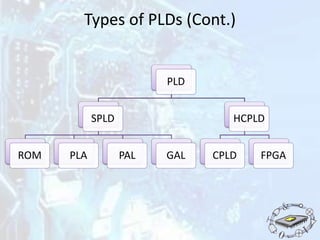
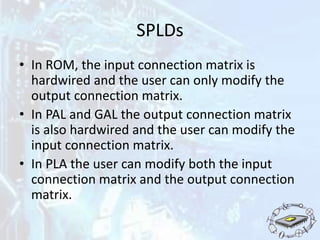
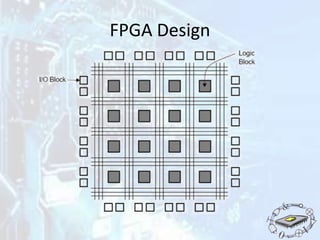
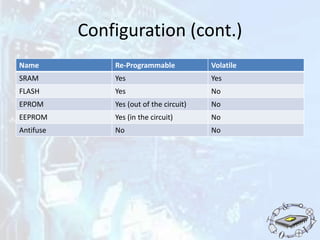
The document discusses programmable logic devices (PLDs), their history, purpose, advantages, and types, including simple PLDs and high capacity PLDs like CPLDs and FPGAs. It highlights the programmability and cost-effectiveness of PLDs, making them suitable for digital logic design and prototyping. The document also outlines the configuration requirements and memory types used in PLDs.