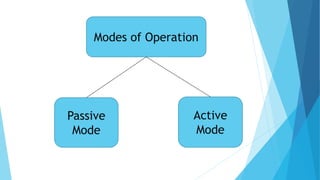
NFC (near field communication) is a short-range wireless communication technology aimed at mobile devices, enabling data exchange by bringing devices close together. Developed by the NFC Forum in 2004, it allows for applications such as mobile payments, access control, and data transfer between devices through two operational modes: active and passive. While NFC offers convenience and secure communication, it has limitations such as a short operational range of about 10 cm and relatively low data transfer rates.