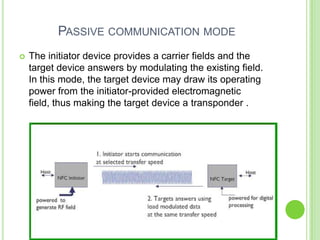
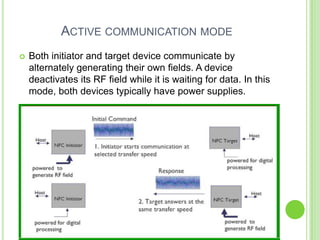
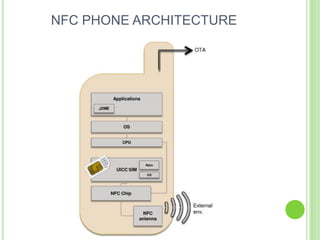
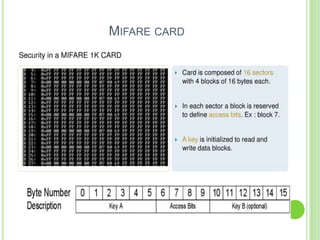
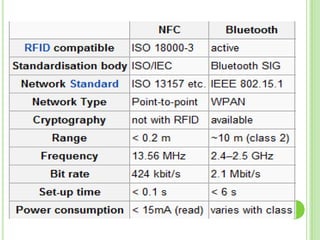
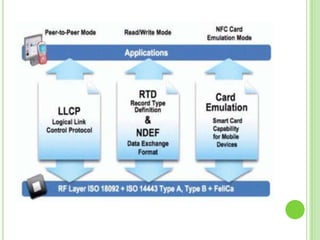
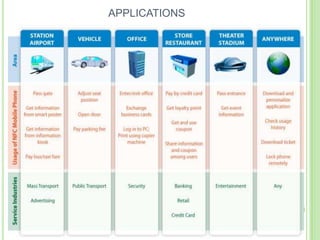
Near field communication (NFC) allows short-range wireless data transfer when devices are brought close together. NFC grew out of RFID technology and was standardized in 2004. It can operate in passive or active mode at 13.56 MHz and up to 424 kbit/s. NFC is used for contactless payments, data sharing, and access in transit systems. While slower than Bluetooth, NFC consumes less power and sets up connections faster. Major trials of NFC payments and ticketing have occurred in several countries. Security relies on encryption and the NFC Forum standardizes protocols. Widespread adoption of NFC in mobile phones is expected in coming years.