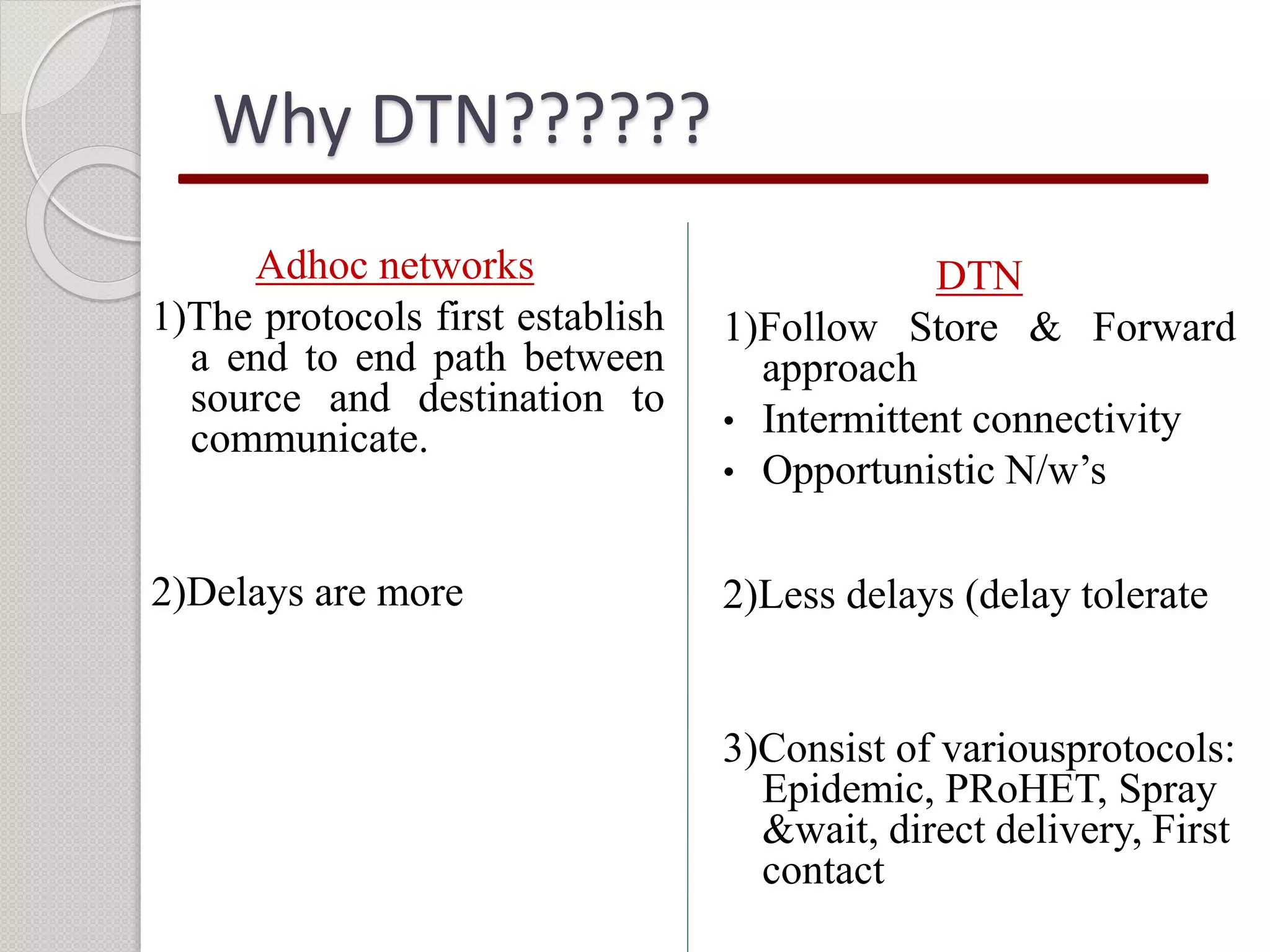
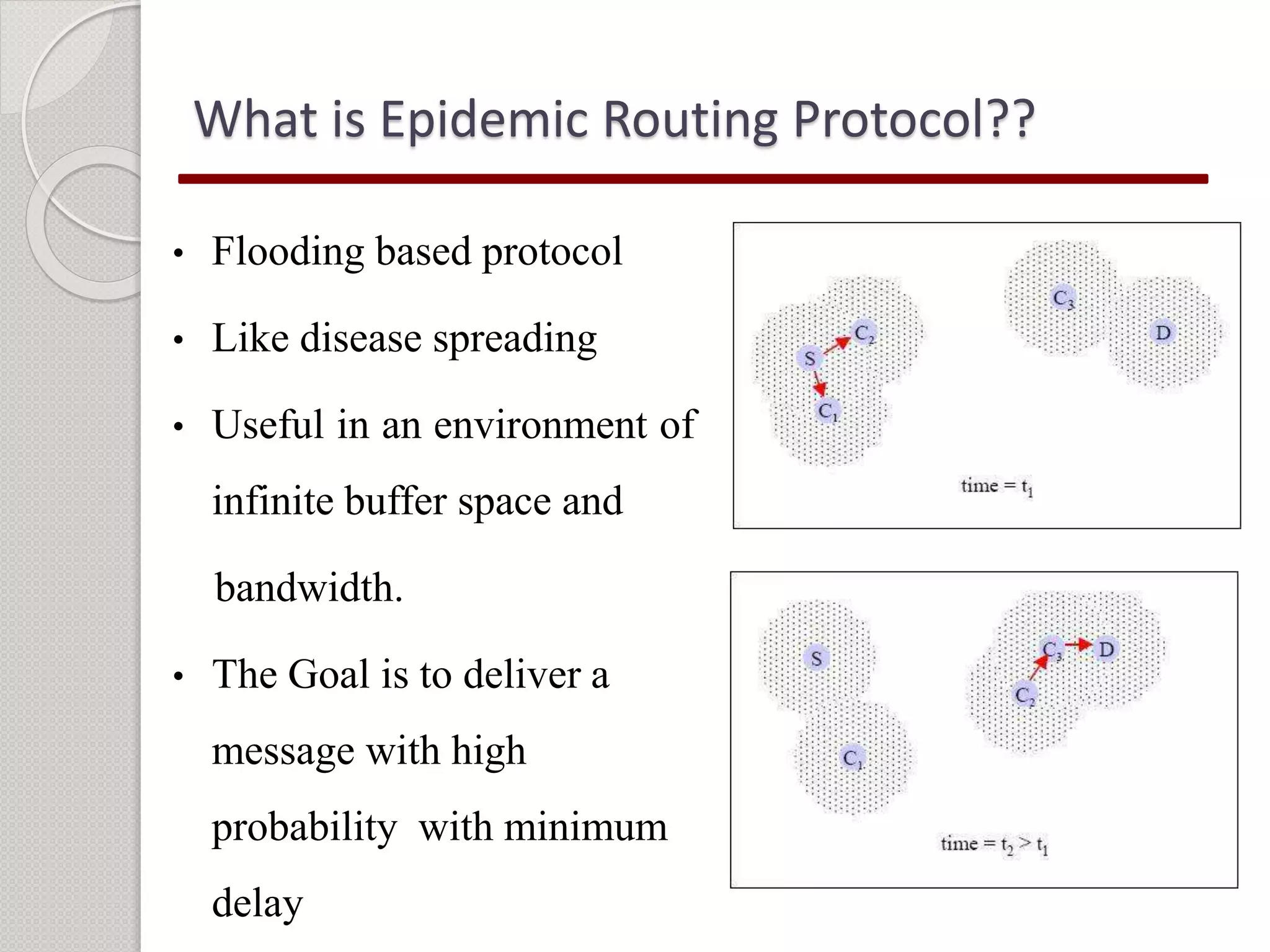
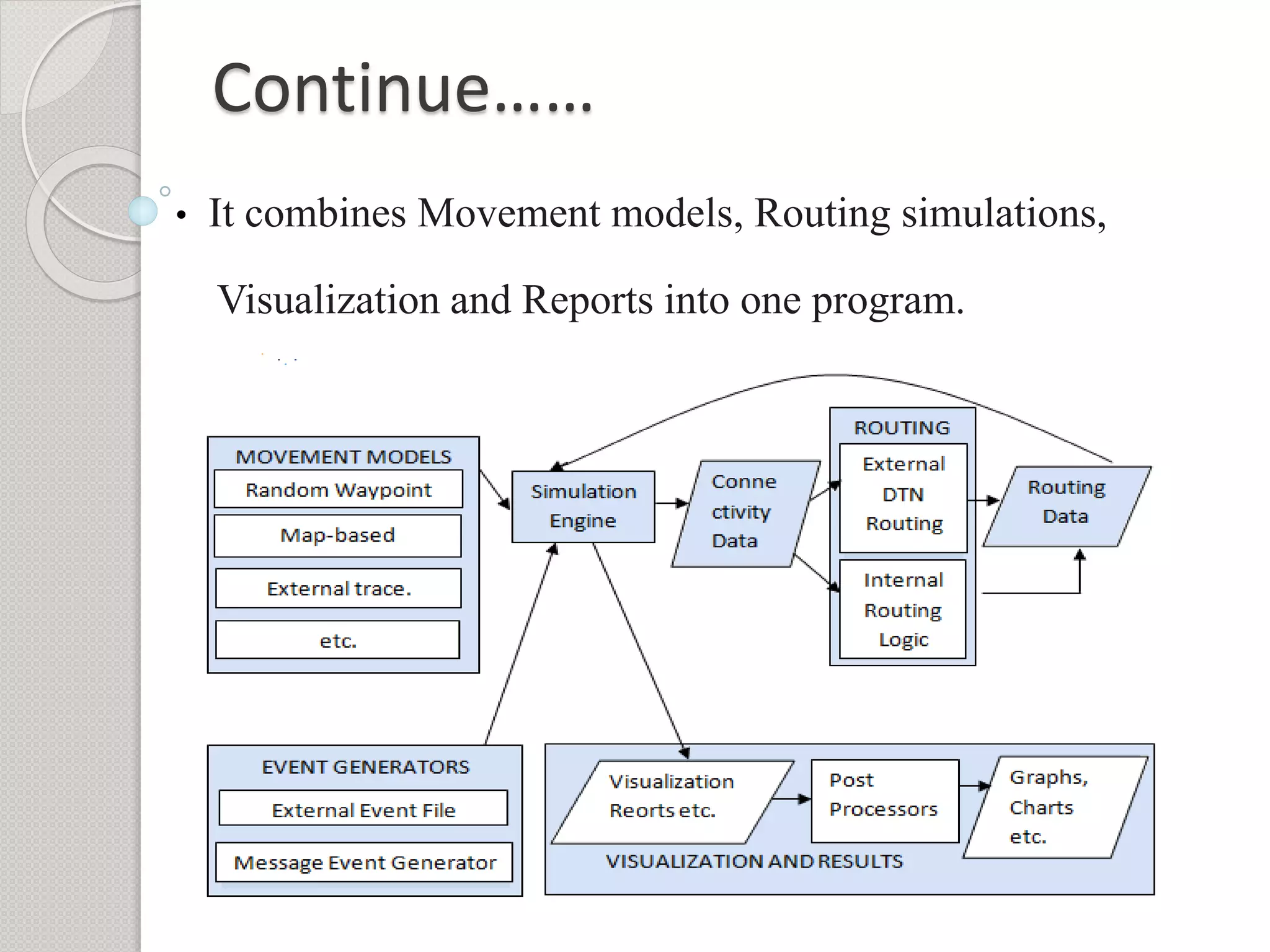
This document summarizes a project seminar presentation on analyzing