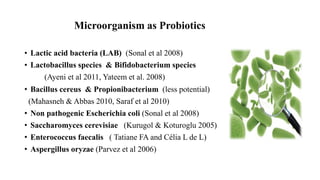
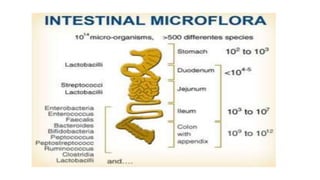
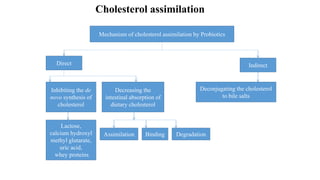
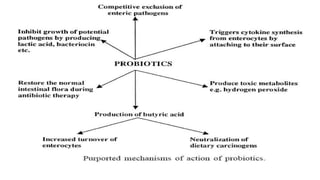
Probiotics are living microorganisms that provide health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. They include lactic acid bacteria like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species. Probiotics can survive the harsh conditions of the gastrointestinal tract, adhere to intestinal cells, produce antimicrobial substances, and modulate the immune system to help crowd out pathogenic bacteria. While generally safe, some risks include mild digestive side effects, infection in immunocompromised individuals, and potential transfer of antibiotic resistance genes. More research is still needed to substantiate health claims and develop targeted "designer" probiotic strains.