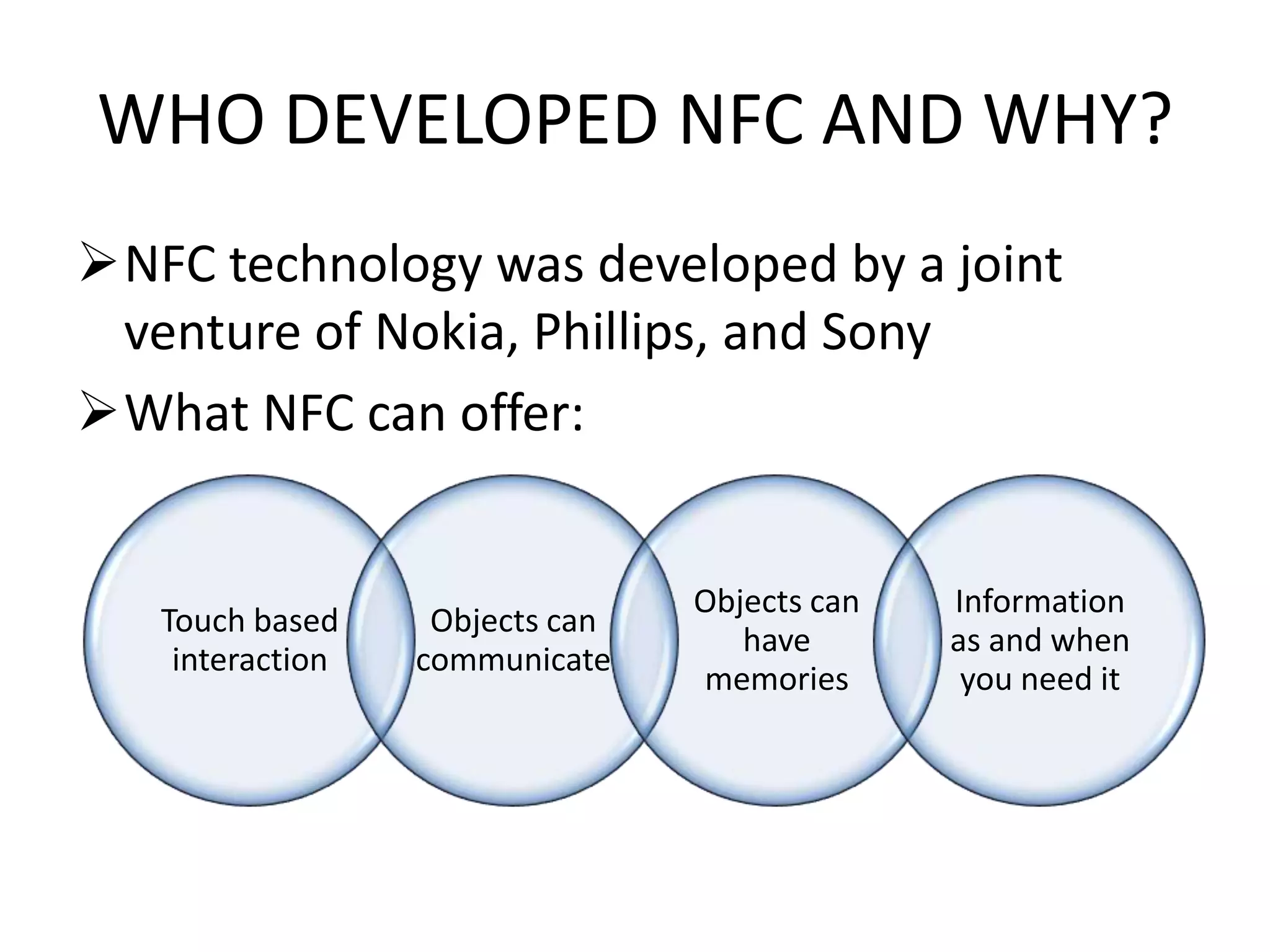
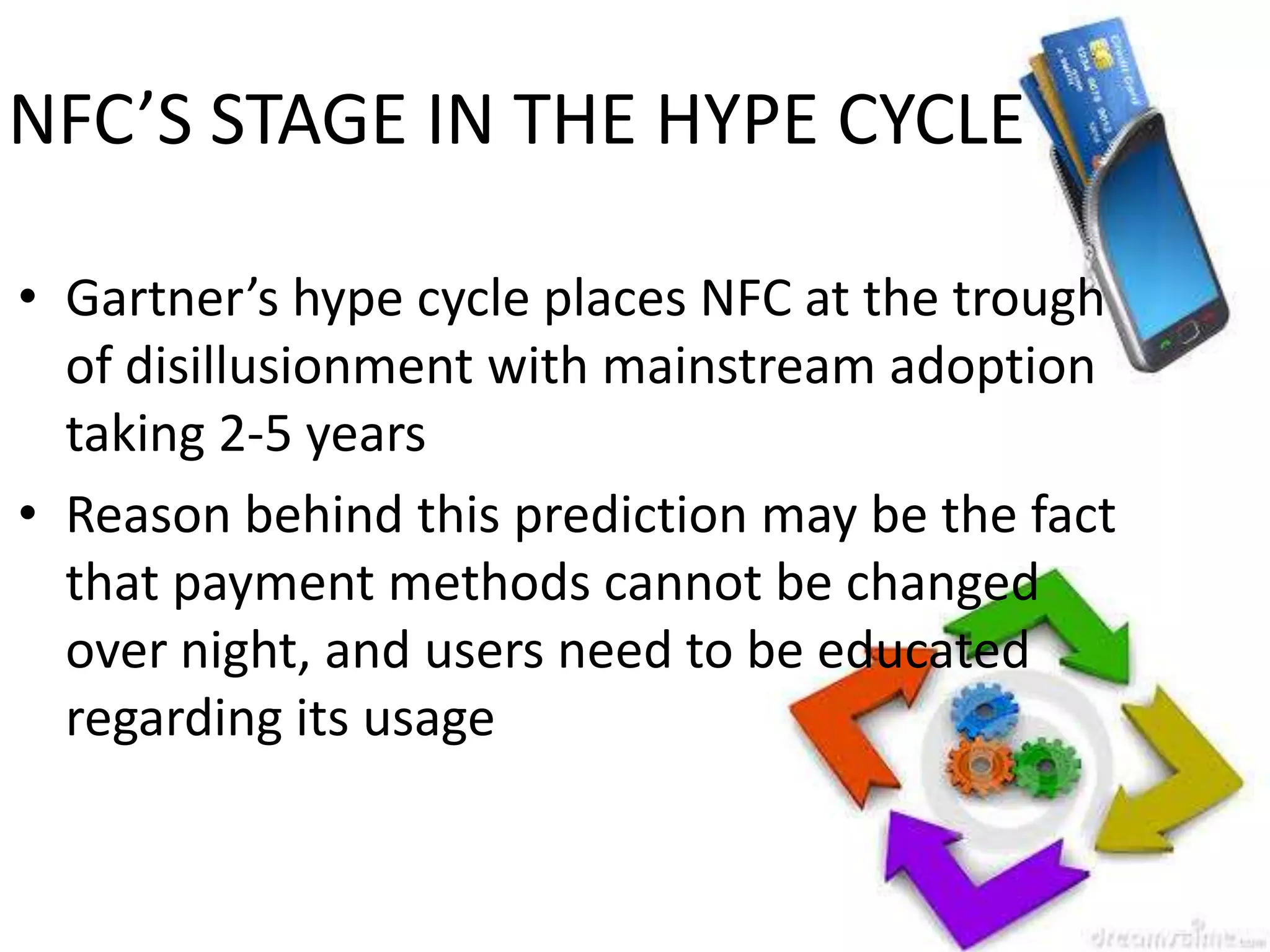
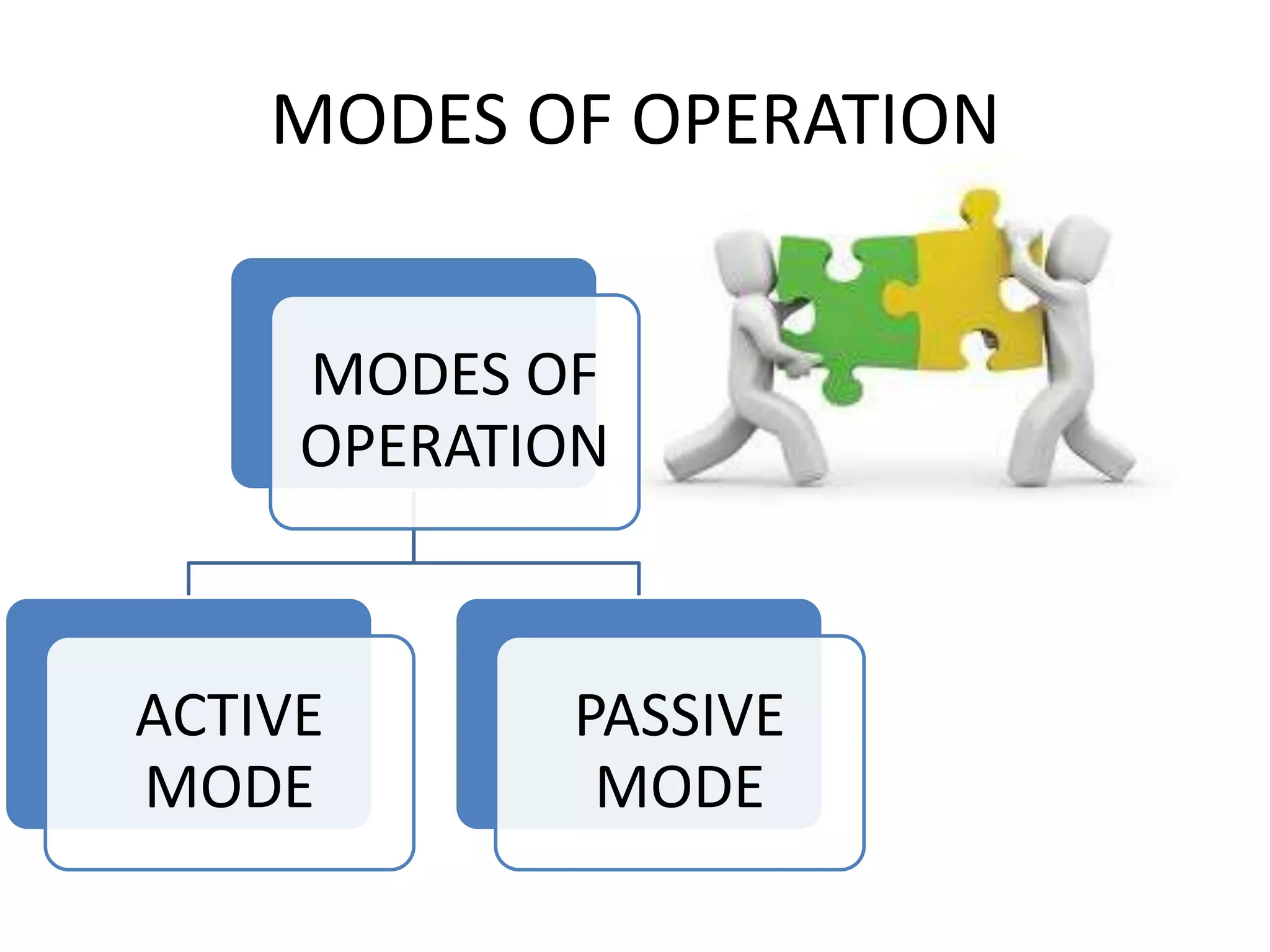
