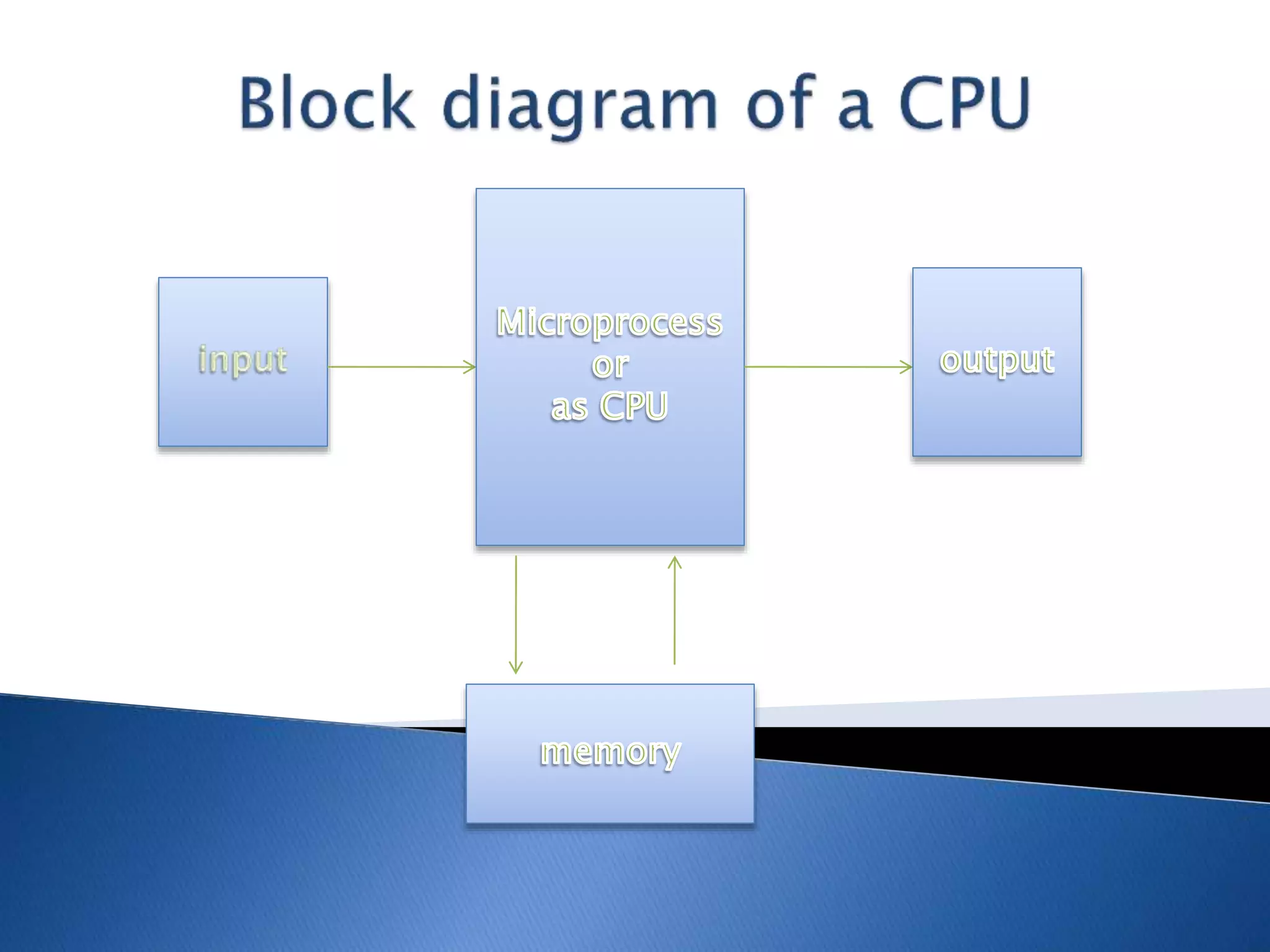
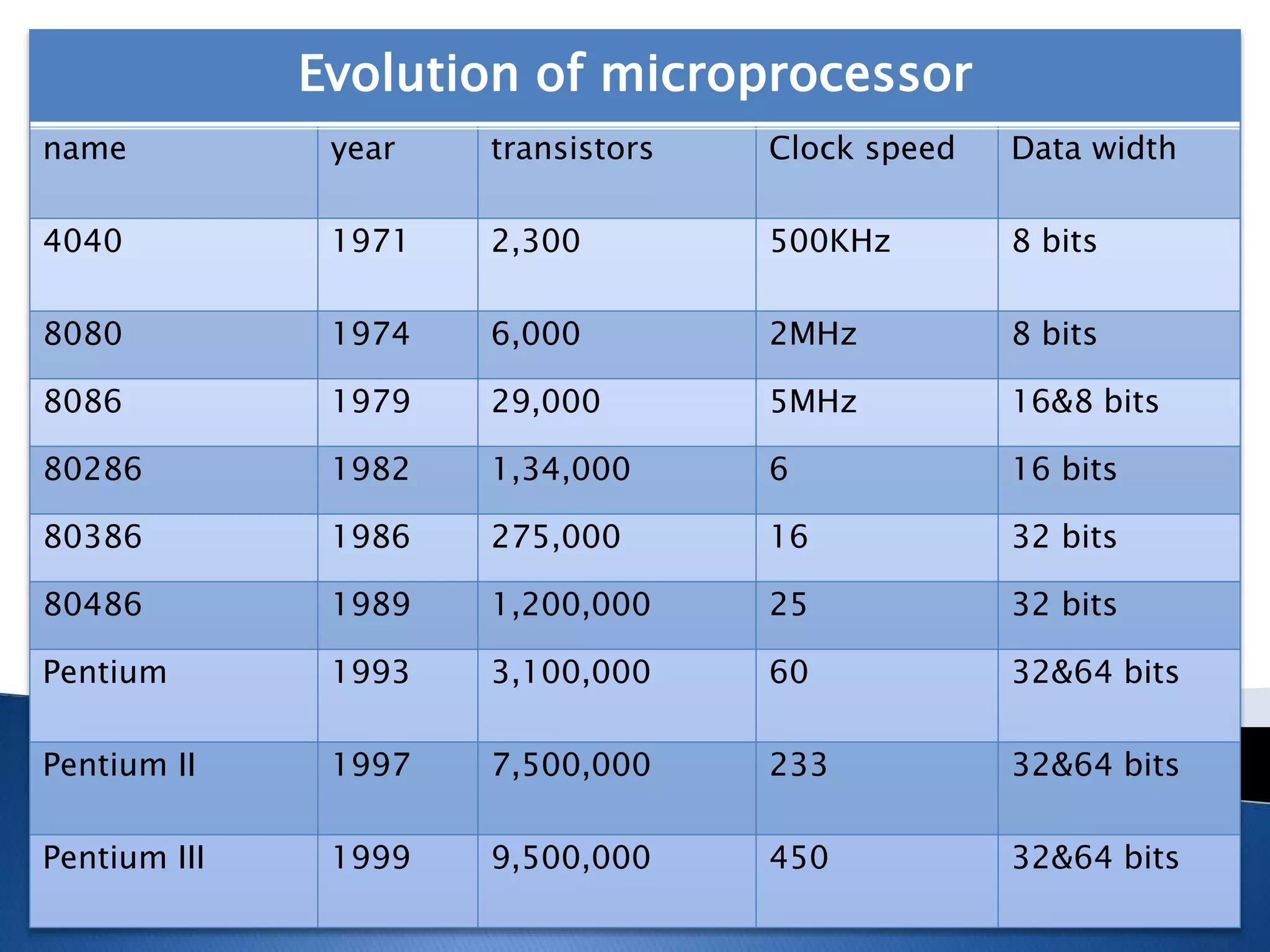
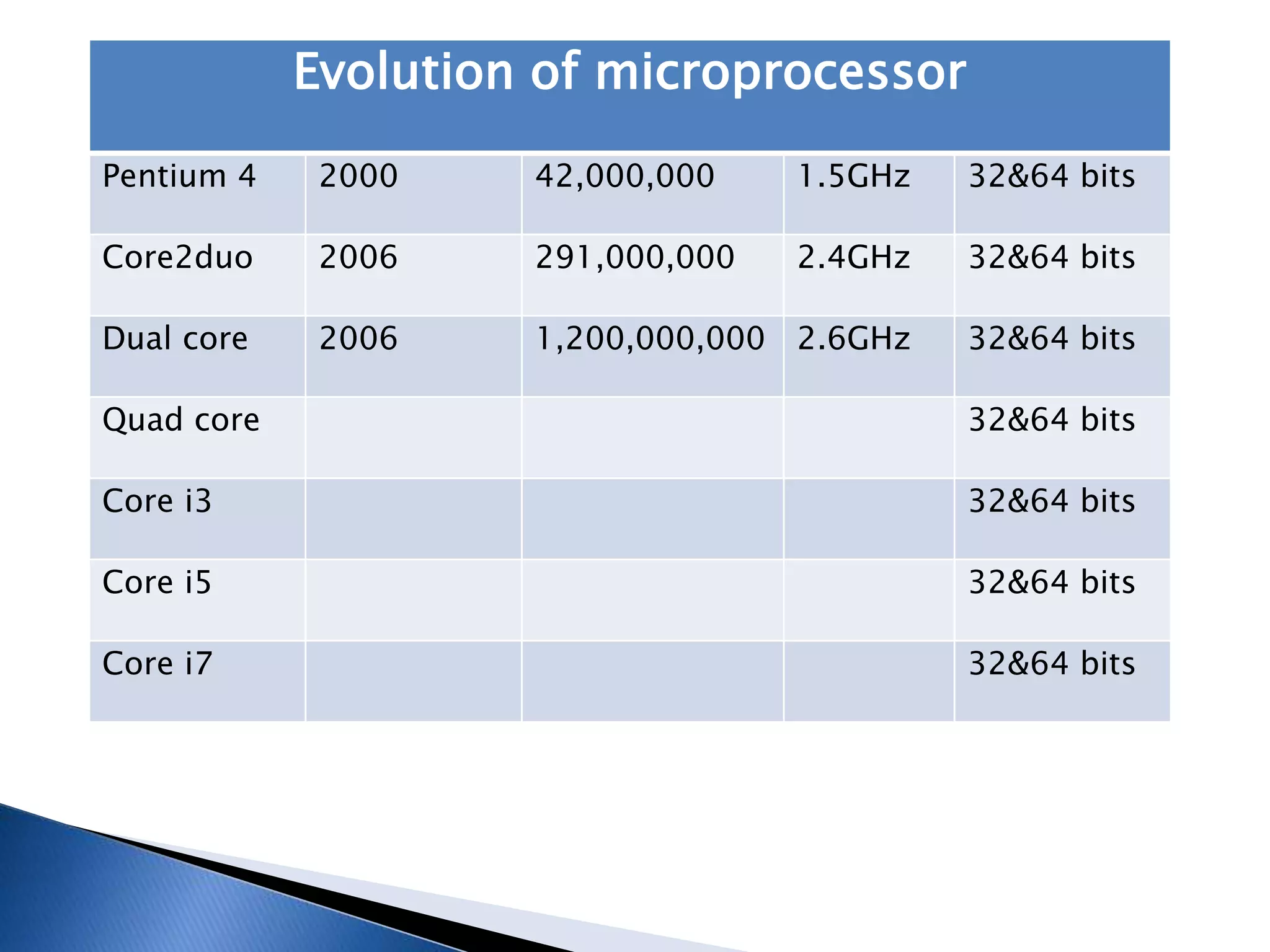
