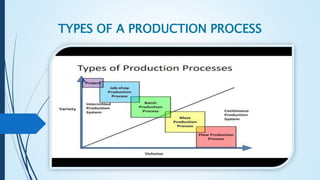
The document explains the production process and categorizes different production systems, including made-to-stock and made-to-order, as well as continuous and intermittent production methods. It discusses their characteristics, advantages, and limitations, emphasizing the importance of integrating feedback and management policies. Various production processes, such as job shop and batch manufacturing, are outlined, highlighting their operational strategies and flexibility requirements.