the performance of the epidemic routing protocol in delay tolerant networks under different mobility models. The key points are:
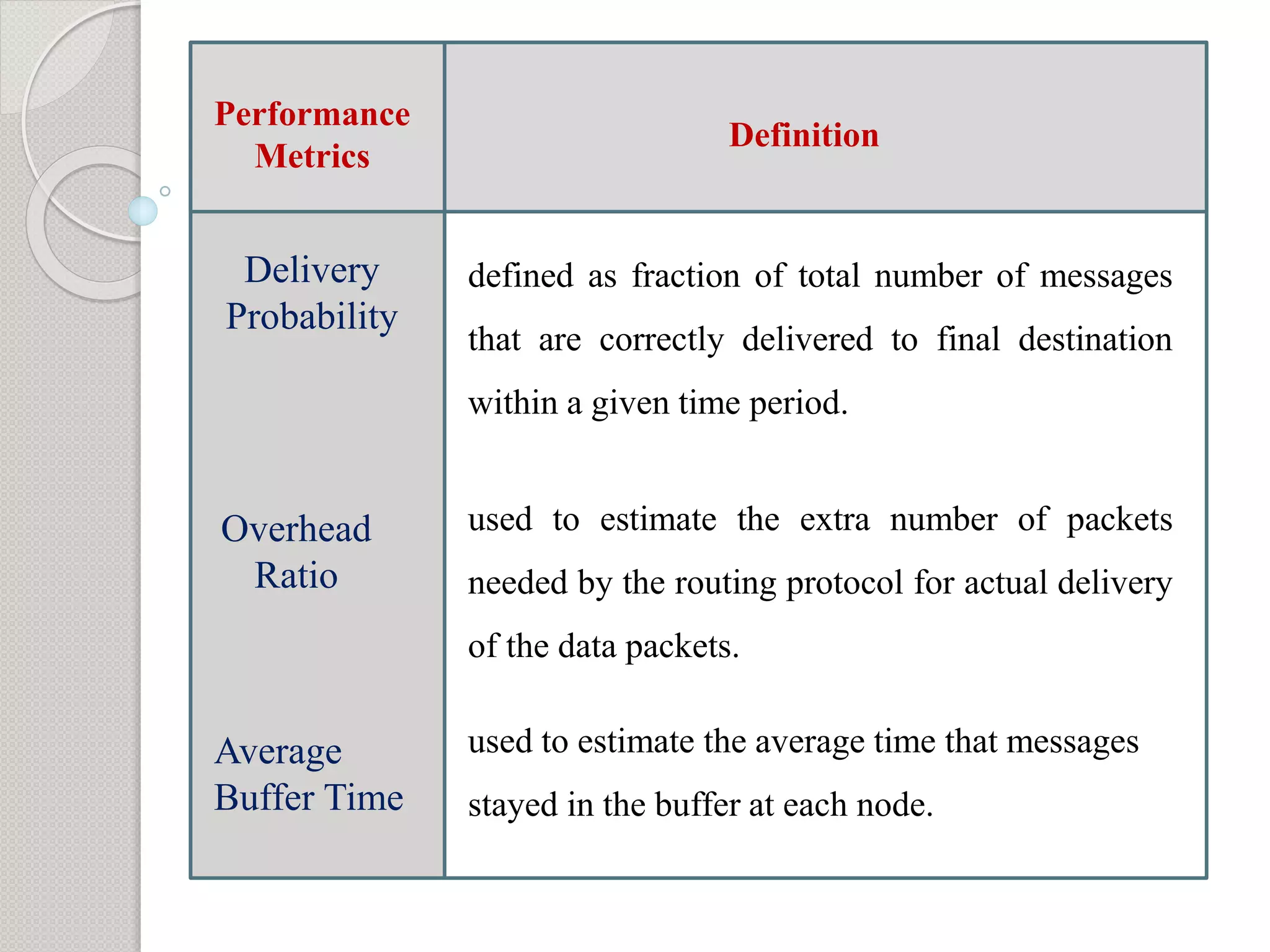