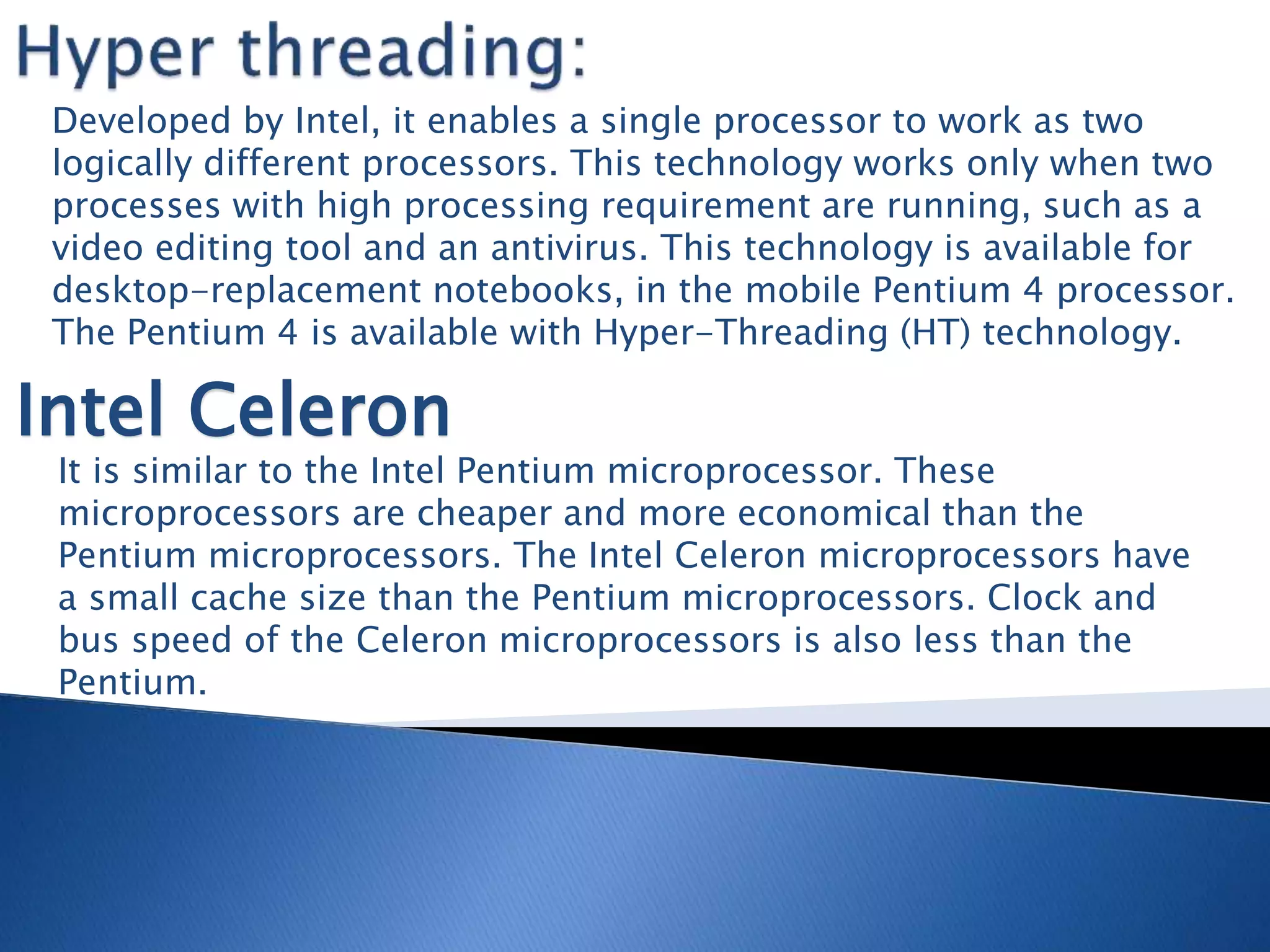
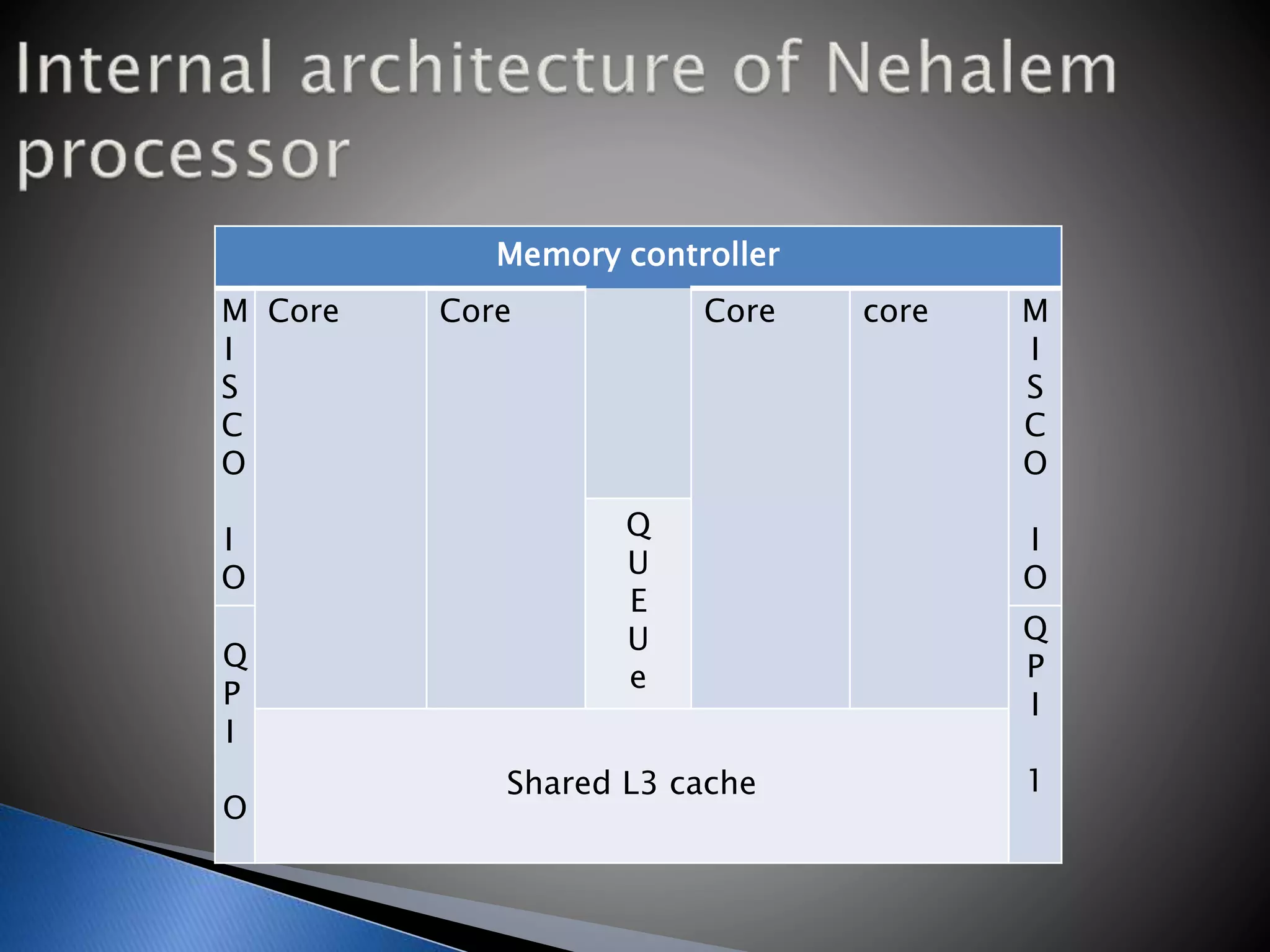
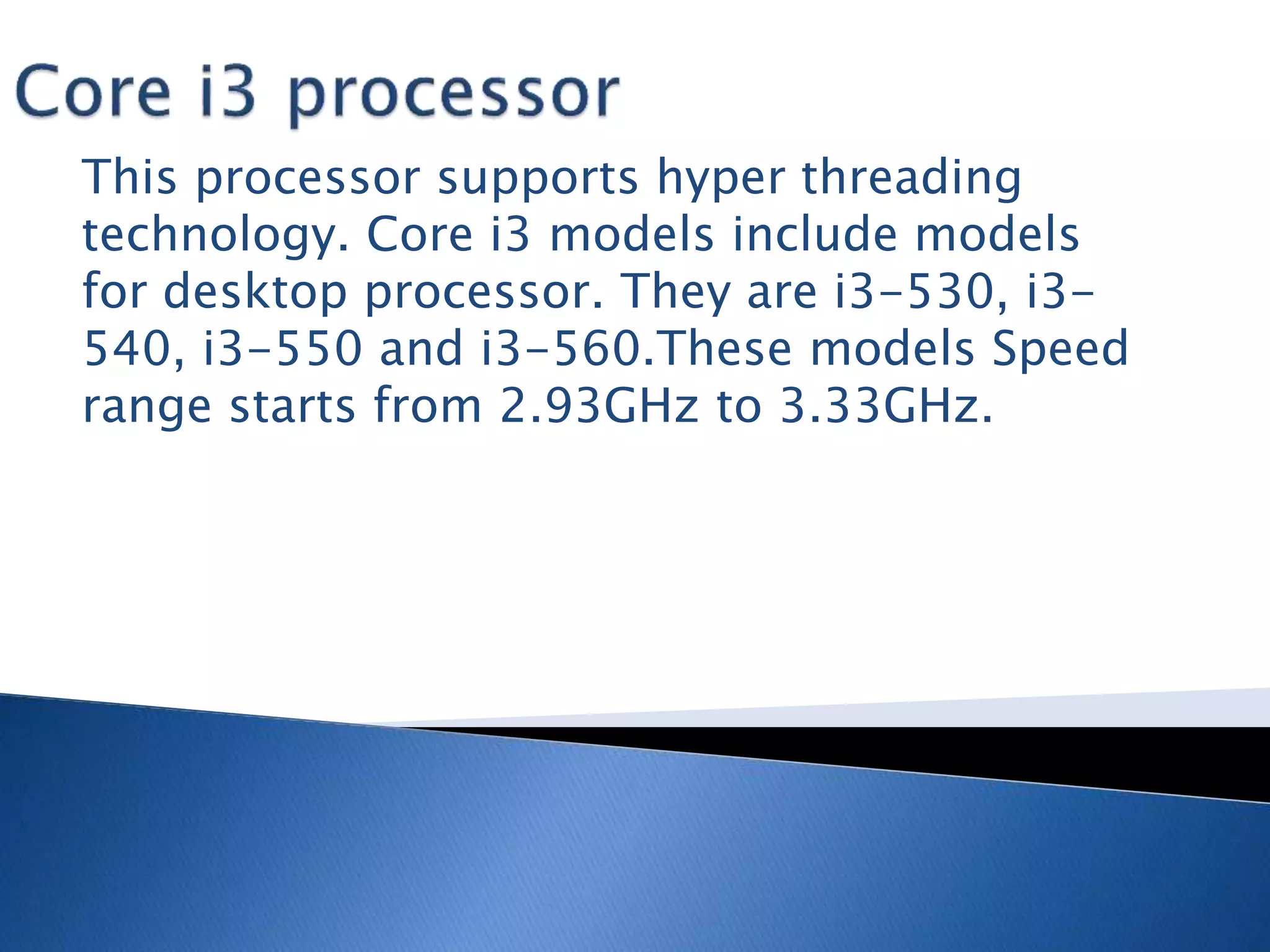
