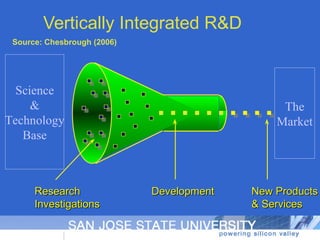
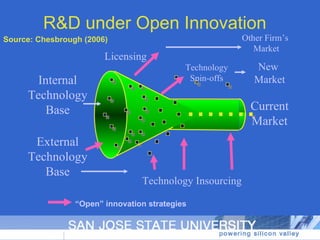
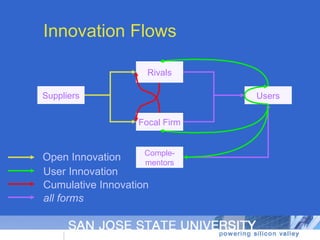
The document discusses open innovation, particularly its incorporation of suppliers, outlining various perspectives and forms of innovation such as user innovation and cumulative innovation. It emphasizes the importance of integrating external sources of innovation and the challenges related to motivating and managing ongoing streams of external innovations. Additionally, it raises questions about defining innovation and ongoing research topics in open innovation practices.