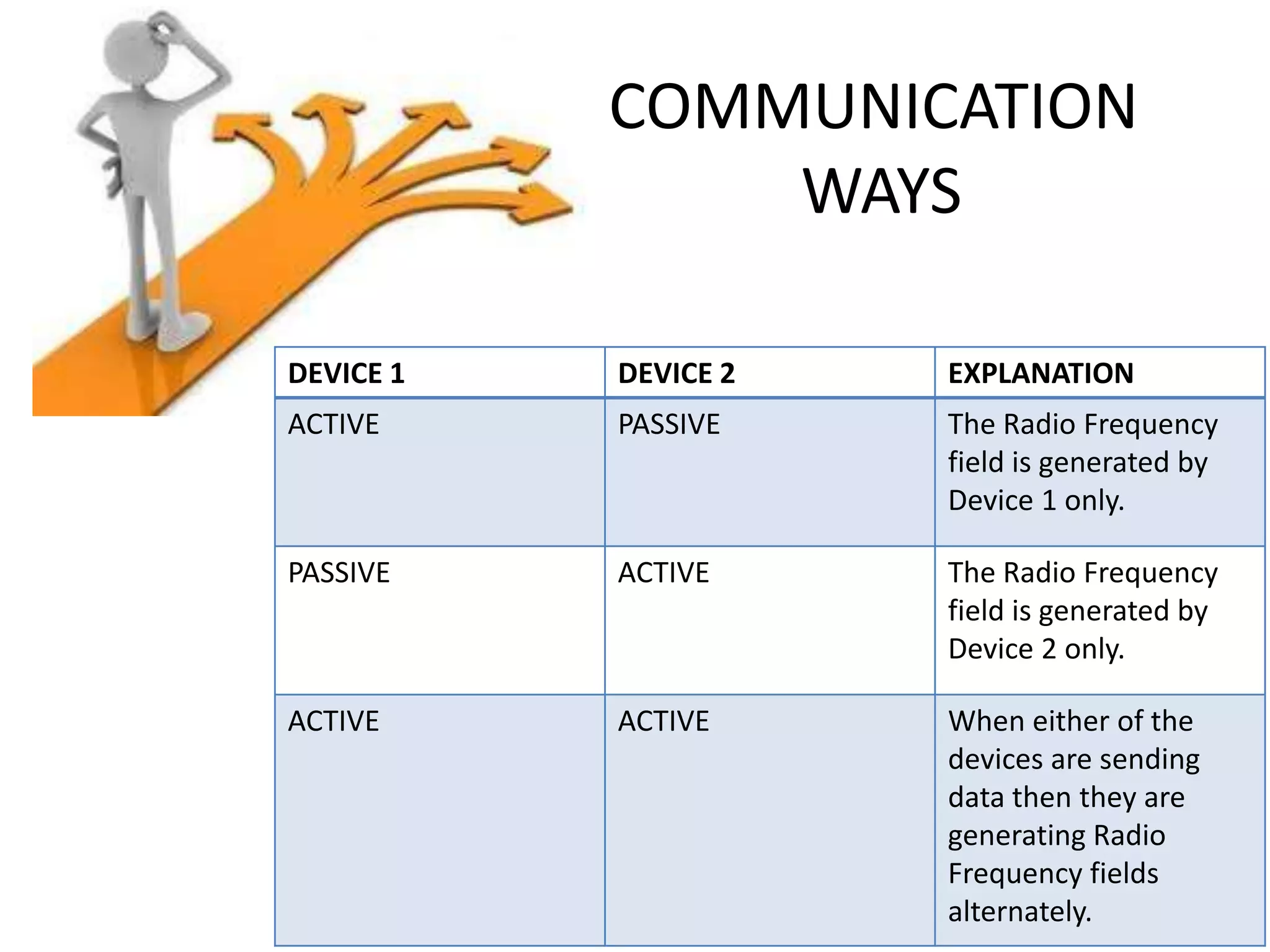
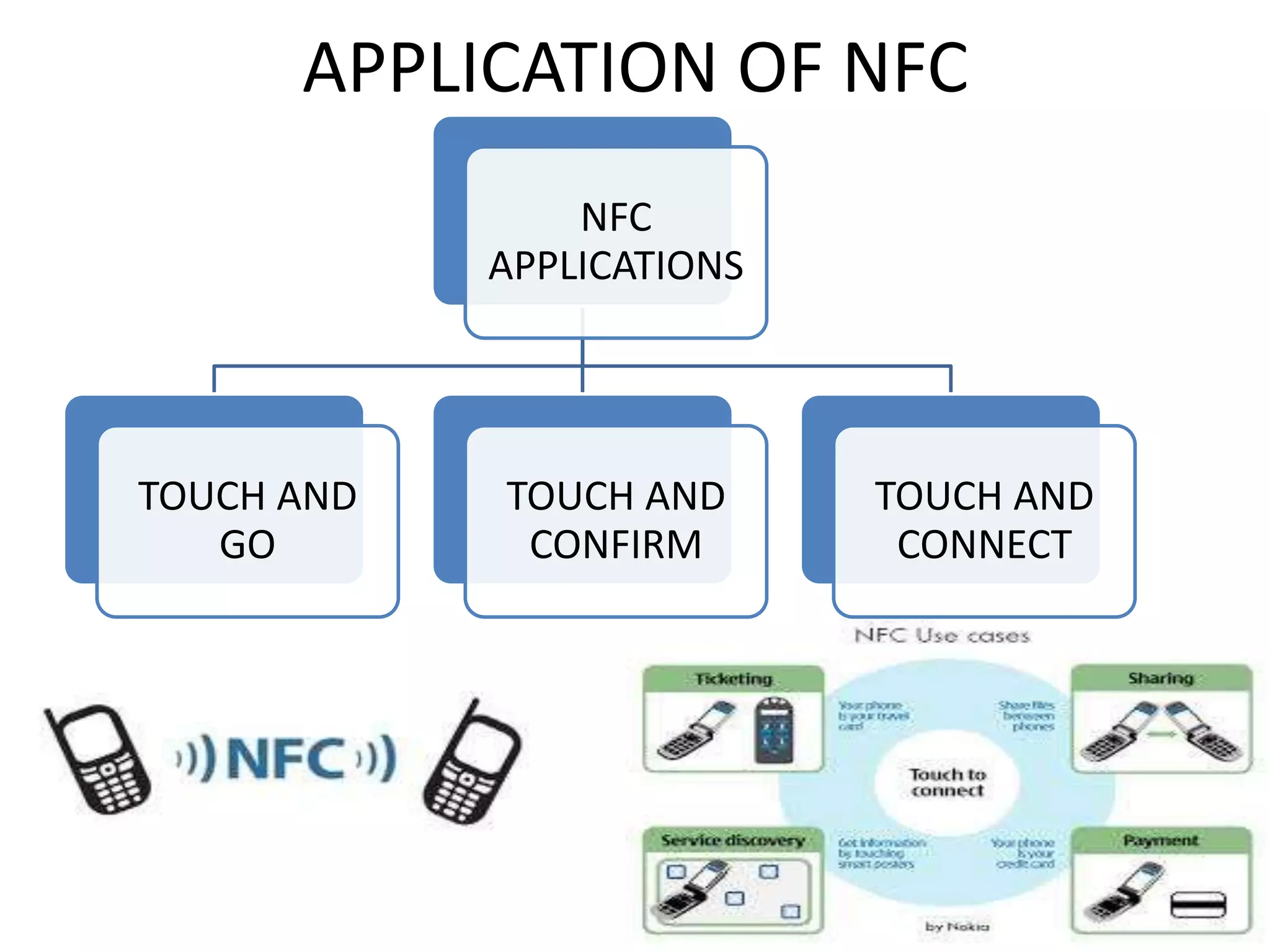
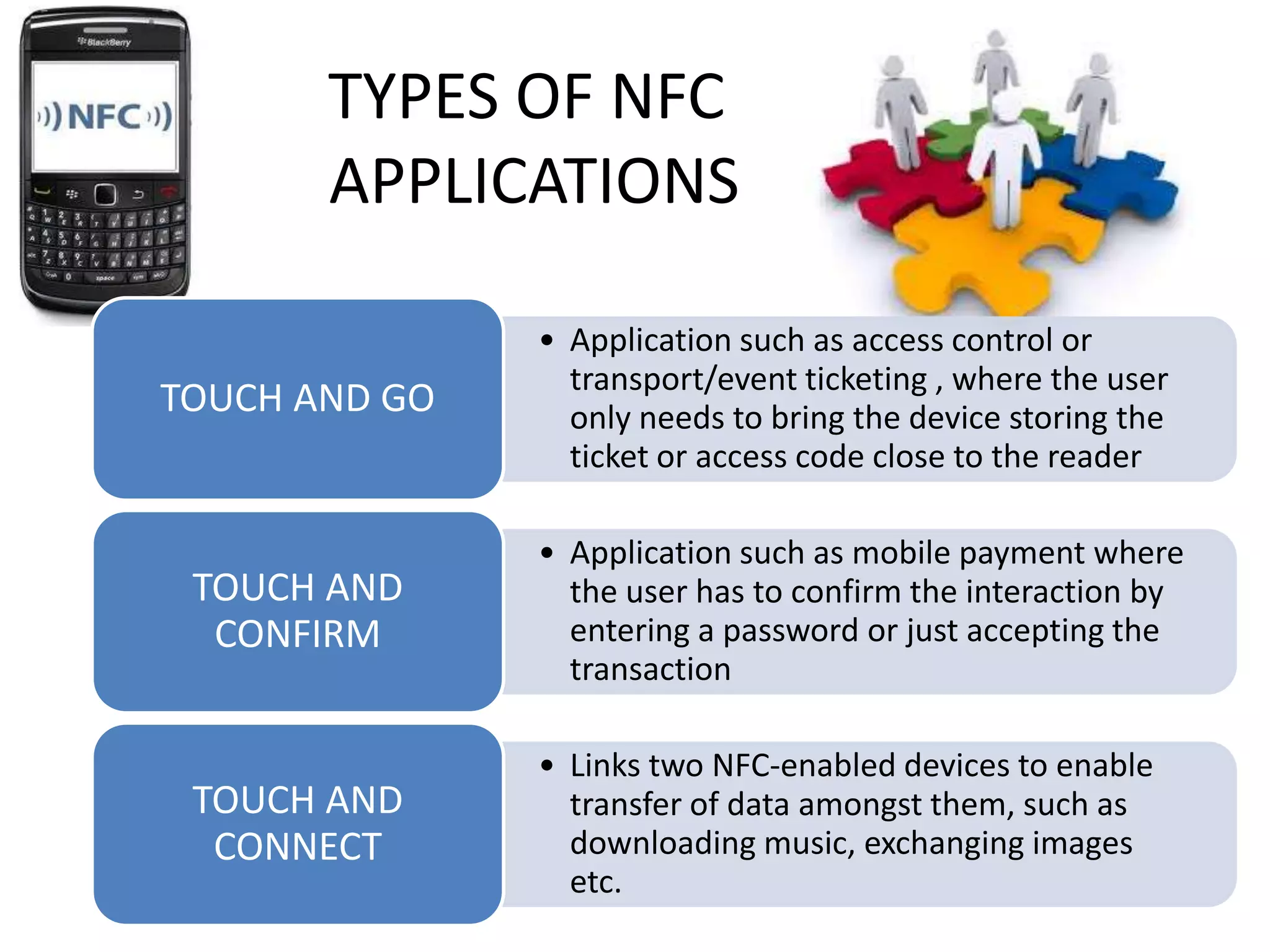
