Embed presentation





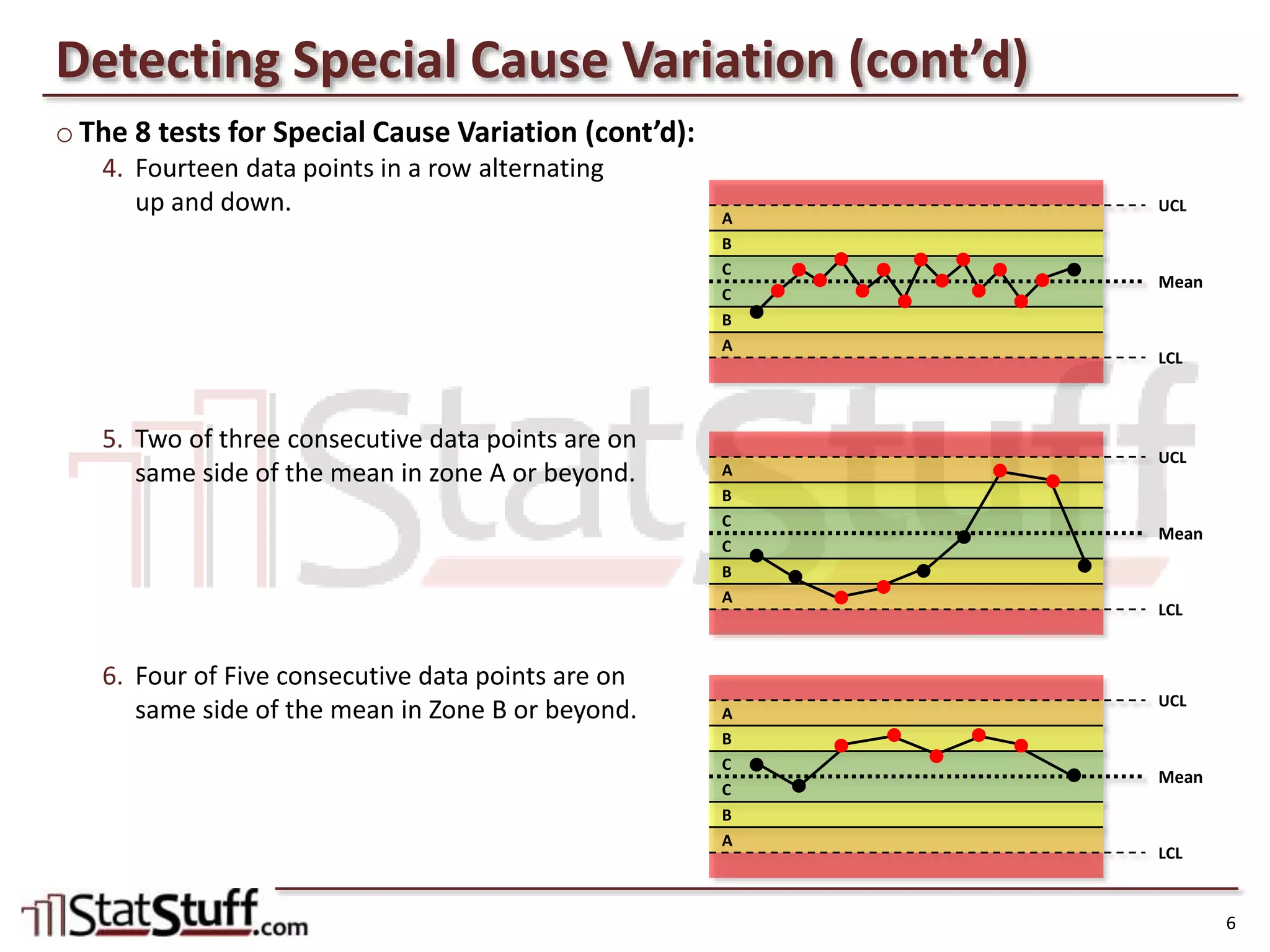



This document discusses testing for special cause variation in statistical process control charts. It begins by reviewing the components of a control chart, including observations, mean, lower and upper control limits. It then describes the eight tests for detecting special cause variation: individual points outside control limits; nine points in a row on the same side of the mean; six points in a row increasing or decreasing; etc. Finally, it explains how to set up these tests in Minitab software. The goal is to identify non-random variation that could indicate problems in the process.








