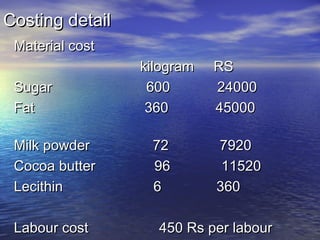
Process costing is a type of costing system used for uniform or homogeneous products where the total manufacturing costs are averaged over all units produced. It involves tracing direct costs and allocating indirect costs through multiple stages of production. The key steps of process costing include determining the physical flow of units, calculating equivalent units, computing equivalent unit costs, summarizing total costs, and assigning costs to completed units and work in process inventory. An example is provided of applying process costing to a chocolate manufacturing process.