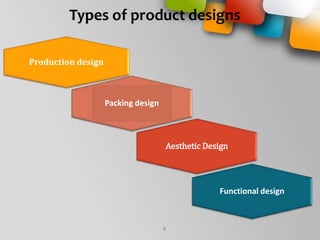
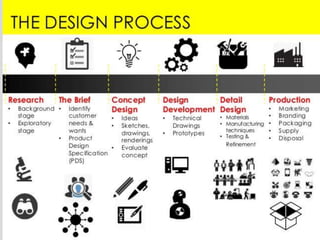
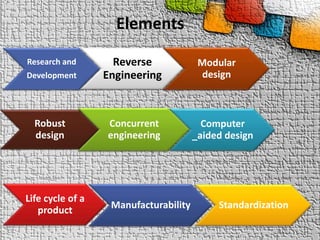
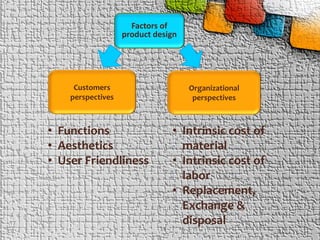
The document explains the concept of product and product design, detailing various types such as functional, aesthetic, production, and packing designs. It highlights the design process, encompassing research and development, reverse engineering, and computer-aided design, while emphasizing the importance of customer perspectives and product life cycles. Key characteristics of effective product design include reliability, functionality, quality, safety, and cost-effectiveness.