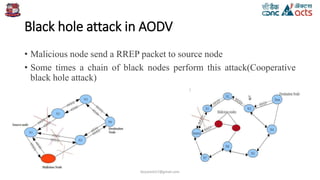
The document discusses a method for detecting black hole attacks in the AODV routing protocol for ad-hoc networks. It proposes an algorithm that maintains a backbone network to monitor and manage nodes, classifying them into regular nodes, backbone nodes, and backbone core nodes to facilitate detection and removal of malicious nodes. The algorithm enables efficient end-to-end checks between source and destination nodes to identify and act against black hole and cooperative black hole attacks.







![Cont’d
• Actions of S
• Divide the data into k equal parts let say Data[1..k].
• end a prelude message to D with shared key k.
• Sends the data to D and after that send a message check having Nr,
to N1.
• If an “ok” is received from N1 the continue data sending.
• if a “not ok” is received from N1 then sets a timer for malicious
removal. If before timeout receive the “removed ok” from N1 then
go to step 2, else terminate.
• D on receiving prelude from S. Wait for data packet and after
receiving data send a postulate message from N1 and S stating the
number of packets received from S.birjutank27@gmail.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swms-150803142449-lva1-app6892/85/Blackhole-Attck-detection-in-AODV-Protocol-9-320.jpg)


