Embed presentation

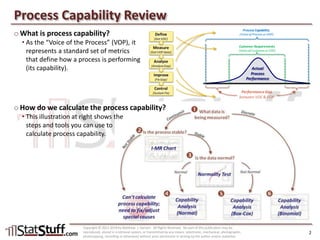
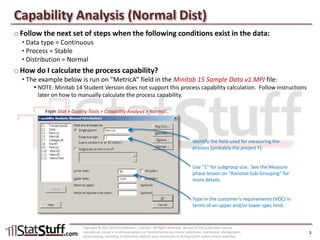
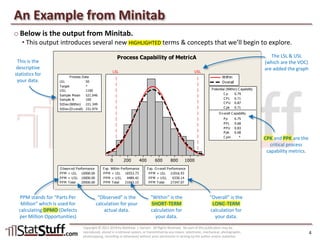
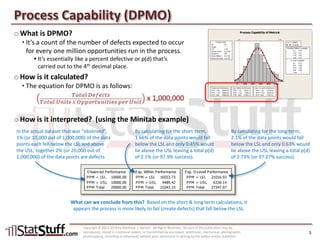
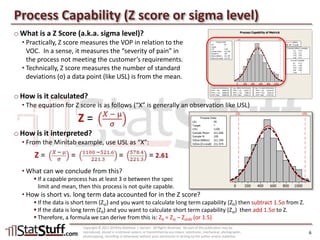
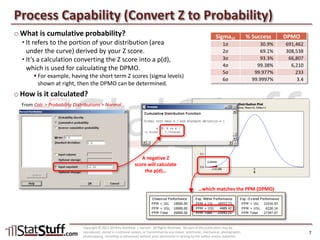
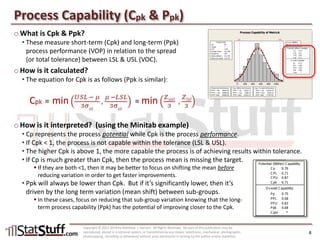
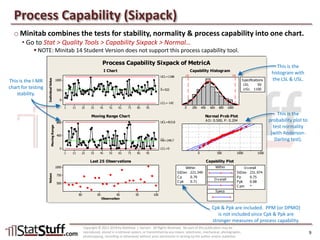

This document provides instruction on assessing the capability of a process that follows a normal distribution. It discusses key metrics like Cp, Cpk, Pp and Ppk which measure process performance relative to customer specifications. The document also explains how to calculate and interpret process capability metrics like DPMO from the output of a process capability analysis in Minitab.









