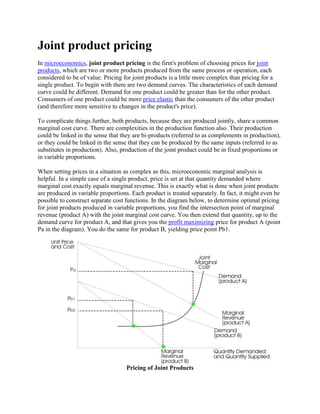
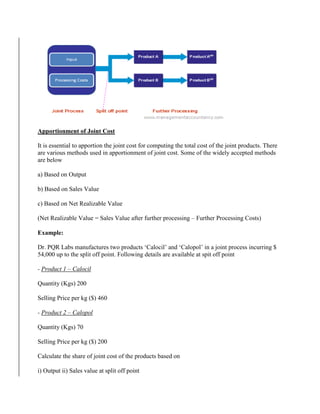
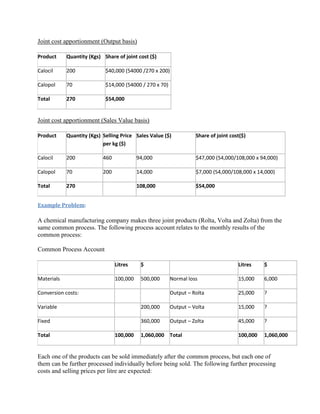
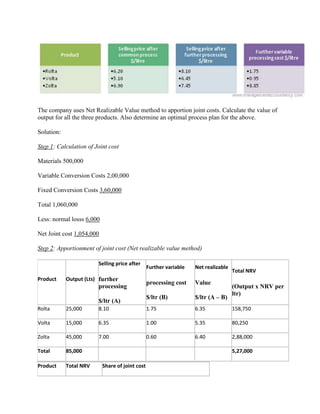
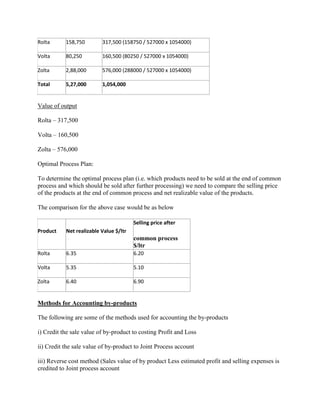
Process costing is an accounting method used to assign costs to units produced in continuous or repetitive processes. Costs like direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead are accumulated and averaged over total units produced during a period, then allocated to individual units. This contrasts with job costing, which tracks costs of individual jobs. Process costing is suitable when identical or similar units are mass produced continuously, as in oil refining or food manufacturing. Key aspects of process costing include determining equivalent units, allocating total costs based on normal or actual output, and assigning costs to completed units and work-in-process inventory.