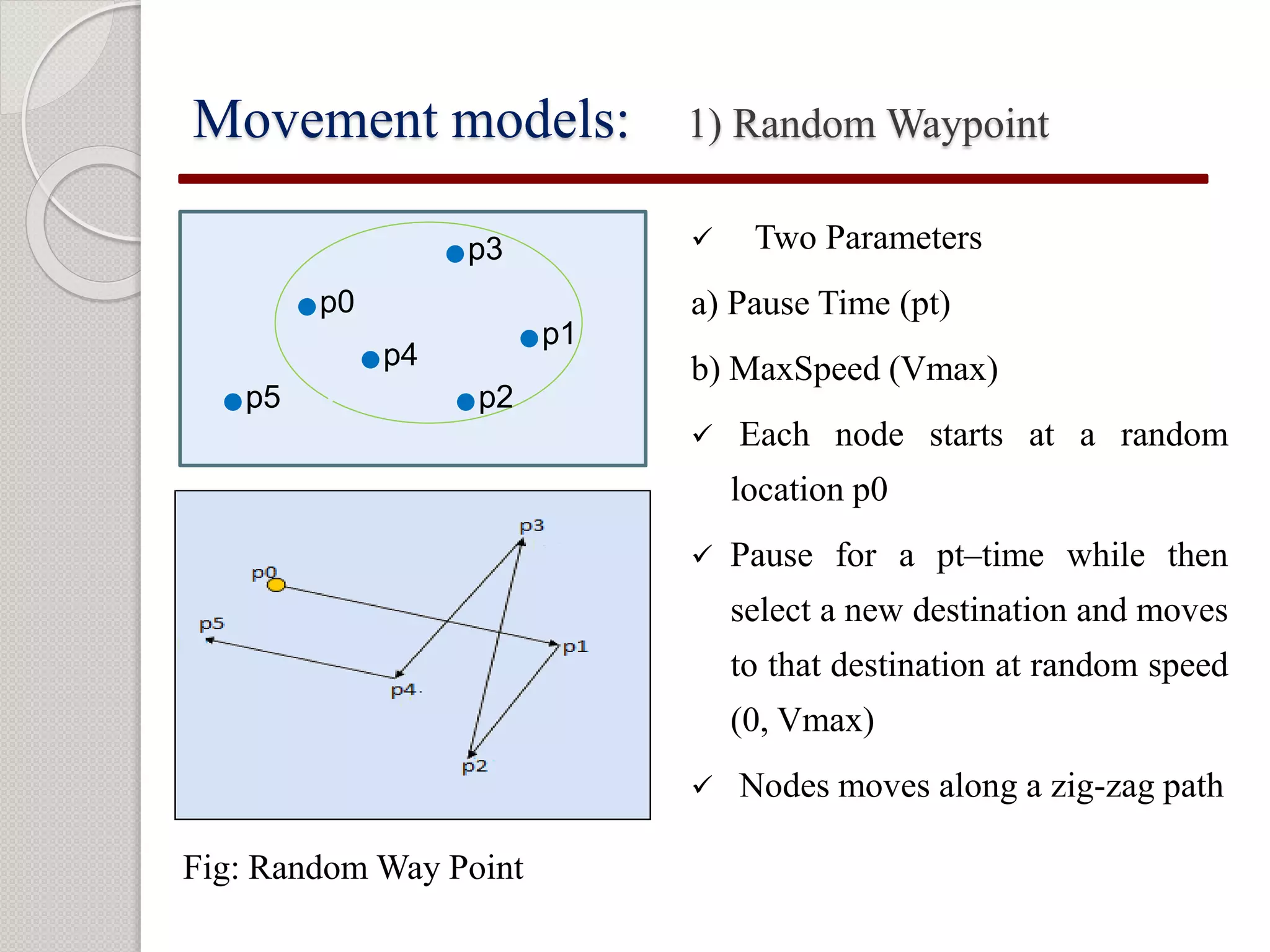
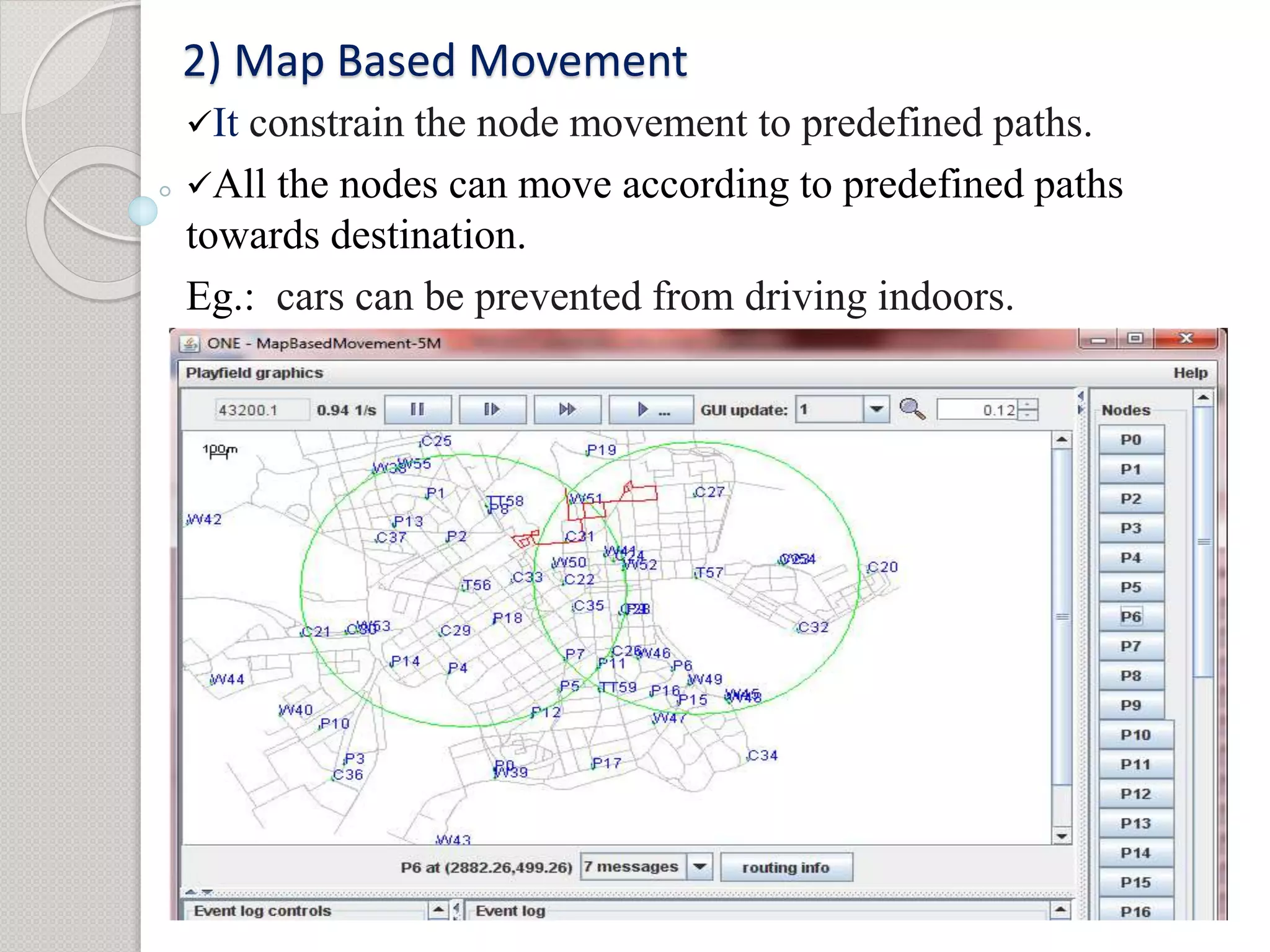
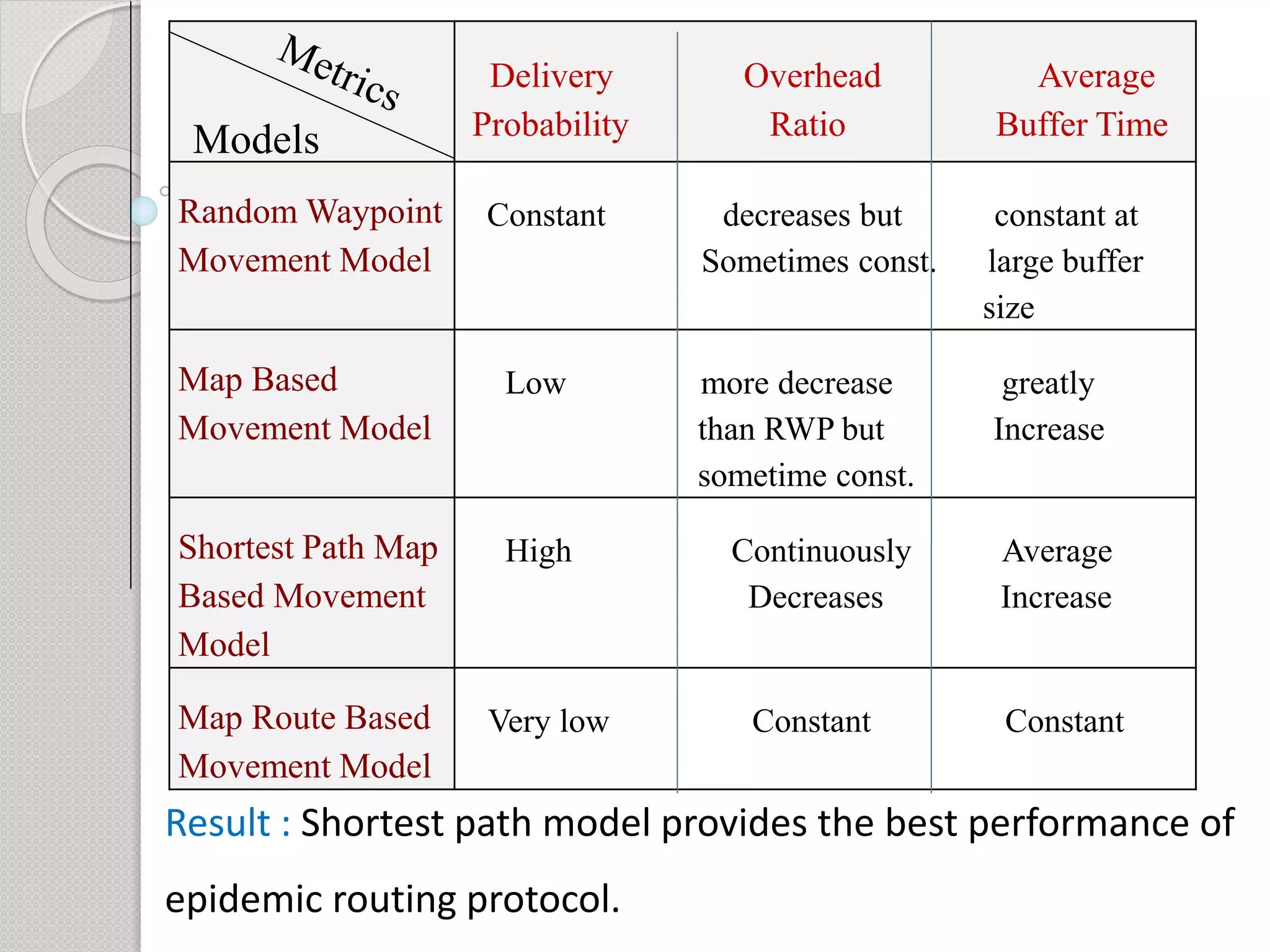
1) The objective is to evaluate the epidemic routing protocol's delivery probability, overhead ratio, and average buffer time when varying the buffer size and under different mobility models including random waypoint, map-based, shortest path, and map route models.
