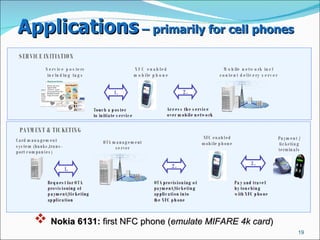
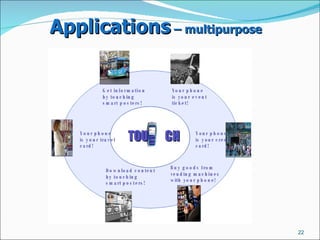
NFC (Near Field Communication) is a short-range wireless communication technology that allows data exchange between devices over short distances typically less than 20 cm. It uses radio frequency identification (RFID) standards to establish communication by bringing two enabled devices in close proximity. Common applications of NFC include contactless payment, data sharing and connectivity with smart posters, tags, or cards. Security is a concern for NFC since communications can potentially be intercepted, though using higher-level encryption protocols can help address this.