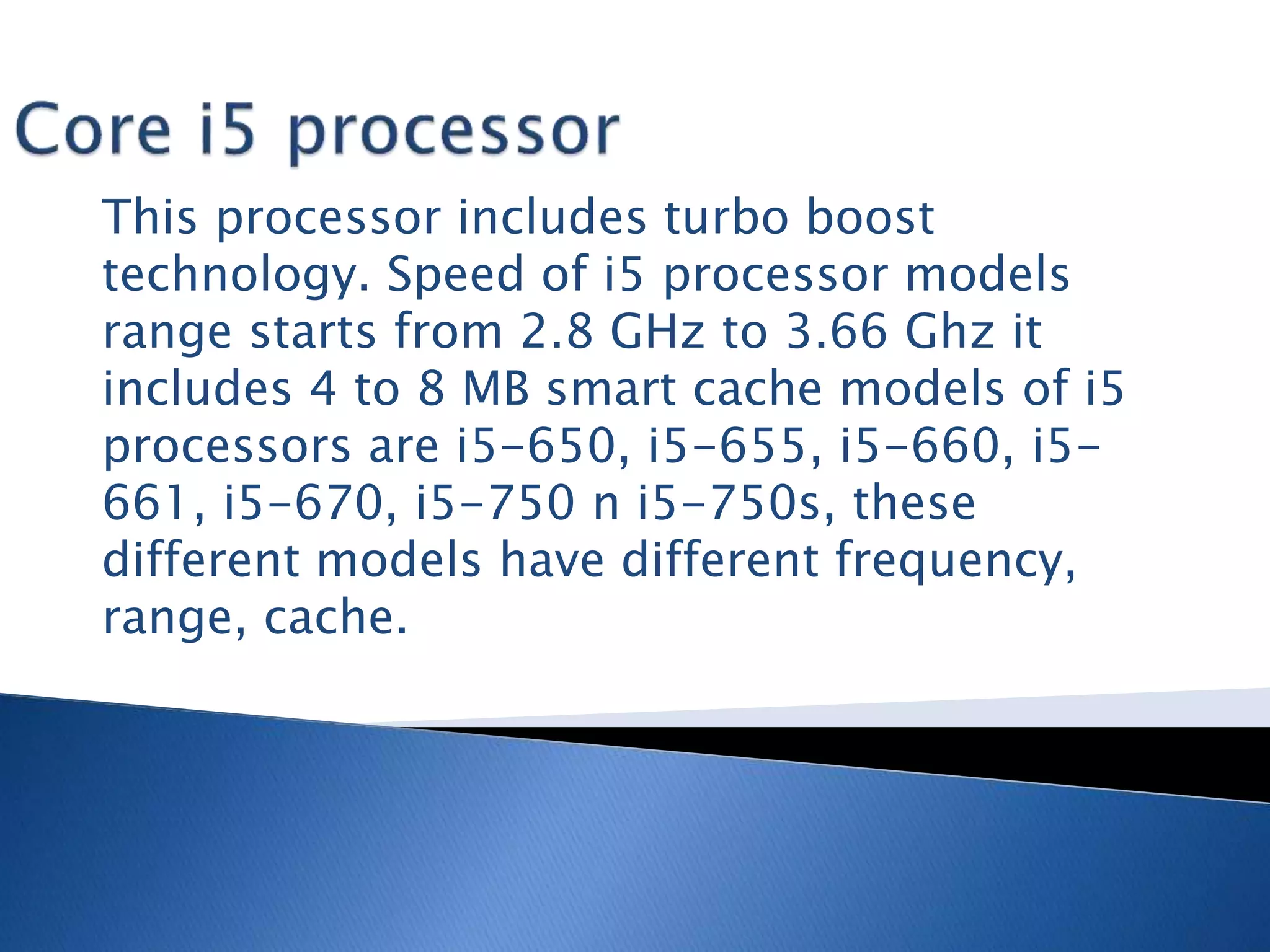
The microprocessor is like the brain of a computer system. It accepts binary data from input devices, processes the data according to instructions, and provides output to output devices. Microprocessors require information stored in external memory like RAM to process data. Key components that affect a microprocessor's speed include its clock speed, front side bus speed, number of transistors, and cache memory. Common microprocessor manufacturers are Intel and AMD, and microprocessor technology has evolved significantly over time to include multiple cores and faster clock speeds.