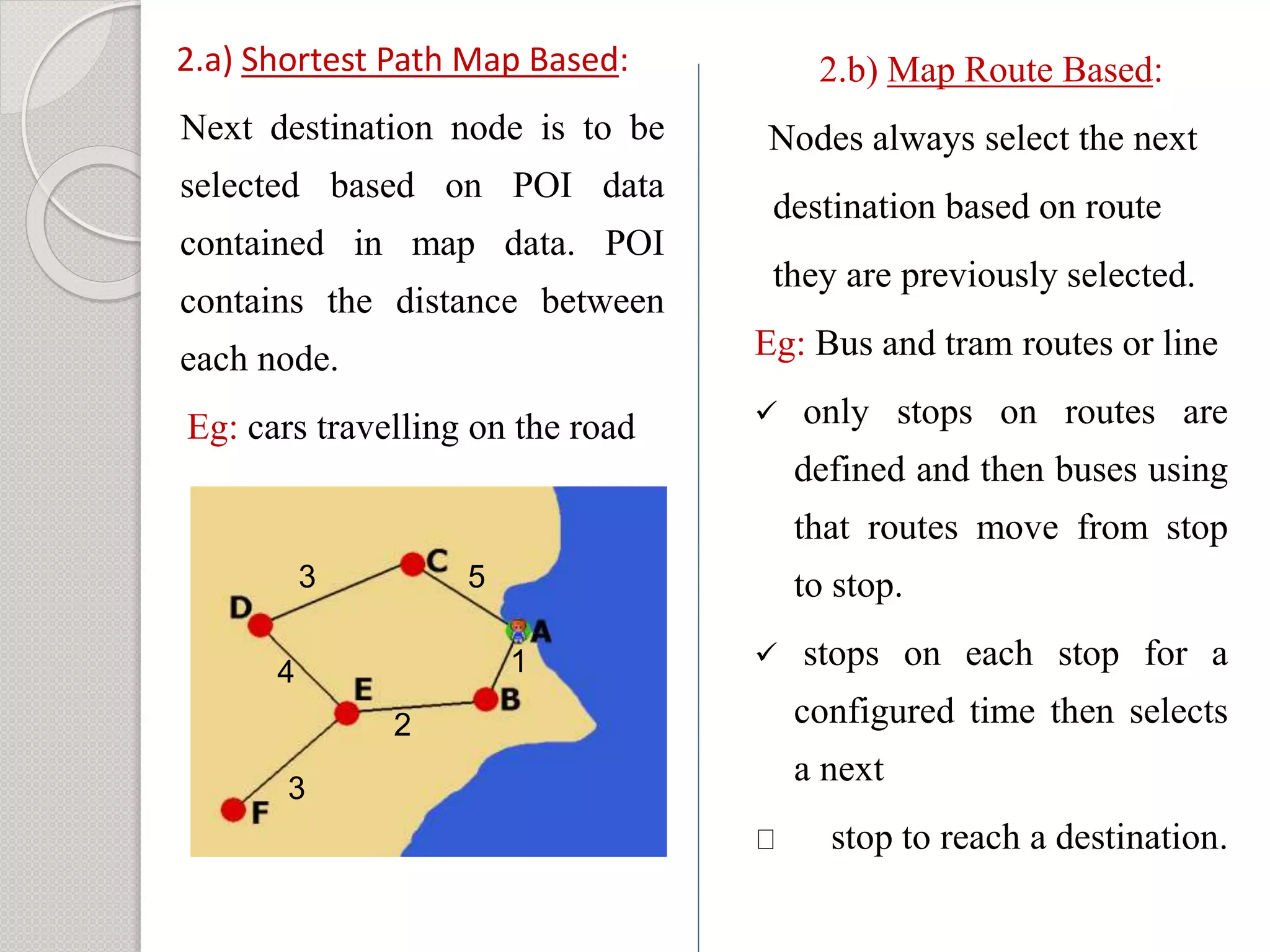
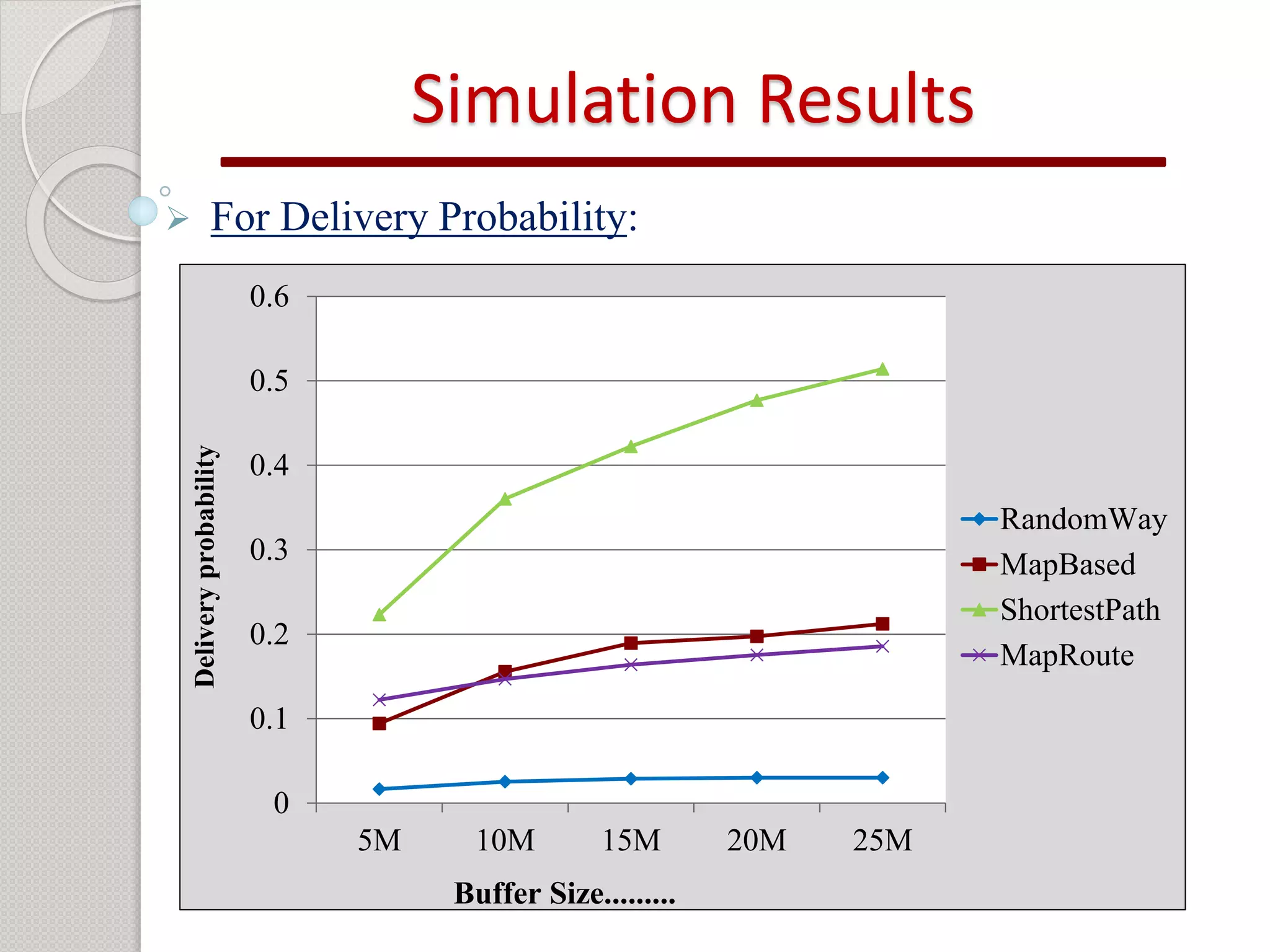
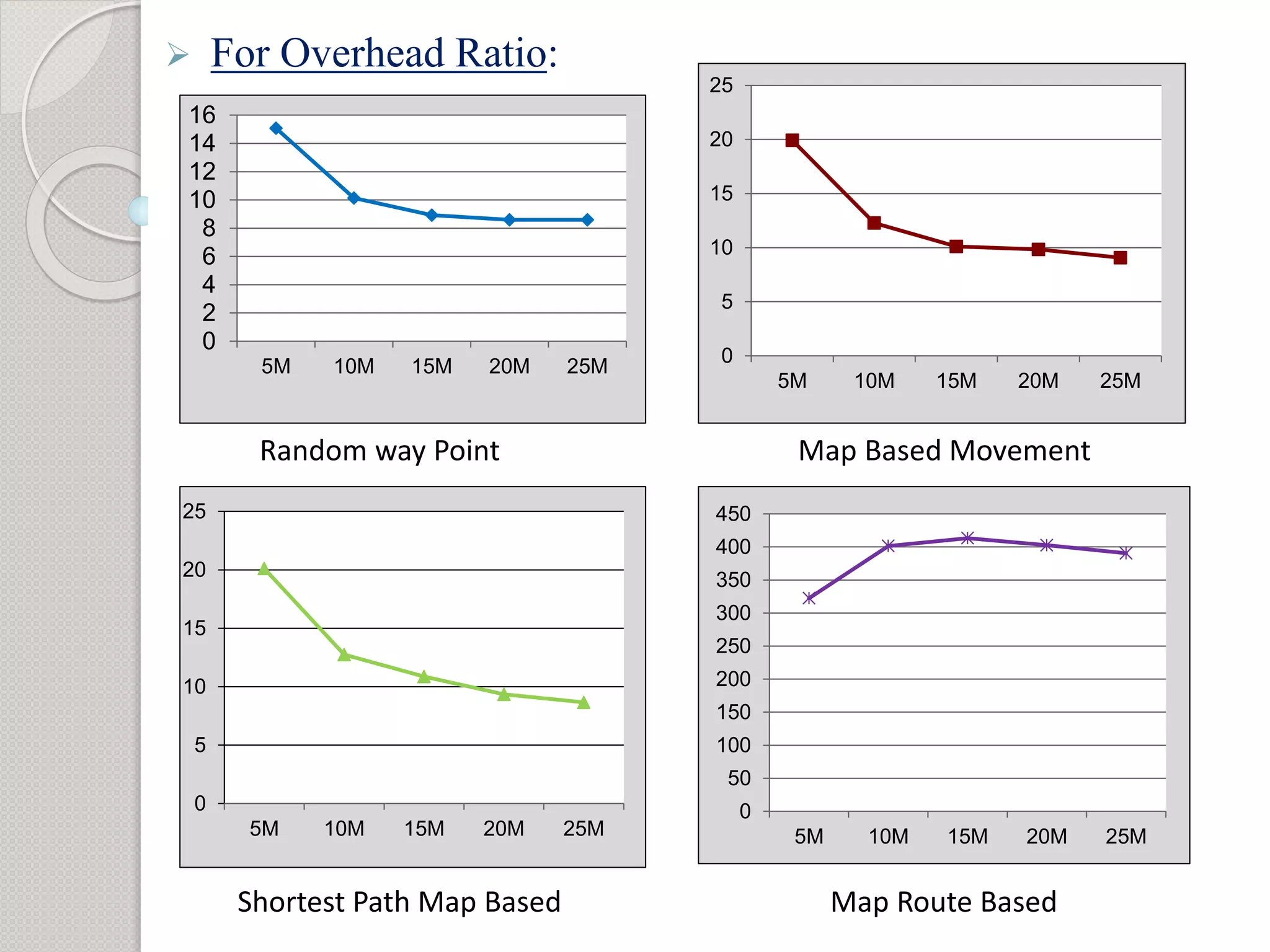
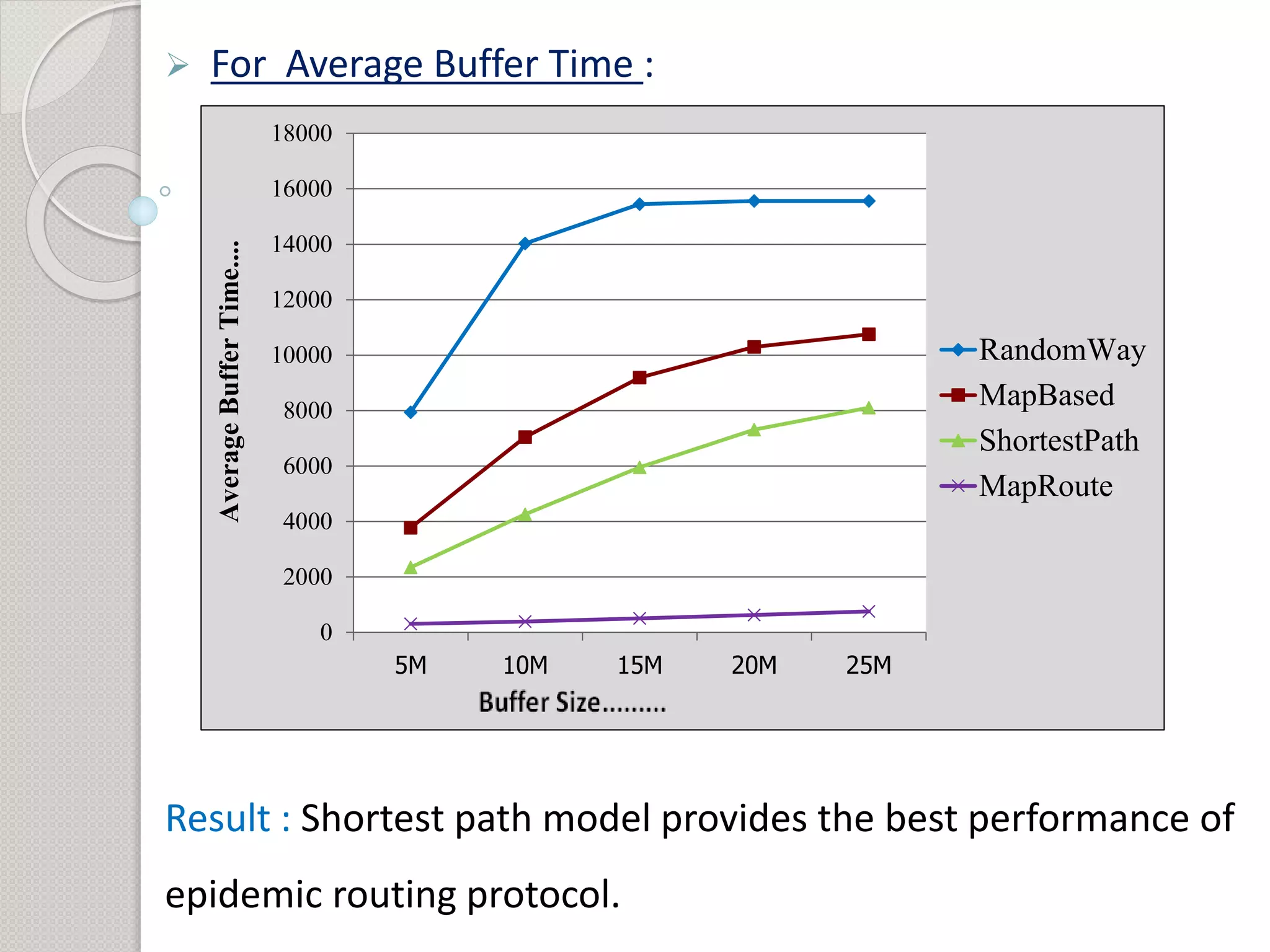
2) Simulation results show that the shortest path mobility model provides the best performance for the epidemic routing protocol in terms of high delivery probability, low overhead ratio, and efficient buffer usage.
