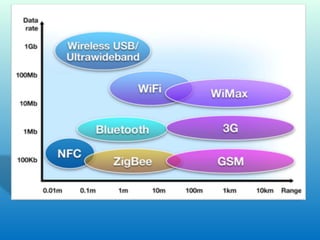
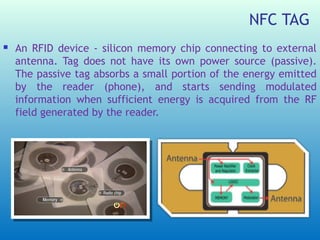
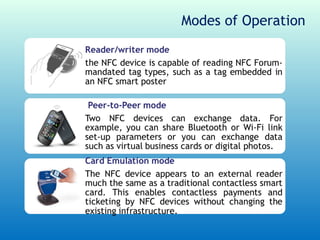
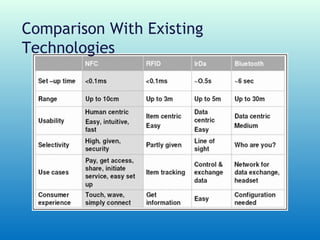
This document examines the future of Near Field Communication (NFC) technology. It begins with an introduction to NFC, describing it as a short-range wireless connection using 13.56 MHz frequency with a maximum bandwidth of 424Kbits/sec. It then discusses how NFC operates using contactless technologies and RFID, requiring a reader and tag. The document outlines current NFC capabilities like data sharing and mobile payments. It envisions a future where NFC powers smart devices for security, vehicle access, and online shopping. Benefits include ease of use, automation, and security, though limitations are short range and low data transfer rates. Overall, the document concludes that NFC will provide convenience for consumers and retailers.