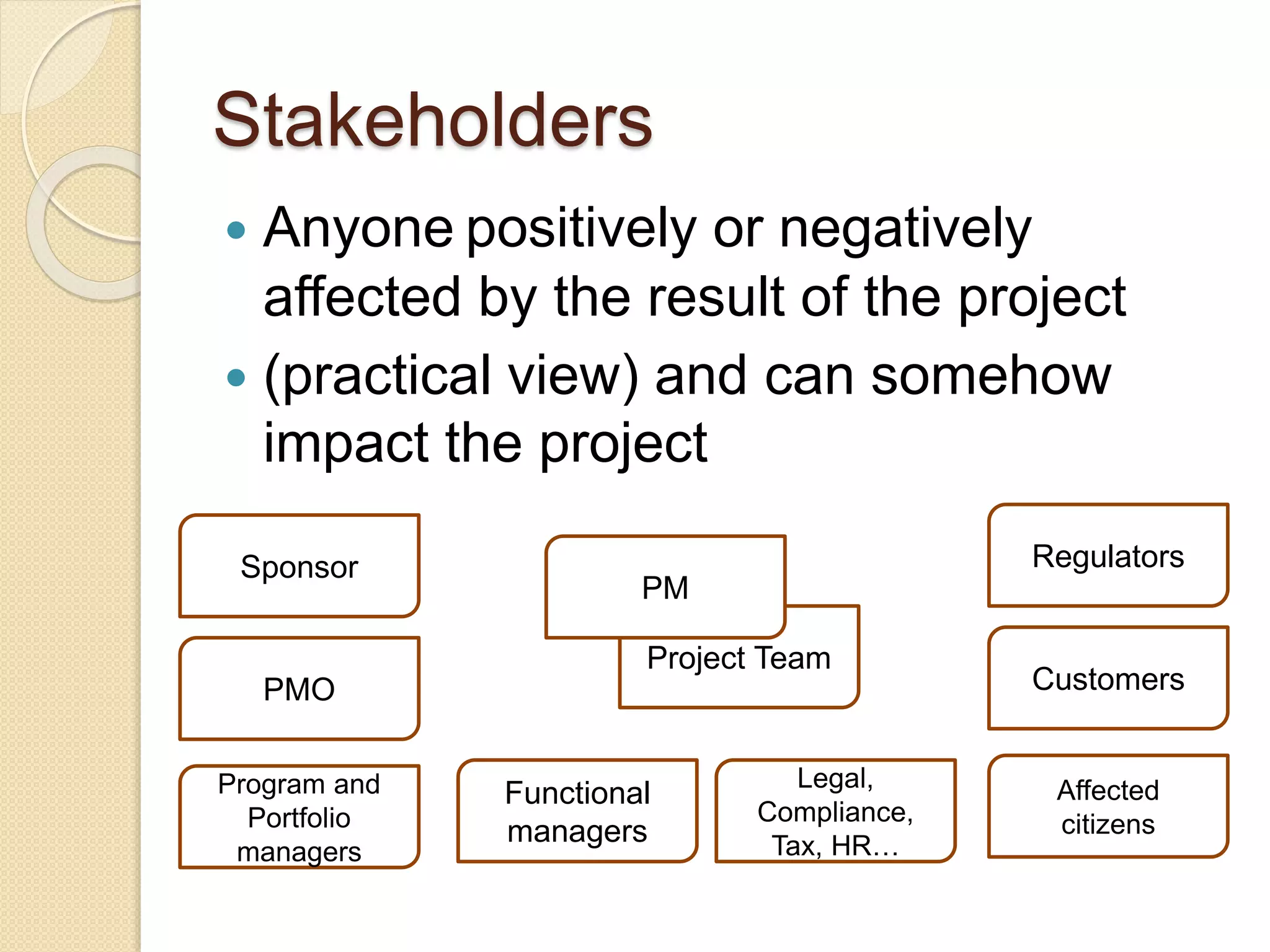
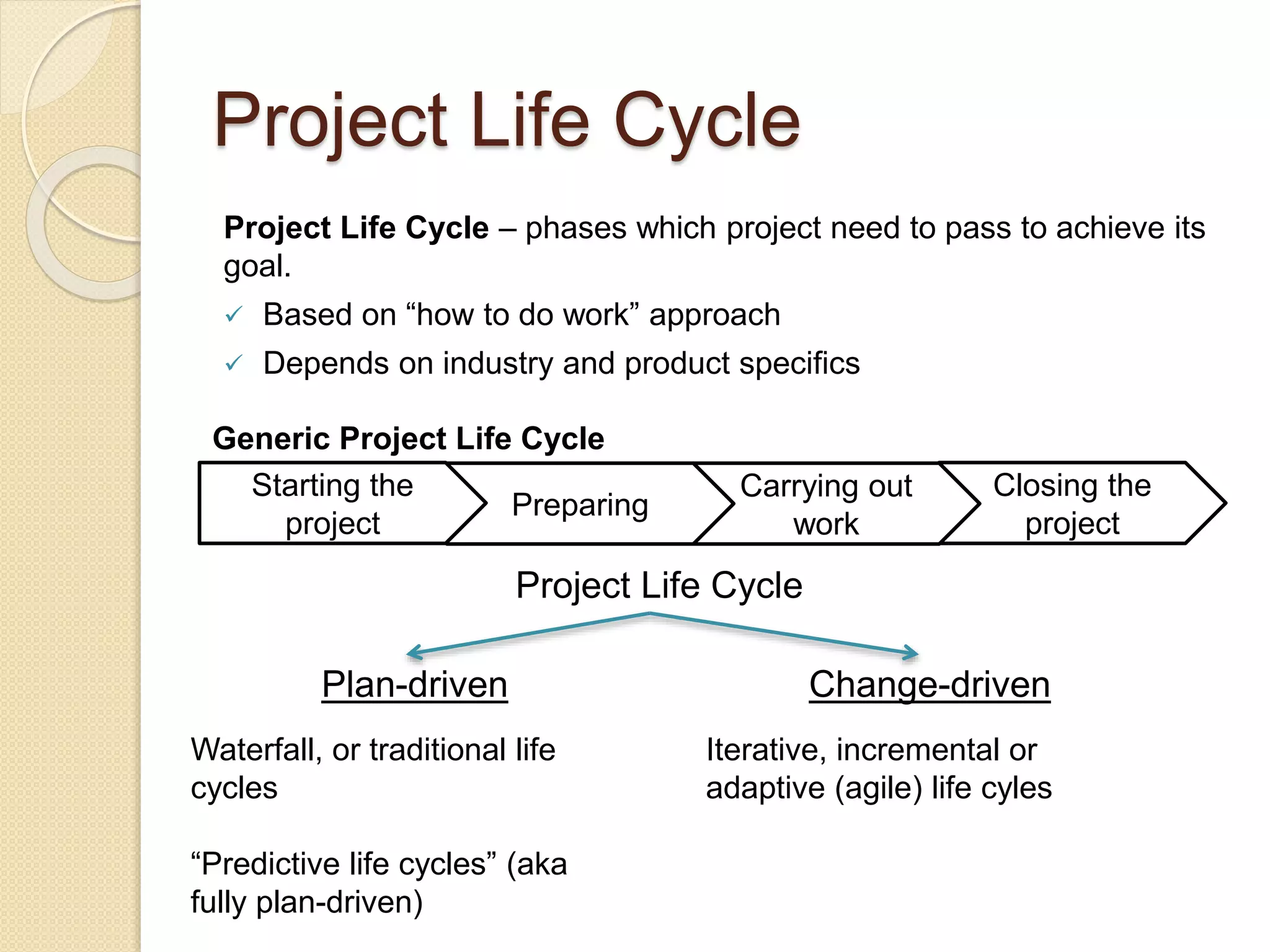
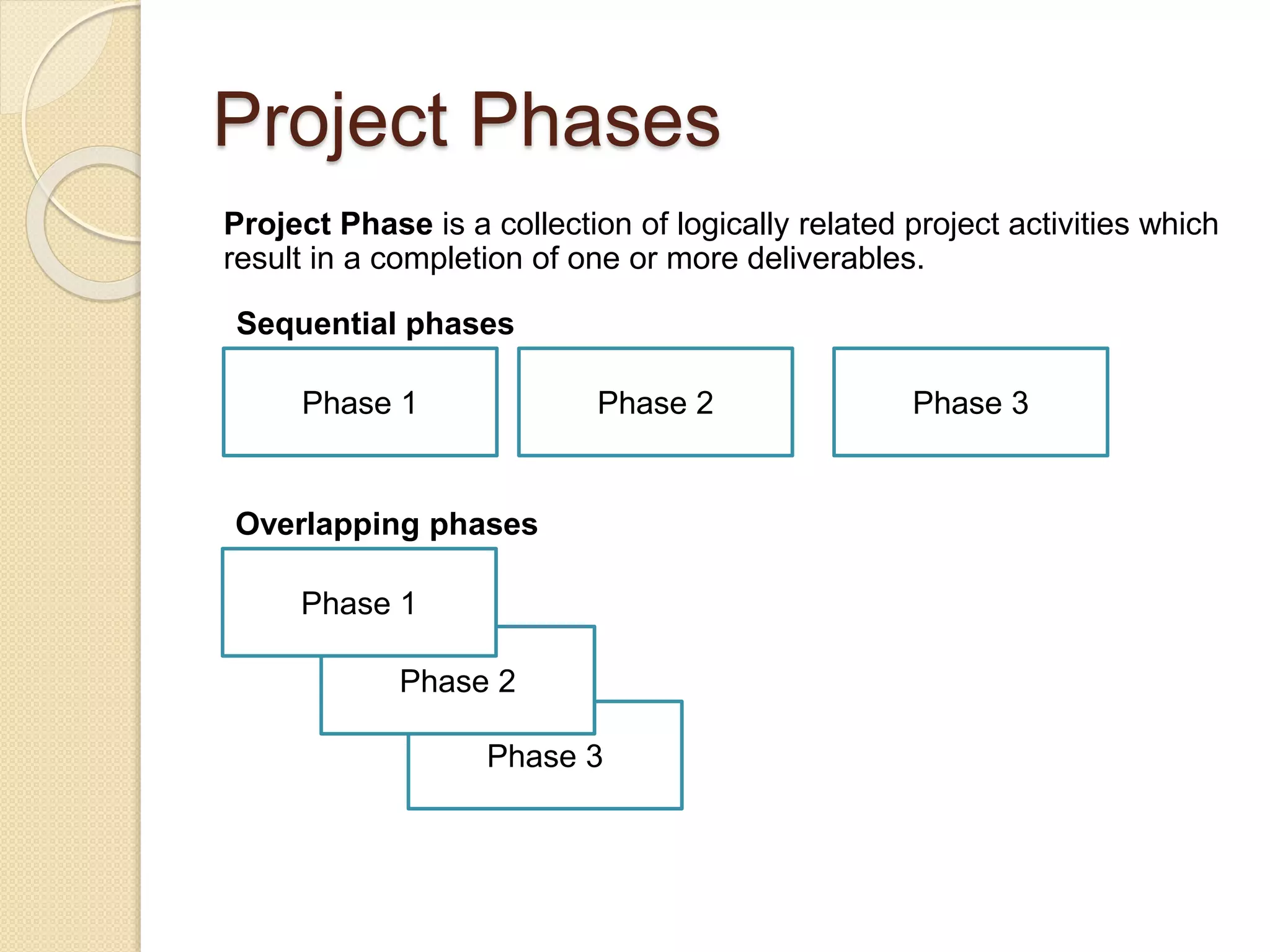
The document outlines a project management framework and PMP preparation course led by Andrey Mikityuk, focusing on defining a project and the role of a project manager. It emphasizes the competencies required for successful project management, the importance of organizational structures and project life cycles, and details various project management processes. Additionally, it covers concepts like enterprise environmental factors and organizational project management maturity, alongside the role of project management offices and stakeholder engagement.