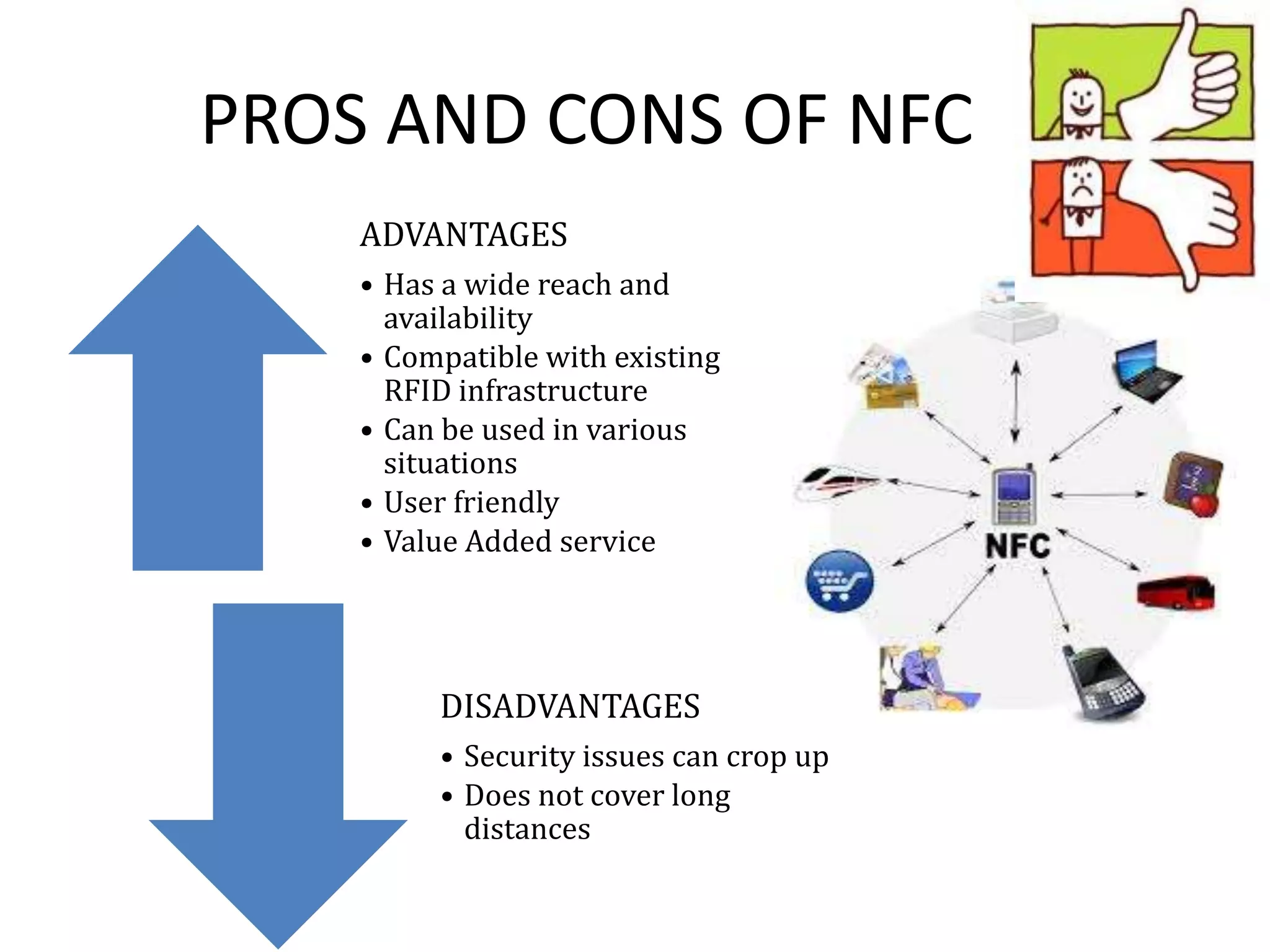
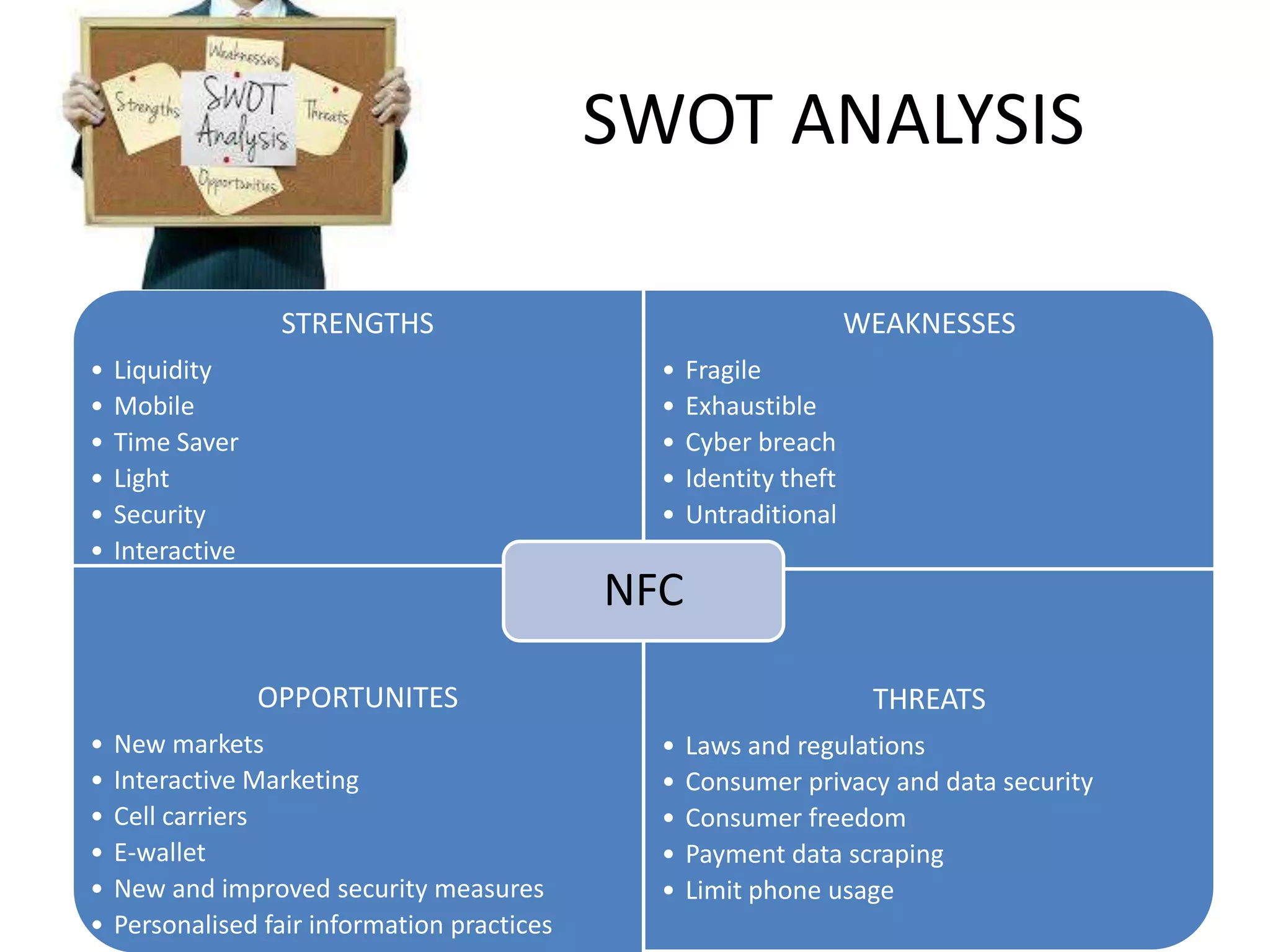
NFC allows contactless data transfer between devices within close proximity using radio frequency identification (RFID). It was developed by Nokia, Phillips, and Sony to enable touch-based interactions and communication between objects and devices. NFC works within a range of about 10 cm using magnetic field induction and operates on an unlicensed radio frequency band. It supports various applications including mobile payments, ticketing, access control, and connecting devices by transferring data through touch. While adoption of NFC may take time as payment methods change slowly, it provides a convenient user-friendly interface and compatibility with existing RFID infrastructure.