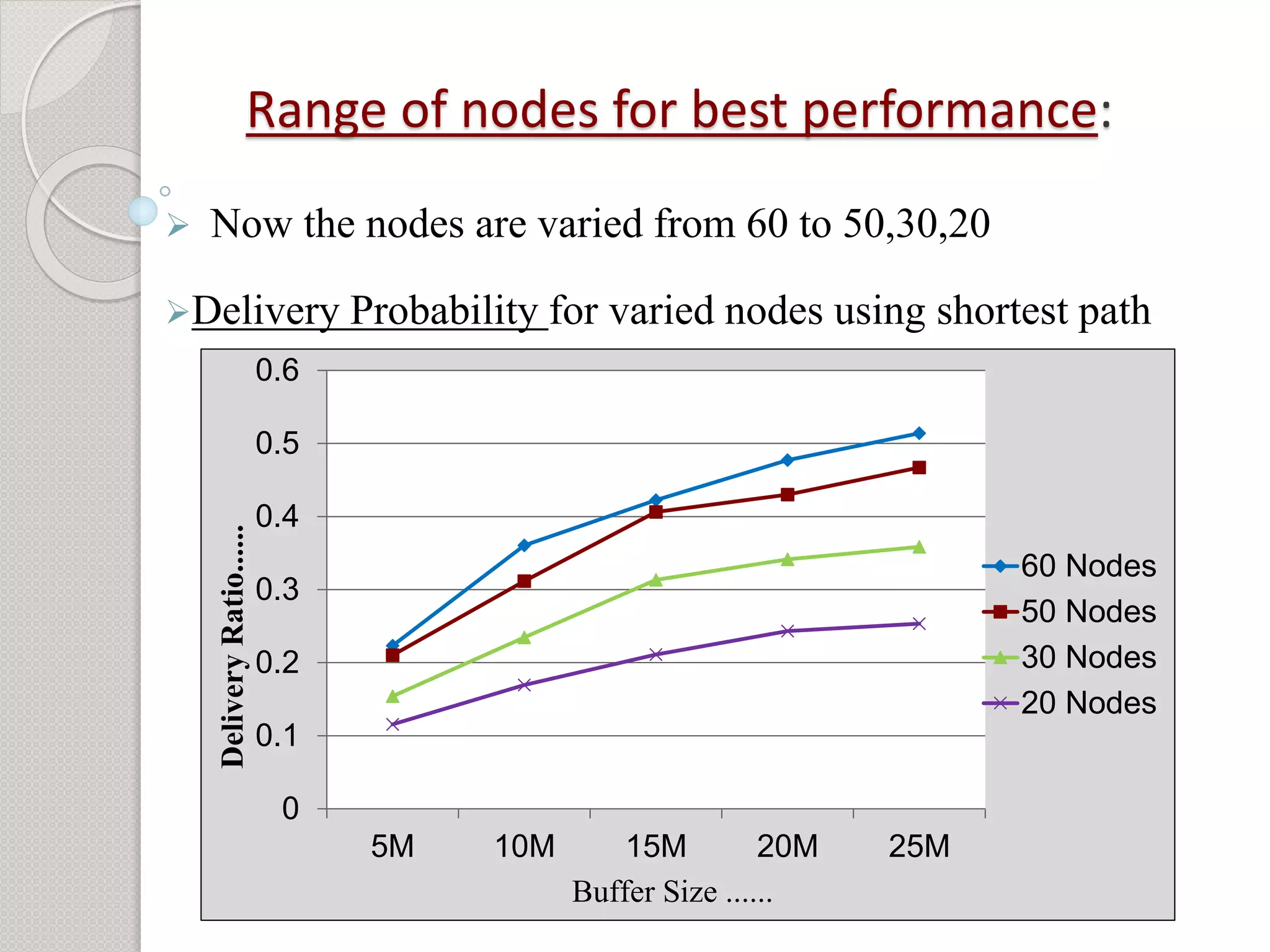
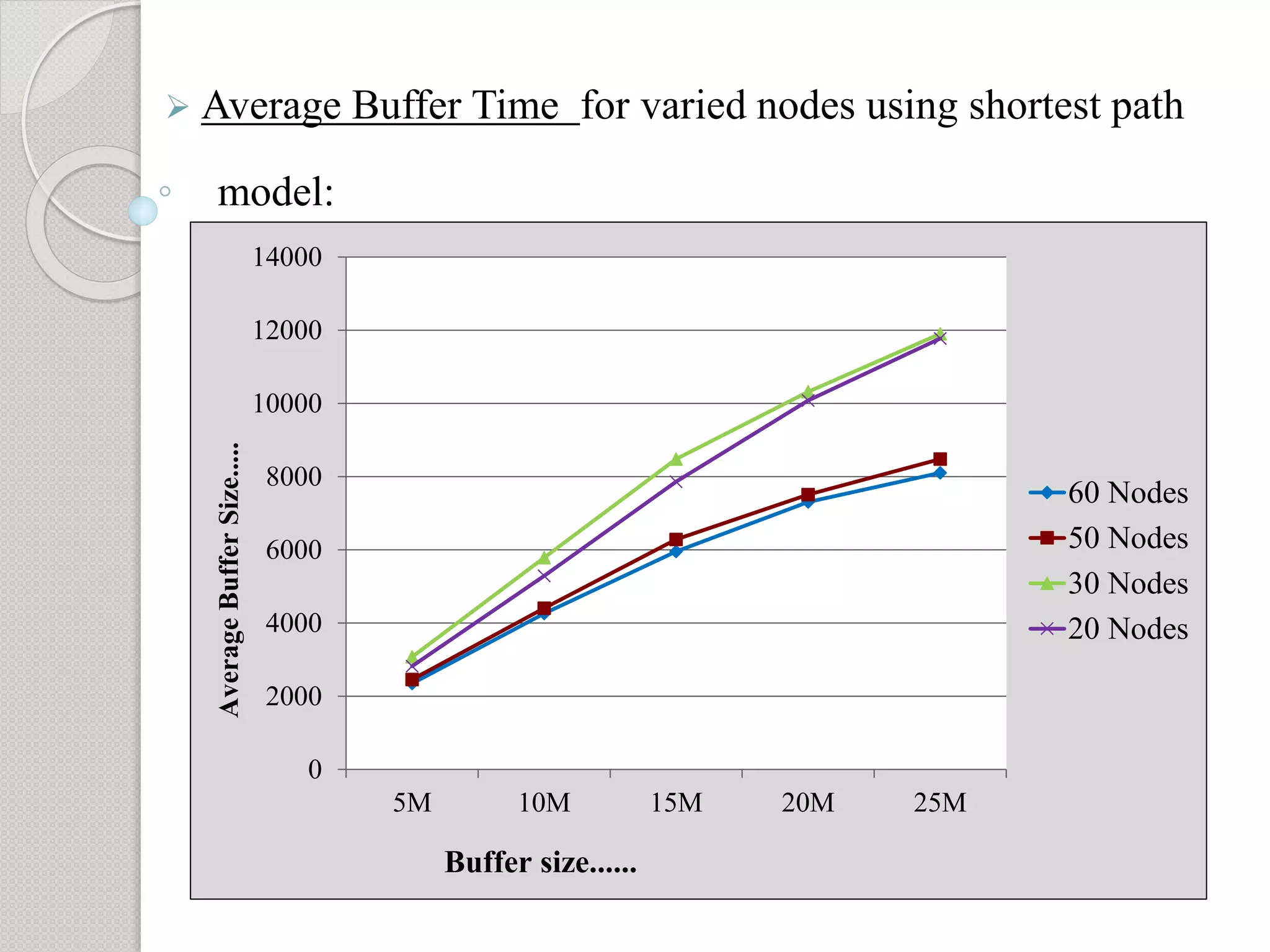
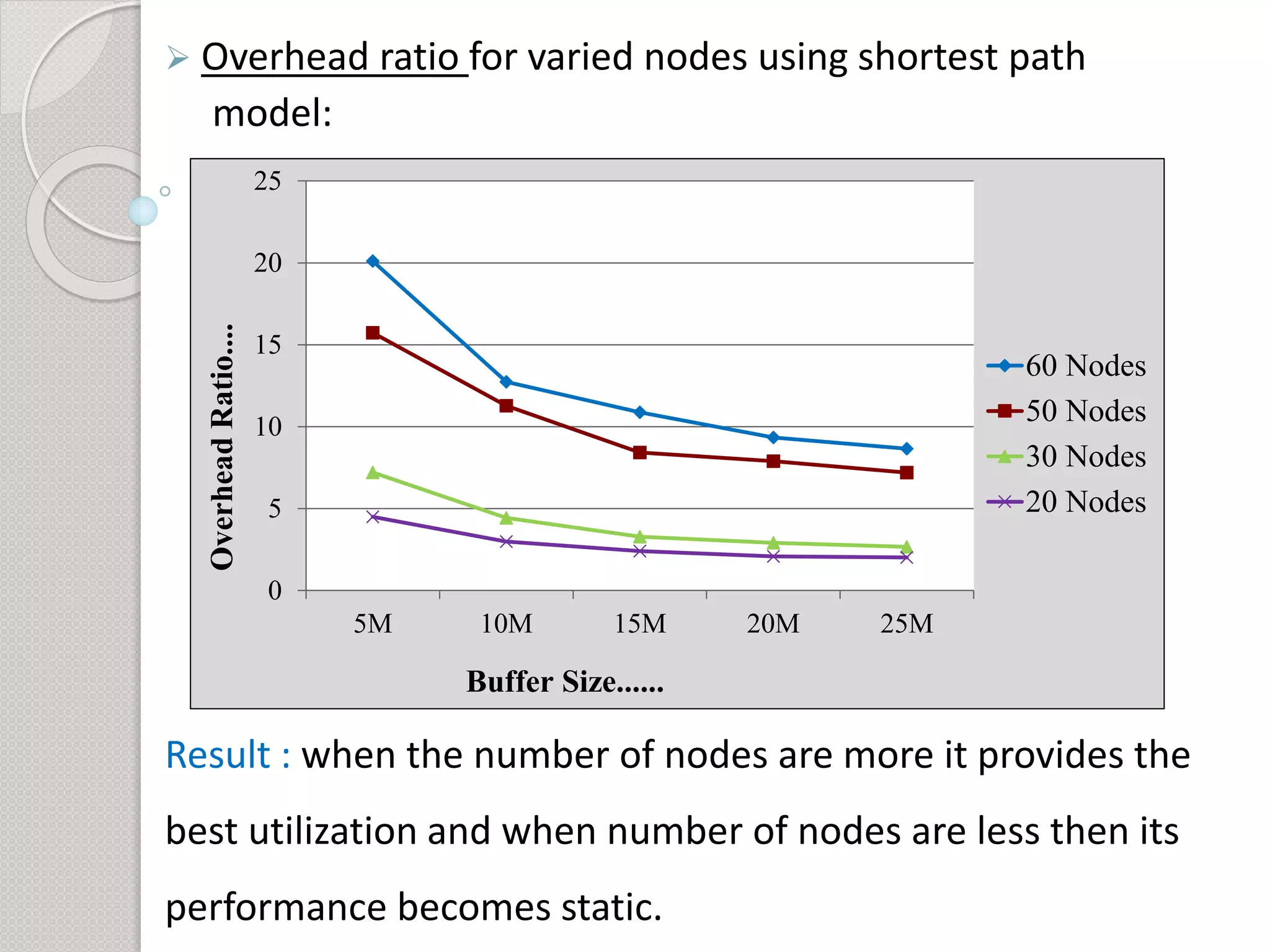
3) Additional analysis varying the number of nodes found that performance is best when more nodes are present and becomes static with






![References
[1] Professor Jorg Ott of Helinski University of Technology: “A Tutorial paper on the
Opportunistic Networking Environment Simulator” presented in May 29, 2008
[2] Paritosh Puri, M.P Singh: “A Survey paper on Delay Tolerant Networking”presented in
2013.
[3] Harminder Singh Bindra and A. L. Sangal:“ The Performance comparison of the
RAPID,
Epidemic, PRoHET routing protocols in DTN ” presented in the April 2, 2012.
[4] Anders Lindgreny, Avri Doria, Olov Schelen: “The Probabilistic Routing in case of DTN
Intermittently Connected Networks” presented in December 2002.
[5] Neena V V, V Mary Anita Rajam: “Performance Analysis of Epidemic Routing Protocol
for
Opportunistic Networks in Different Mobility Patterns ” presentesd in Jan. 09, 2013.
[6] Forrest Warthman : “A Tutorial Delay tolerant networks” presented in May 3, 2003.
[7] Sushant Jain, Kevin Fall, Rabin Patra: “Routing in DTN” presented in Aug 4, 2008.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectseminar-141007081457-conversion-gate02/75/Project-24-2048.jpg)
